The Structure And Physiology Of The Human Brain

Structure Of Human Brain Anatomy And Physiology At a high level, the brain can be divided into the cerebrum, brainstem and cerebellum. the cerebrum (front of brain) comprises gray matter (the cerebral cortex) and white matter at its center. the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Learn about the parts of the brain and their functions. get a diagram of human brain anatomy and key facts about this important organ.

Basics Of Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain An Introduction For The brain is a central focus of neuroscience, responsible for controlling bodily functions, interpreting sensory input, and shaping individual identity. studying its neuroanatomy—the structure of the nervous system—reveals how each region contributes to cognition and behavior. Your brain is a complex organ that regulates everything you do, like your senses, emotions, thoughts, memories, movement and behavior. it even controls body processes you don’t have to think about, like your breathing, body temperature and your heart rate. The brain is an organ composed of nervous tissue that commands task evoked responses, movement, senses, emotions, language, communication, thinking, and memory. the three main parts of the human brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The human brain is the central organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. it consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. the brain controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system.

The Human Brain Its Configuration Structure Development And The brain is an organ composed of nervous tissue that commands task evoked responses, movement, senses, emotions, language, communication, thinking, and memory. the three main parts of the human brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The human brain is the central organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. it consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. the brain controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system. For this laboratory, we will consider the brain in terms of the medical scheme (figure 1): divided into two hemispheres, the cerebrum is the largest region of the human brain – the two hemispheres together account for ~ 85% of total brain mass. The brain consists of many parts that function as an integrated whole. the major parts are the medulla, pons, and midbrain (collectively called the brain stem), the cerebellum, the hypothalamus, the thala mus, and the cerebrum. Organization of the nervous (neural) system in human beings is classified in two ways: central nervous (neural) system (cns). peripheral nervous (neural) system (pns). the brain and spinal cord make up the cns. these are made up of ectoderm and are arranged in a neural tube configuration. The human brain is the center of the human nervous system. it has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is larger than expected on the basis of body size when compared to other primates.

Human Brain Human Physiology At 150 Piece S ह य मन फ ज य ल ज For this laboratory, we will consider the brain in terms of the medical scheme (figure 1): divided into two hemispheres, the cerebrum is the largest region of the human brain – the two hemispheres together account for ~ 85% of total brain mass. The brain consists of many parts that function as an integrated whole. the major parts are the medulla, pons, and midbrain (collectively called the brain stem), the cerebellum, the hypothalamus, the thala mus, and the cerebrum. Organization of the nervous (neural) system in human beings is classified in two ways: central nervous (neural) system (cns). peripheral nervous (neural) system (pns). the brain and spinal cord make up the cns. these are made up of ectoderm and are arranged in a neural tube configuration. The human brain is the center of the human nervous system. it has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is larger than expected on the basis of body size when compared to other primates.

Human Brain Anatomy Physiology3d Stock Illustration 1835524453 Organization of the nervous (neural) system in human beings is classified in two ways: central nervous (neural) system (cns). peripheral nervous (neural) system (pns). the brain and spinal cord make up the cns. these are made up of ectoderm and are arranged in a neural tube configuration. The human brain is the center of the human nervous system. it has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is larger than expected on the basis of body size when compared to other primates.
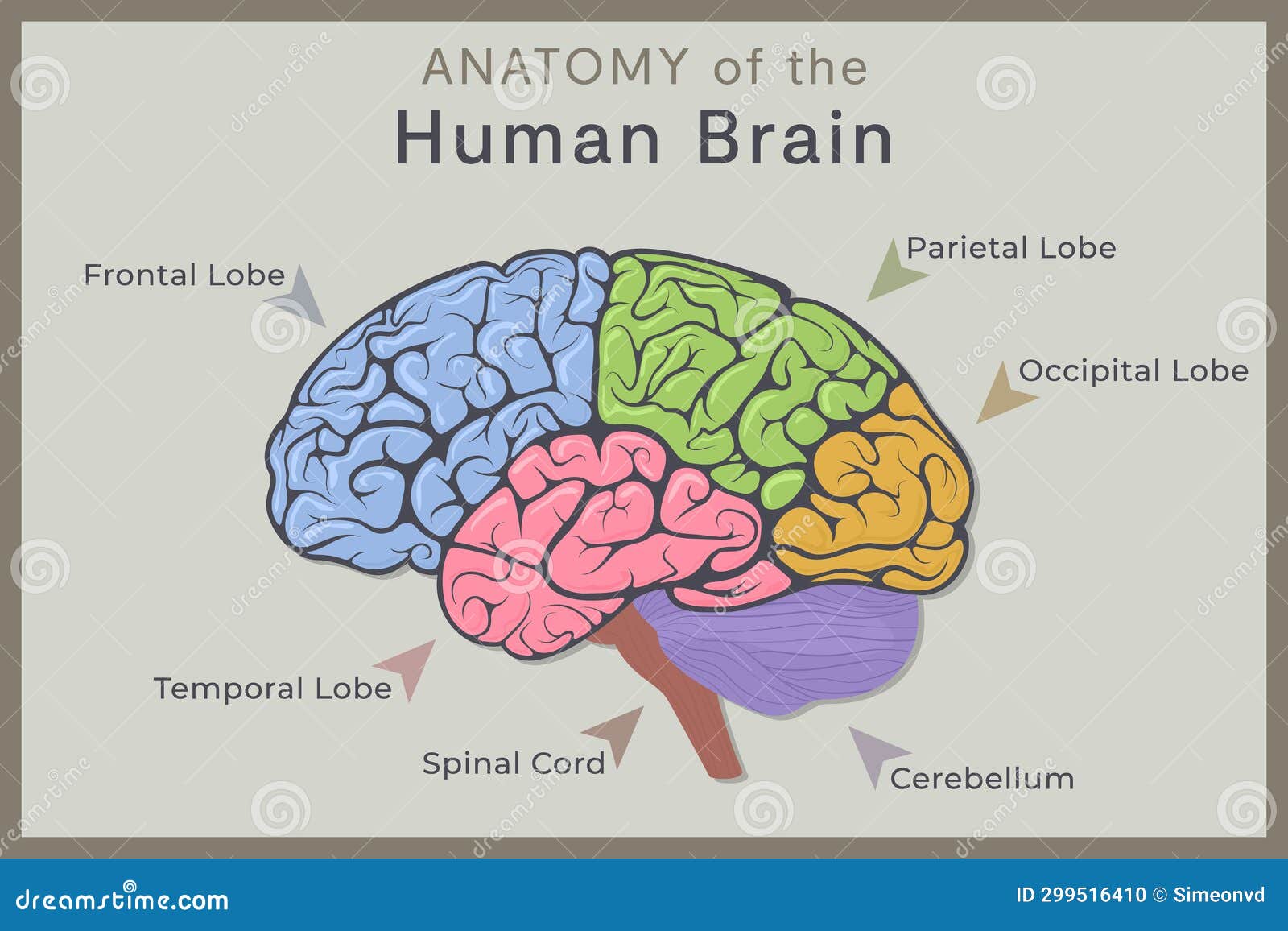
Anatomy Of The Human Brain Structure And Functions Vector
Comments are closed.