Thoracic Region Anatomy Every Chest Cavity Structure Labeled

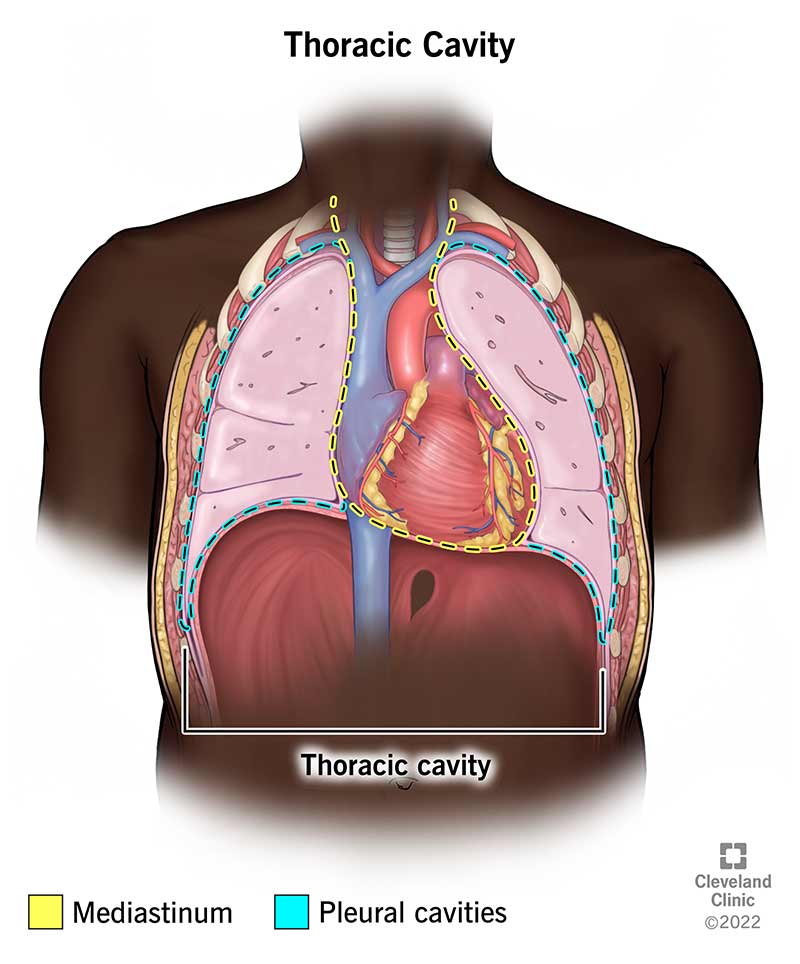
Anatomy Of The Thoracic Cavity Your thoracic cavity is a space in your chest that contains your heart, lungs and other organs and tissues. the pleural cavities and mediastinum are its main parts. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. it contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures.

