The Memory Hierarchy Topics Pdf Dynamic Random Access Memory Cpu

Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory Pdf Dynamic Random Access Fundamental idea of a memory hierarchy: for each level k, the faster and smaller device at the level serves as a cache for the larger and slower device at level k 1. The memory hierarchy goal fact: large memories are slow and fast memories are small.
Memory Hierarchy Pdf Random Access Memory Dynamic Random Access The document discusses the memory hierarchy, including ram (sram and dram), disk storage, and i o buses. ram is volatile and used for main memory, while disks are non volatile but much slower. Today’s goals explore the memory systems available in modern computers understand capabilities and limitations of each discuss the memory hierarchy how it improves performance through caching describe software patterns that caching is designed to support. Positioning time (random access time): time to move disk arm to desired cylinder (seek time) plus time for desired sector to rotate under disk head (rotational latency). Big idea: the memory hierarchy creates a large pool of storage that costs as much as the cheap storage near the bottom, but that serves data to programs at the rate of the fast storage near the top.

Pptx Memory Hierarchy Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Main Memory Random Positioning time (random access time): time to move disk arm to desired cylinder (seek time) plus time for desired sector to rotate under disk head (rotational latency). Big idea: the memory hierarchy creates a large pool of storage that costs as much as the cheap storage near the bottom, but that serves data to programs at the rate of the fast storage near the top. Locality: how to create illusion of fast access to capacious data from the perspective of memory hierarchy, locality is using the data in at any particular level more frequently than accessing storage at next slower level. Access time dominated by seek time and rotational latency. first bit in a sector is the most expensive, the rest are free. sram access time is about 4 ns doubleword, dram about 60 ns. To create this illusion of lots of fast memory, we create a hierarchical memory structure, with multiple levels. an example of a structure with 4 levels is shown in figure 5.1. studying such hierarchical structure in more detail is the topic of this chapter. Typical bus structure connecting cpu and memory a bus is a collection of parallel wires that carry address, data, and control signals. buses are typically shared by multiple devices. cpu chip system bus.
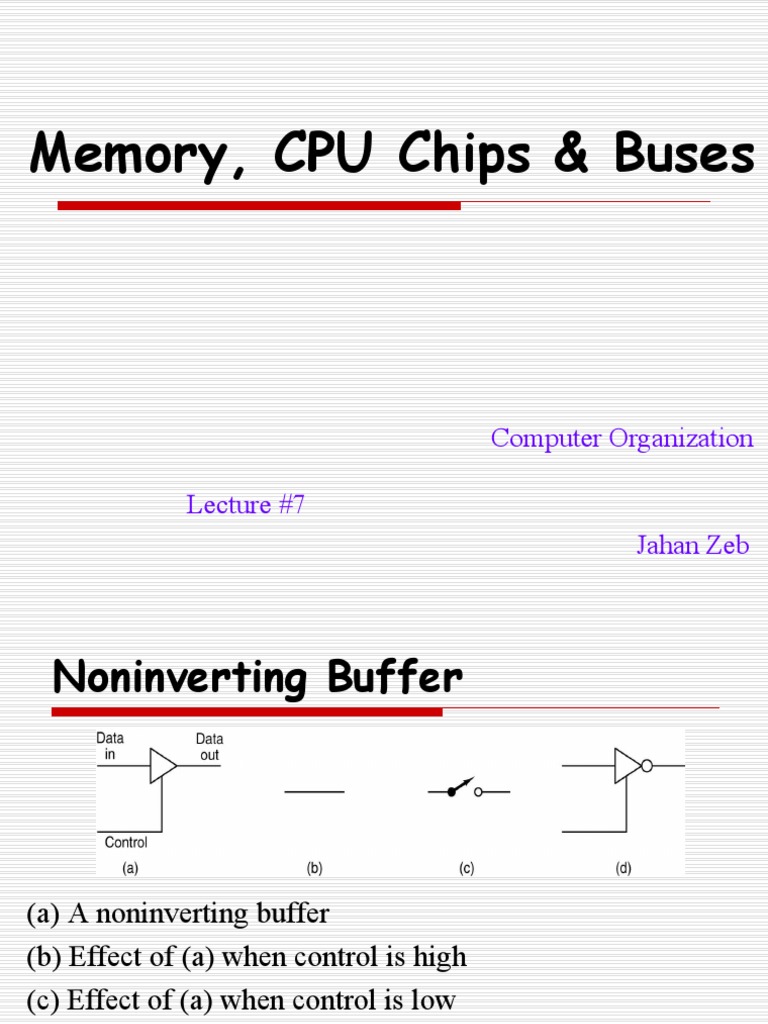
Lecture 7 Memory Cpu Chips Buses 012443 Pdf Dynamic Random Locality: how to create illusion of fast access to capacious data from the perspective of memory hierarchy, locality is using the data in at any particular level more frequently than accessing storage at next slower level. Access time dominated by seek time and rotational latency. first bit in a sector is the most expensive, the rest are free. sram access time is about 4 ns doubleword, dram about 60 ns. To create this illusion of lots of fast memory, we create a hierarchical memory structure, with multiple levels. an example of a structure with 4 levels is shown in figure 5.1. studying such hierarchical structure in more detail is the topic of this chapter. Typical bus structure connecting cpu and memory a bus is a collection of parallel wires that carry address, data, and control signals. buses are typically shared by multiple devices. cpu chip system bus.
Comments are closed.