Thorax 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials
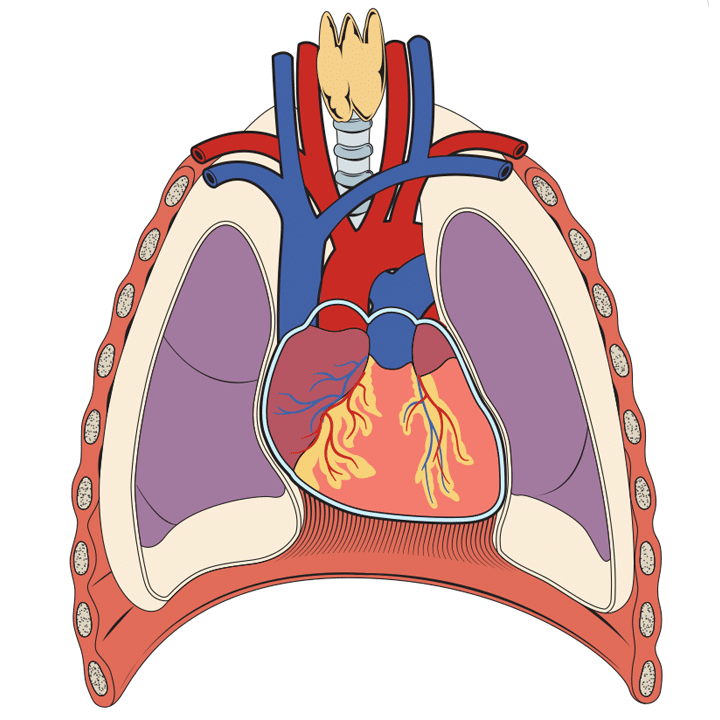
Thorax 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. it is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, and shoulder girdle. Your thoracic cavity (chest cavity) is a space inside your thorax (chest) that contains your heart, lungs and other organs and tissues. it’s the second biggest hollow space in your body, with only your abdominal cavity being larger.

Thorax 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials Explore the anatomy of the human thorax. this comprehensive guide covers the thoracic cavity's vital structures and their functions. learn more here. Do you want to find out more about the anatomy of the thorax? click now to learn more about the thoracic wall, cavity, organs, and blood vessels at kenhub!. Thorax, the part of an animal’s body between its head and its midsection. in vertebrates (fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals), the thorax is the chest, with the chest being that part of the body between the neck and the abdomen. The thorax, commonly known as the chest, is a central region of the human body. it acts as a protective enclosure for internal organs and is involved in essential bodily processes. this article explores its location, anatomical structure, the organs it houses, and its functions. locating the thorax: structure and boundaries the thorax is situated in the upper part of the human trunk, between.

Thorax 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials Thorax, the part of an animal’s body between its head and its midsection. in vertebrates (fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals), the thorax is the chest, with the chest being that part of the body between the neck and the abdomen. The thorax, commonly known as the chest, is a central region of the human body. it acts as a protective enclosure for internal organs and is involved in essential bodily processes. this article explores its location, anatomical structure, the organs it houses, and its functions. locating the thorax: structure and boundaries the thorax is situated in the upper part of the human trunk, between. The thorax, commonly known as the chest, is a vital region of the human body that provides protection to critical organs, including the heart and lungs, while also playing a role in respiration and structural support. Its walls are formed by the 12 pairs of ribs, attached to the sides of the spine and curving toward the front. the principal organs in the thoracic cavity are the heart with its major blood vessels and the lungs with the bronchi, which bring in the body's air supply. Overall, the thoracic wall is formed by the following structures: posteriorly twelve thoracic vertebrae and their intervertebral discs. skeleton of the thoracic cage, intercostal spaces, lungs and pleura, diaphragm. The thorax houses and protects the heart, lungs, and great vessels. on account of the domed shape of the diaphragm, the thoracic wall also offers protection to some essential abdominal viscera.
