The Probability Sampling And Non Probability Sampling Method Vector

Probability And Non Probability Sampling Pdf The probability is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely the desired outcome is to occur. for example, tossing a coin twice will yield "head head", "head tail", "tail head", and "tail tail" outcomes. How likely something is to happen. many events can't be predicted with total certainty. the best we can say is how likely they are to happen, using the idea of probability. when a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes: also: when a single die is thrown, there are six possible outcomes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.

Non Probability Sampling Pdf Sampling Statistics Survey Methodology The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1 (inclusive). if the probability of an event is 0, then the event is impossible. on the other hand, an event with probability 1 is certain to occur. in general, the higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. Probability is all about how likely is an event to happen. for a random experiment with sample space s, the probability of happening of an event a is calculated by the probability formula n(a) n(s). A probability of 0 means an event is impossible, while a probability of 1 means it is certain. it covers fundamental concepts, formulas, and theorems to analyse outcomes in daily decisions, research, and industries. What is probability? definition, formula, and examples of classical probability, relative frequency of probability, and subjective probability.

Probability Sampling And Non Probability Sampling Vector Image A probability of 0 means an event is impossible, while a probability of 1 means it is certain. it covers fundamental concepts, formulas, and theorems to analyse outcomes in daily decisions, research, and industries. What is probability? definition, formula, and examples of classical probability, relative frequency of probability, and subjective probability. Learn all about probability like definition, formula, types, probability terms, and their definitions. check out solved problems on finding the probability. Conditional probability. theorem of total probability. bayes theorem. independence of two events. mutual independence of n events. sampling with and without replacement. random variables. univariate distributions discrete, continuous, mixed. standard distributions hypergeometric, binomial, geometric, poisson, uni form, normal, exponential. Probability is the branch of mathematics where we determine how likely an event is to occur. it is represented as a numeric value ranging from 0 to 1. probability can be calculated as: total outcomes represent the complete set of possible results an event can produce. The concept of probability is one of the foundations of general statistics. the likelihood of a particular outcome among the set of possible outcomes is expressed by a number from 0 to 1, with 0 representing an impossible outcome and 1 representing the absolute certainty of that outcome.

An Overview Of Non Probability Sampling Methods And Their Applications Learn all about probability like definition, formula, types, probability terms, and their definitions. check out solved problems on finding the probability. Conditional probability. theorem of total probability. bayes theorem. independence of two events. mutual independence of n events. sampling with and without replacement. random variables. univariate distributions discrete, continuous, mixed. standard distributions hypergeometric, binomial, geometric, poisson, uni form, normal, exponential. Probability is the branch of mathematics where we determine how likely an event is to occur. it is represented as a numeric value ranging from 0 to 1. probability can be calculated as: total outcomes represent the complete set of possible results an event can produce. The concept of probability is one of the foundations of general statistics. the likelihood of a particular outcome among the set of possible outcomes is expressed by a number from 0 to 1, with 0 representing an impossible outcome and 1 representing the absolute certainty of that outcome.

Type The Non Probability Sampling Method Charts Vector Image Probability is the branch of mathematics where we determine how likely an event is to occur. it is represented as a numeric value ranging from 0 to 1. probability can be calculated as: total outcomes represent the complete set of possible results an event can produce. The concept of probability is one of the foundations of general statistics. the likelihood of a particular outcome among the set of possible outcomes is expressed by a number from 0 to 1, with 0 representing an impossible outcome and 1 representing the absolute certainty of that outcome.
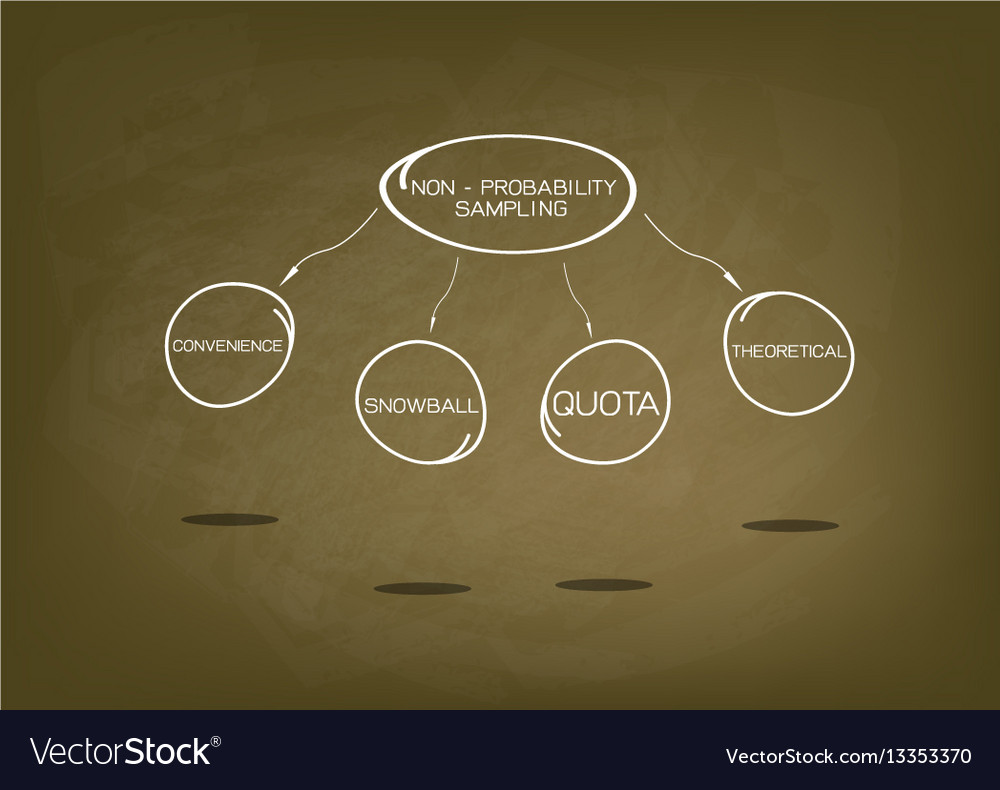
Type Non Probability Sampling Method Charts Vector Image
Comments are closed.