Types Of Variables Discrete Continuous Categorical
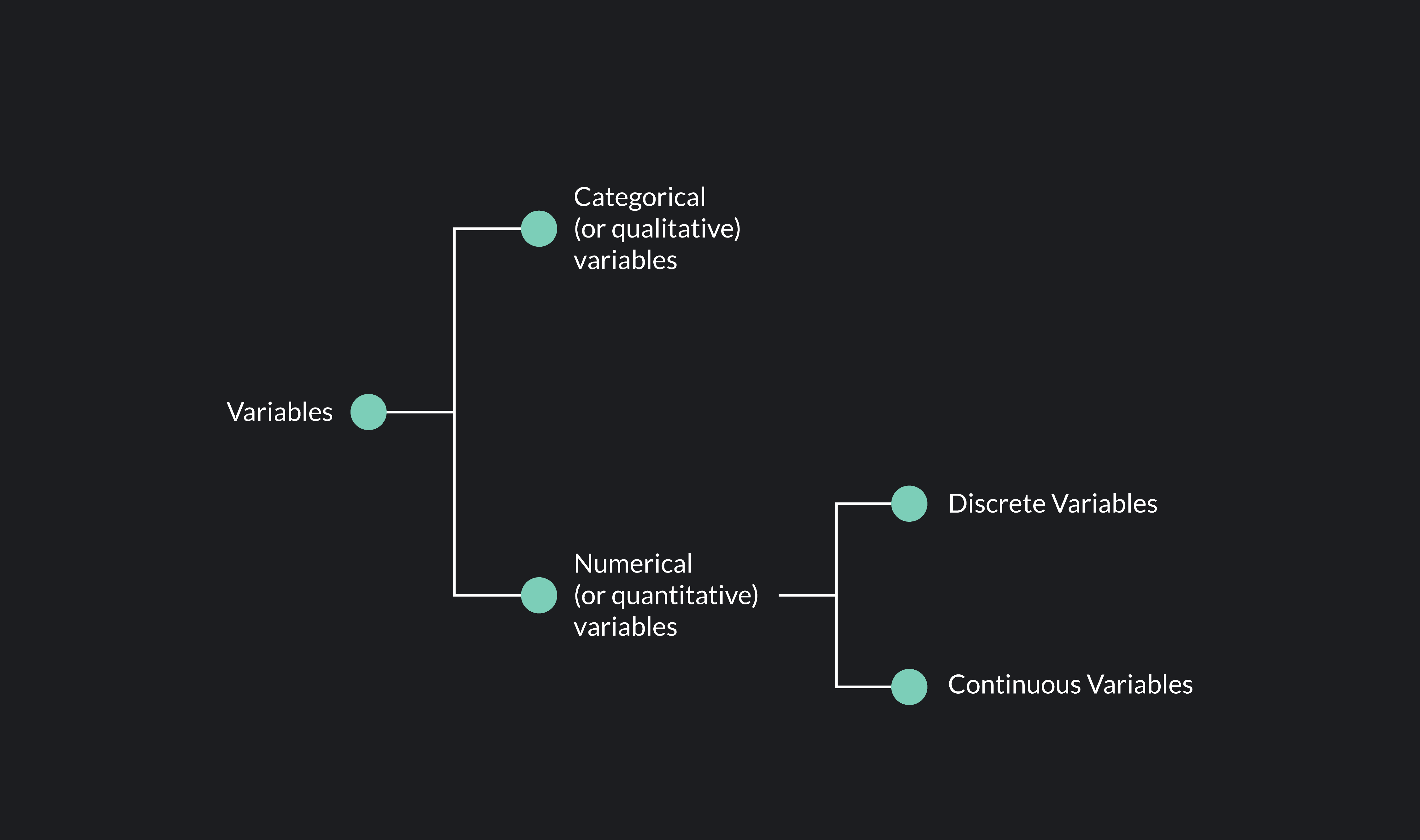
Discrete Vs Continuous Variables Meaning And Differences Outlier Qualitative (categorical) variables that describe qualities or characteristics (like gender, blood type, or color) quantitative (numerical) variables that express quantities or amounts the discrete versus continuous classification we’ll explore below specifically refers to how quantitative variables behave. Discrete variables are defined only on a finite set or a countably infinite set. minitab refers to discrete variables as numeric variables that have a countable number of values between any two values. for example, the number of customer complaints or the number of flaws or defects.
