Which Holds More Data Raster Or Vector Gis Nibhtrate

Which Holds More Data Raster Or Vector Gis Nibhtrate Compare raster and vector data models in gis. understand their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases to choose the best for your needs. Discover the key differences between vector and raster mapping formats, from data storage and visualization to accuracy and cost considerations in gis applications.

Which Holds More Data Raster Or Vector Gis Nibhtrate Raster maps inherently reflect only one attribute or characteristic for an area. since most input data is in vector form, data must undergo vector to raster conversion. Different from vector, raster is well suited for continuous data, such as satellite images, aerial photography, and elevation models. unlike vector data, raster data allows for multiple bands, which refer to layers of data for each pixel. Both raster and vector data play crucial roles in gis and mapping. raster is best for continuous data analysis, while vector excels in representing discrete features with precision. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.
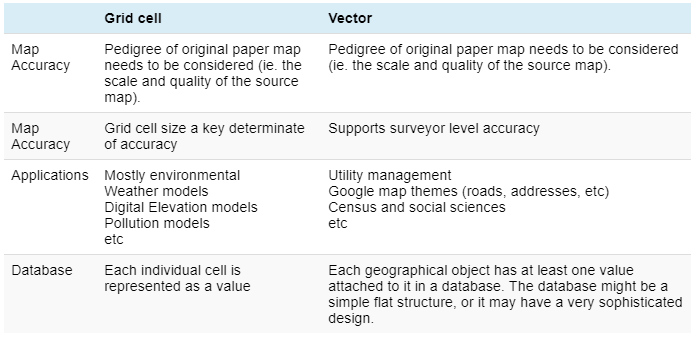
Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Both raster and vector data play crucial roles in gis and mapping. raster is best for continuous data analysis, while vector excels in representing discrete features with precision. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Raster data tends to be larger in size compared to vector data, as each cell in the grid contains a value. this can make raster data more memory intensive and slower to process, especially for large datasets. The two primary types of data used in gis application are vector and raster with each having distinct set of characteristic and applications. in this blog, our experts will provide you a quick peep into the gis data types, differences, and advantages. At the core of any gis application lies the fundamental choice between vector and raster data models. this decision significantly impacts how geographic information is represented, processed, and analyzed. Rasters capture continuous data, while vectors represent discrete data. points represent individual locations on the earth's surface. each point is defined by its coordinates, typically as latitude and longitude. points are used to mark specific landmarks or points of interest.
Comments are closed.