Thoracic Region Anatomy Every Chest Cavity Structure Doovi Pertaining to the chest (thorax); called also pectoral. Thoracic surgeons specialize in treating disorders of the heart, lungs, esophagus, and major blood vessels in the chest. learn more about these surgeons, what they do, the conditions they treat,. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. Thoracic cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. it is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. among the major organs contained in the thoracic cavity are the heart and lungs.
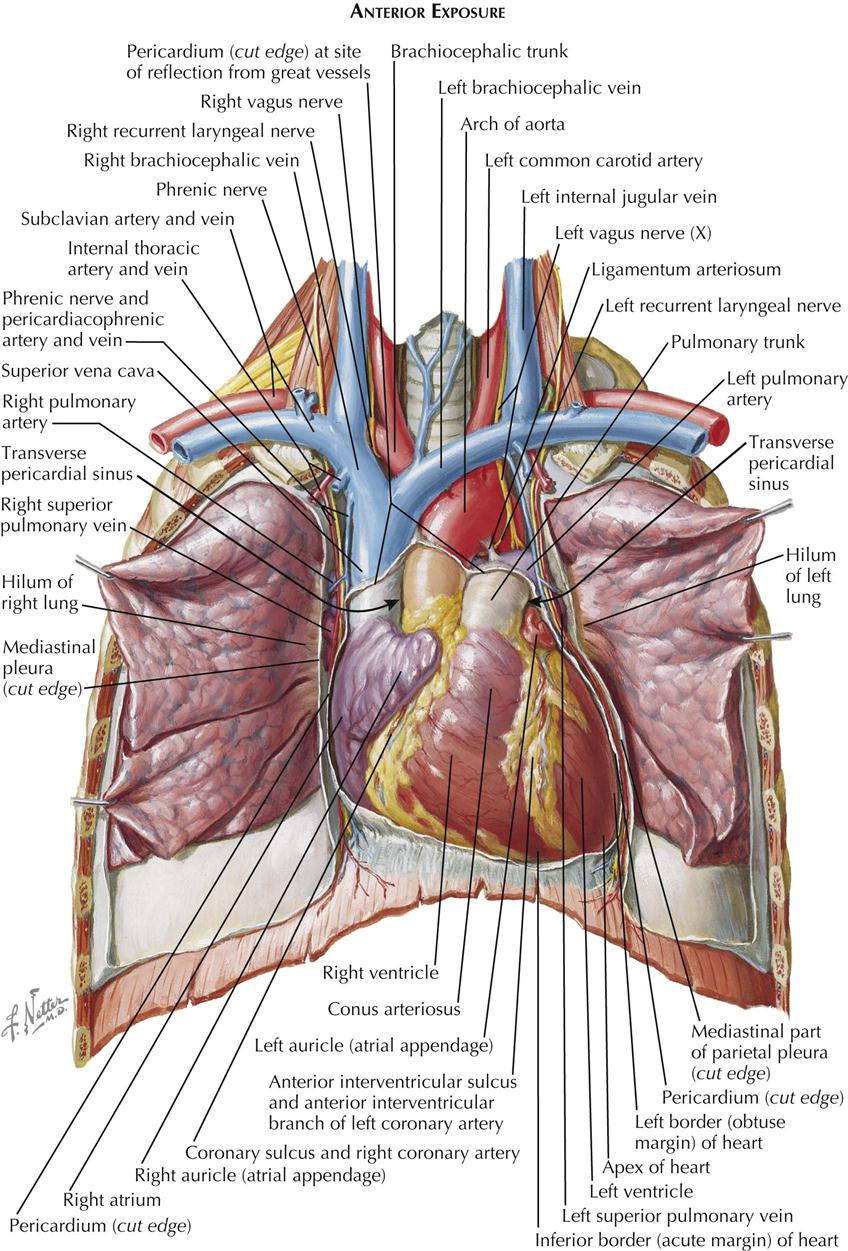
Thoracic Cavity Labeled The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. Thoracic cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. it is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. among the major organs contained in the thoracic cavity are the heart and lungs. Explore the anatomy of the human thorax. this comprehensive guide covers the thoracic cavity's vital structures and their functions. learn more here. Its upper boundary is the superior thoracic aperture, or thoracic inlet. inferiorly, the diaphragm, a dome shaped muscle, forms the floor of the thoracic cavity, separating it from the abdominal cavity. the framework of the thorax is primarily composed of its skeletal components, forming the thoracic cage. It is a bony, muscular, and vascular framework that encloses the thoracic cavity and facilitates the movement of air during breathing. the thorax is divided into bony structures, muscles, vessels, nerves, and the thoracic cavity. Thoracic outlet syndrome, or tos, is actually a trio of three syndromes neurogenic tos, venous tos, and arterial tos. neurogenic tos is the most common form of tos. in neurogenic tos, the brachial plexus is compressed by its surrounding structures in the thoracic outlet. these compressive structures are the first rib, the anterior scalene muscle, and the middle scalene muscle. compression of.
Thoracic Cavity Labeled Explore the anatomy of the human thorax. this comprehensive guide covers the thoracic cavity's vital structures and their functions. learn more here. Its upper boundary is the superior thoracic aperture, or thoracic inlet. inferiorly, the diaphragm, a dome shaped muscle, forms the floor of the thoracic cavity, separating it from the abdominal cavity. the framework of the thorax is primarily composed of its skeletal components, forming the thoracic cage. It is a bony, muscular, and vascular framework that encloses the thoracic cavity and facilitates the movement of air during breathing. the thorax is divided into bony structures, muscles, vessels, nerves, and the thoracic cavity. Thoracic outlet syndrome, or tos, is actually a trio of three syndromes neurogenic tos, venous tos, and arterial tos. neurogenic tos is the most common form of tos. in neurogenic tos, the brachial plexus is compressed by its surrounding structures in the thoracic outlet. these compressive structures are the first rib, the anterior scalene muscle, and the middle scalene muscle. compression of.

Thoracic Cavity Vector Illustration Drawing Labeled Cartoondealer It is a bony, muscular, and vascular framework that encloses the thoracic cavity and facilitates the movement of air during breathing. the thorax is divided into bony structures, muscles, vessels, nerves, and the thoracic cavity. Thoracic outlet syndrome, or tos, is actually a trio of three syndromes neurogenic tos, venous tos, and arterial tos. neurogenic tos is the most common form of tos. in neurogenic tos, the brachial plexus is compressed by its surrounding structures in the thoracic outlet. these compressive structures are the first rib, the anterior scalene muscle, and the middle scalene muscle. compression of.

Structure Of Thoracic Cavity Diagram Quizlet
Comments are closed.