Vector Vs Raster Data Explained Beginner Friendly Gis Course

Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Welcome back to learn gis with anna! 🌍 ever wondered how gis data is structured? everything in gis is built on two main data types: vector and raster. Let’s dive into the key differences between raster and vector data, explore their pros and cons, and see how they are used in real world applications — visually explained for better.
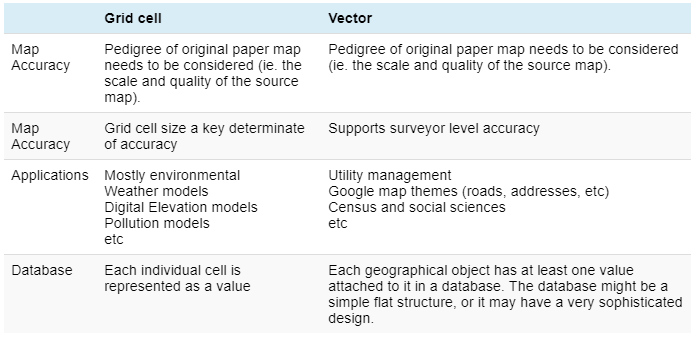
Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis While raster data divides space into a grid of pixels, vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to define locations and shapes. each has its strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Each of these models has its own advantages and disadvantages. the vector model uses points and line segments to identify locations on the earth while the raster model uses a series of cells to represent locations on the earth. the figure represents vector (left) versus raster (right) data. In this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. there are two essential methods used to store information in a geographic information system – gis for both reflections: raster and vector data model.

Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Each of these models has its own advantages and disadvantages. the vector model uses points and line segments to identify locations on the earth while the raster model uses a series of cells to represent locations on the earth. the figure represents vector (left) versus raster (right) data. In this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. there are two essential methods used to store information in a geographic information system – gis for both reflections: raster and vector data model. In gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. understanding the differences between these data types and when to use them is essential for effective gis analysis. Vector data analysis and raster data analysis represent the two basic types of gis analyses. they are treated separately because a gis package cannot run them together in the same operation. although some gis packages allow the use of vector data in some raster data operations, the data are converted into raster data before the operation starts. The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries. Whether you're new to gis or looking to refresh your understanding, this video covers the foundational concepts of vector and raster data models — the two main formats used to represent.
Comments are closed.