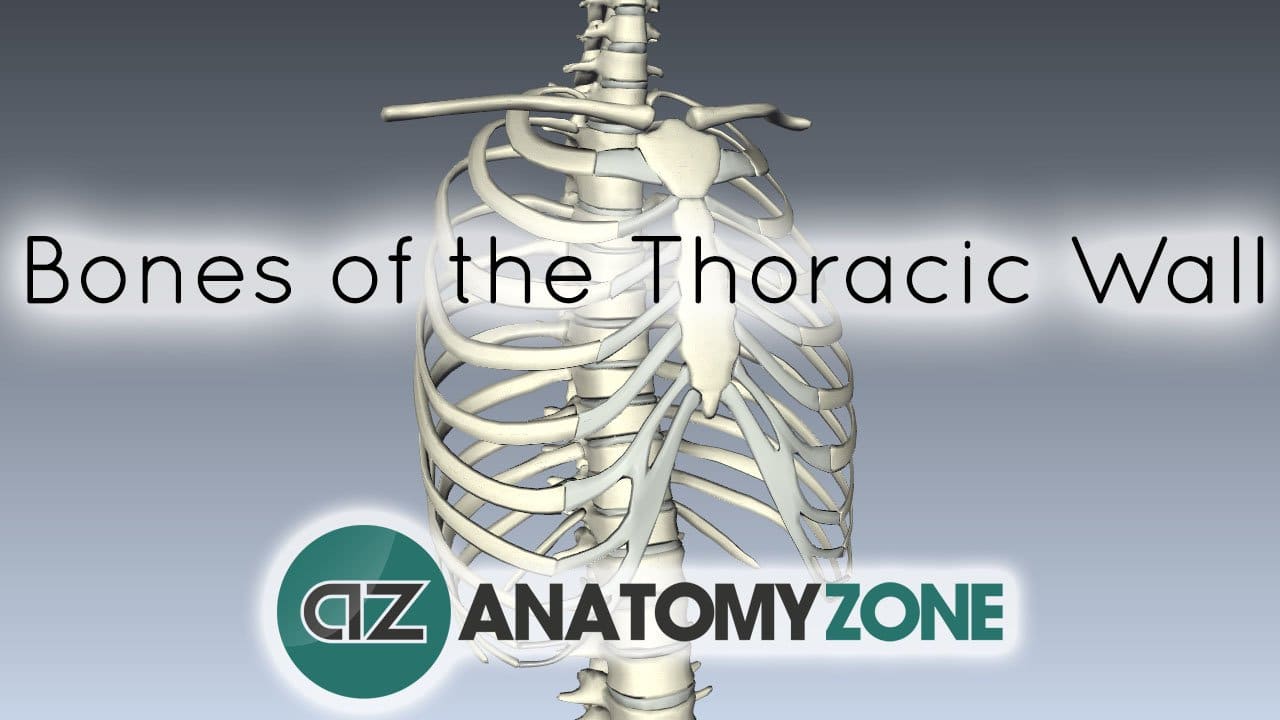
Thorax 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials The thorax, commonly known as the chest, is a vital region of the human body that provides protection to critical organs, including the heart and lungs, while also playing a role in respiration and structural support. Its walls are formed by the 12 pairs of ribs, attached to the sides of the spine and curving toward the front. the principal organs in the thoracic cavity are the heart with its major blood vessels and the lungs with the bronchi, which bring in the body's air supply. Overall, the thoracic wall is formed by the following structures: posteriorly twelve thoracic vertebrae and their intervertebral discs. skeleton of the thoracic cage, intercostal spaces, lungs and pleura, diaphragm. The thorax houses and protects the heart, lungs, and great vessels. on account of the domed shape of the diaphragm, the thoracic wall also offers protection to some essential abdominal viscera.
3d Human Anatomy Thorax Turbosquid 2230044 Overall, the thoracic wall is formed by the following structures: posteriorly twelve thoracic vertebrae and their intervertebral discs. skeleton of the thoracic cage, intercostal spaces, lungs and pleura, diaphragm. The thorax houses and protects the heart, lungs, and great vessels. on account of the domed shape of the diaphragm, the thoracic wall also offers protection to some essential abdominal viscera.
Comments are closed.