Variance Analysis Principlesofaccounting

Practical Accounting 2 Standard Costing Variance Analysis Pdf The red population has mean 100 and variance 100 (sd=10) while the blue population has mean 100 and variance 2500 (sd=50) where sd stands for standard deviation. in probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The variance reflects the variability of your dataset by taking the average of squared deviations from the mean.

Variance Analysis Amity School Of Business Pdf Cost Cost Accounting Variance is a statistical measurement of how large of a spread there is within a data set. it measures how far each number in the set is from the mean (average), and thus from every other number. Variance is defined as the square of the standard deviation, i.e., taking the square of the standard deviation for any group of data gives us the variance of that data set. Variance is a measure of variability in statistics. it assesses the average squared difference between data values and the mean. unlike some other statistical measures of variability, it incorporates all data points in its calculations by contrasting each value to the mean. To calculate the variance follow these steps: then for each number: subtract the mean and square the result (the squared difference). then calculate the average of those squared differences. (why square?) you and your friends have just measured the heights of your dogs (in millimeters):.

Chapter 10 Variance Analysis Pdf Cost Accounting Variance Variance is a measure of variability in statistics. it assesses the average squared difference between data values and the mean. unlike some other statistical measures of variability, it incorporates all data points in its calculations by contrasting each value to the mean. To calculate the variance follow these steps: then for each number: subtract the mean and square the result (the squared difference). then calculate the average of those squared differences. (why square?) you and your friends have just measured the heights of your dogs (in millimeters):. What is variance in statistics. learn its symbol, equation, and properties. how to find it explained with examples. Learn the meaning of variance in statistics, how to calculate variance, examples of variance, and its importance in data analysis with solved problems. The variance (var) tells you how much the results deviate from the expected value. if the variance (σ 2) is large, the values scatter around the expected value. What is variance? variance is a measure of how spread out a data set is, and we calculate it by finding the average of each data point's squared difference from the mean.

Chapter11 Variance Analysis Control Pdf Labour Economics Variance What is variance in statistics. learn its symbol, equation, and properties. how to find it explained with examples. Learn the meaning of variance in statistics, how to calculate variance, examples of variance, and its importance in data analysis with solved problems. The variance (var) tells you how much the results deviate from the expected value. if the variance (σ 2) is large, the values scatter around the expected value. What is variance? variance is a measure of how spread out a data set is, and we calculate it by finding the average of each data point's squared difference from the mean.
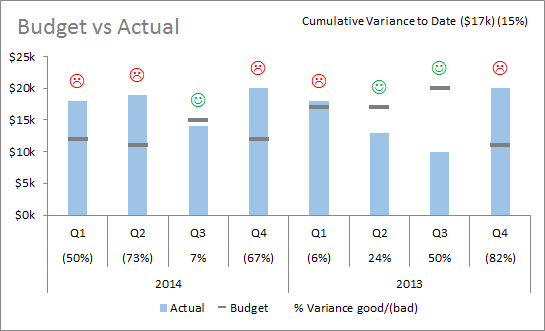
Variance Analysis Chart Ponasa The variance (var) tells you how much the results deviate from the expected value. if the variance (σ 2) is large, the values scatter around the expected value. What is variance? variance is a measure of how spread out a data set is, and we calculate it by finding the average of each data point's squared difference from the mean.
Comments are closed.