Continuous Vs Discrete Vs Categorical Axis What Is The Difference Each of these types of variables can be broken down into further types. quantitative variables when you collect quantitative data, the numbers you record represent real amounts that can be added, subtracted, divided, etc. there are two types of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous. Variables may be classified into two main categories: categorical and numeric. each category is then classified in two subcategories: nominal or ordinal for categorical variables, discrete or continuous for numeric variables. these types are briefly outlined in this section. Here are some examples to help you differentiate between discrete and continuous variables: exercise: discrete or continuous? – is age discrete or continuous? age is a discrete variable when counted in years, for example when you ask someone about their age in a questionnaire. Categorical variables are also known as discrete or qualitative variables. categorical variables can be further categorized as either nominal, ordinal or dichotomous.

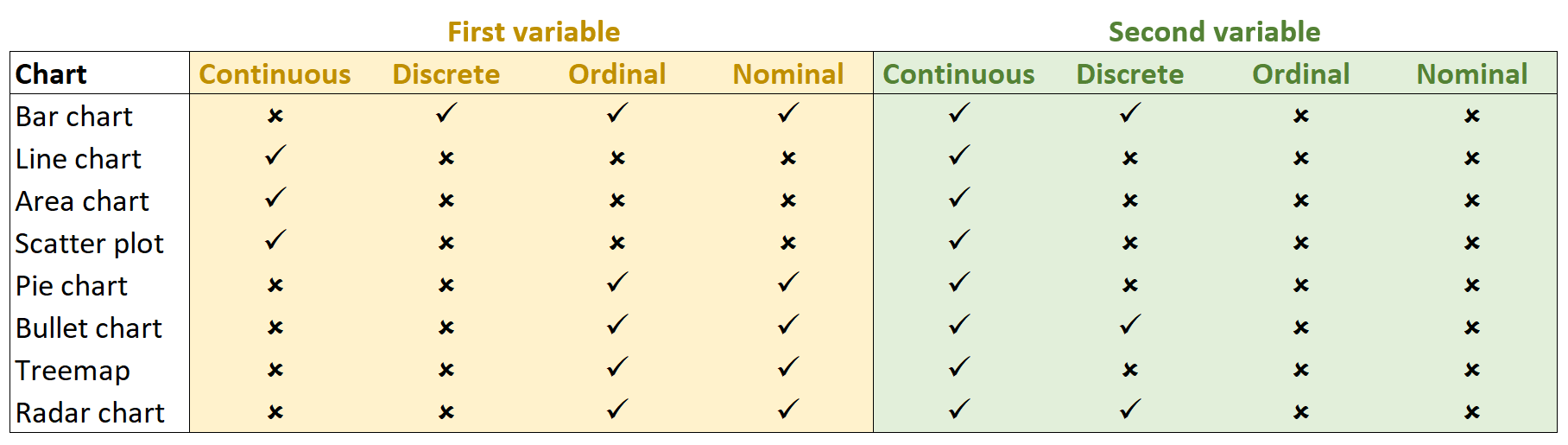
Continuous Vs Discrete Vs Categorical Axis What Is The Difference Here are some examples to help you differentiate between discrete and continuous variables: exercise: discrete or continuous? – is age discrete or continuous? age is a discrete variable when counted in years, for example when you ask someone about their age in a questionnaire. Categorical variables are also known as discrete or qualitative variables. categorical variables can be further categorized as either nominal, ordinal or dichotomous. Exact distance between ordered categories are unknown interval variable: categories are non overlapping intervals (e.g., functional life. n: nominal when measured as public private school . un. vari. s) for any types of explanatory variables in modeling quantitative: base functions like polynomial or other cont. Quantitative variables may be discrete or continuous. discrete variables can only take on a limited number of values (e.g., only whole numbers) while continuous variables can take on any value and any value between two values (e.g., out to an infinite number of decimal places). Quantitative variables are often further classified as either: discrete, when the variable takes on a countable number of values. most often these variables indeed represent some kind of count such as the number of prescriptions an individual takes daily. continuous, when the variable can take on any value in some range of values. Covers use of variables in statistics categorical vs. quantitative, discrete vs. continuous, univariate vs. bivariate data. includes free video lesson.

Continuous Vs Discrete Vs Categorical Axis What Is The Difference Exact distance between ordered categories are unknown interval variable: categories are non overlapping intervals (e.g., functional life. n: nominal when measured as public private school . un. vari. s) for any types of explanatory variables in modeling quantitative: base functions like polynomial or other cont. Quantitative variables may be discrete or continuous. discrete variables can only take on a limited number of values (e.g., only whole numbers) while continuous variables can take on any value and any value between two values (e.g., out to an infinite number of decimal places). Quantitative variables are often further classified as either: discrete, when the variable takes on a countable number of values. most often these variables indeed represent some kind of count such as the number of prescriptions an individual takes daily. continuous, when the variable can take on any value in some range of values. Covers use of variables in statistics categorical vs. quantitative, discrete vs. continuous, univariate vs. bivariate data. includes free video lesson.
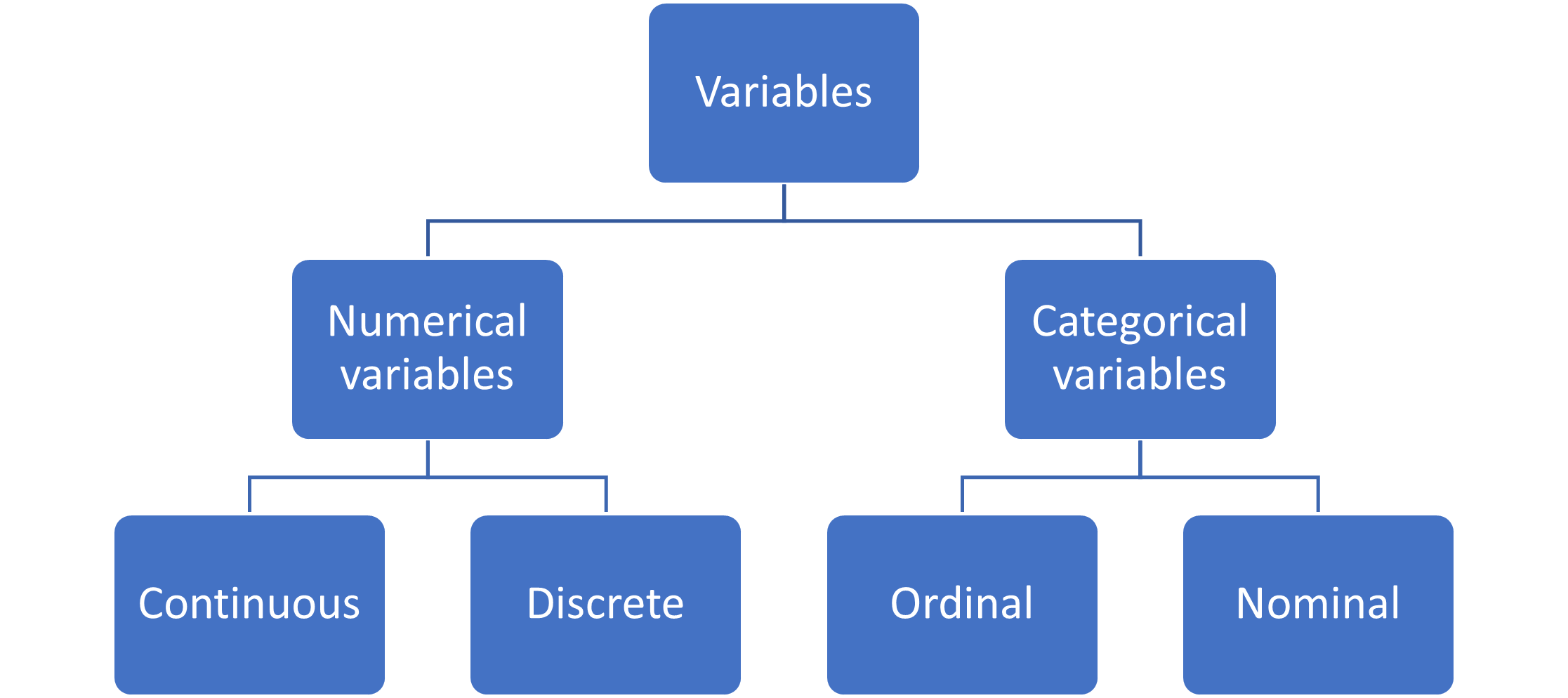
Continuous Vs Discrete Vs Categorical Axis What Is The Difference Quantitative variables are often further classified as either: discrete, when the variable takes on a countable number of values. most often these variables indeed represent some kind of count such as the number of prescriptions an individual takes daily. continuous, when the variable can take on any value in some range of values. Covers use of variables in statistics categorical vs. quantitative, discrete vs. continuous, univariate vs. bivariate data. includes free video lesson.
Comments are closed.