Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg
Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg The robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m. l2 = 0.2 m. Learn block diagram reduction techniques & transfer function derivation with solved examples. control systems engineering resource.

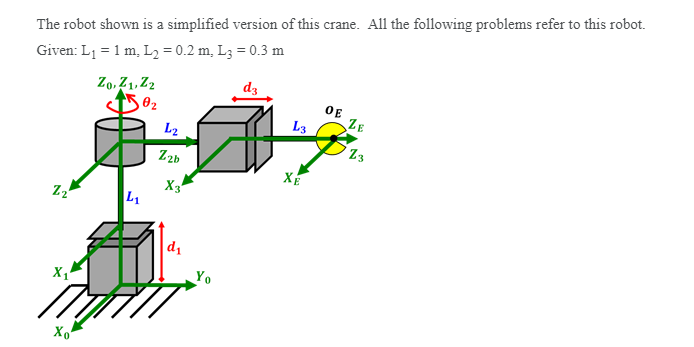
Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg The robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1=1m, l2=0.2m, l3=0.3m. the robot is shown in its home configuration. take note of the coordinate frame for the robot's initial alignment!. The robot has 3 degrees of freedom, as it can move in three different directions: up and down (joint 1), back and forth (joint 2), and left and right (joint 3). Assuming that all the joints are allowed to rotate 360 degrees, determine the workspace of the robot. sketch the workspace envelope, and show the size and dimensions of the envelope in your sketch. Solution for the robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given l = 1m, l = 0.2m, l = 0.3m z0.21, z2 = 0.2l2, z2b ds oe = l3, ze.

Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg Assuming that all the joints are allowed to rotate 360 degrees, determine the workspace of the robot. sketch the workspace envelope, and show the size and dimensions of the envelope in your sketch. Solution for the robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given l = 1m, l = 0.2m, l = 0.3m z0.21, z2 = 0.2l2, z2b ds oe = l3, ze. Here’s the best way to solve it. the robot's joint classification is prp, where p stands for prismatic joint and r sta … the robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m, l2 = 0.2 m. Consider the simplified robot shown in figure 33. suppose the robot’s cartesian coordinates are known at all times, as are those of its goal location. however, the locations of the obstacles are unknown. the robot can sense obstacles in its immediate proximity, as illustrated in this figure. For simplicity, let us assume the robot's motion is noise free, and the state space is discrete. figure 25.33 is only one example; in this exercise you are required to address all possible grid worlds with a valid path from the start to the goal location. The robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m. l2 = 0.2 m. l3 = 0.3 m 20,21,22 oe 16 13 which of the following joint values correspond to the robot's singularities? di=o di = 1 d = 1 ♡ ez=0 02 = 1 62 = 1 2 62 = 1 2 v d3=0 d3 = 0.5 d3=0.5.
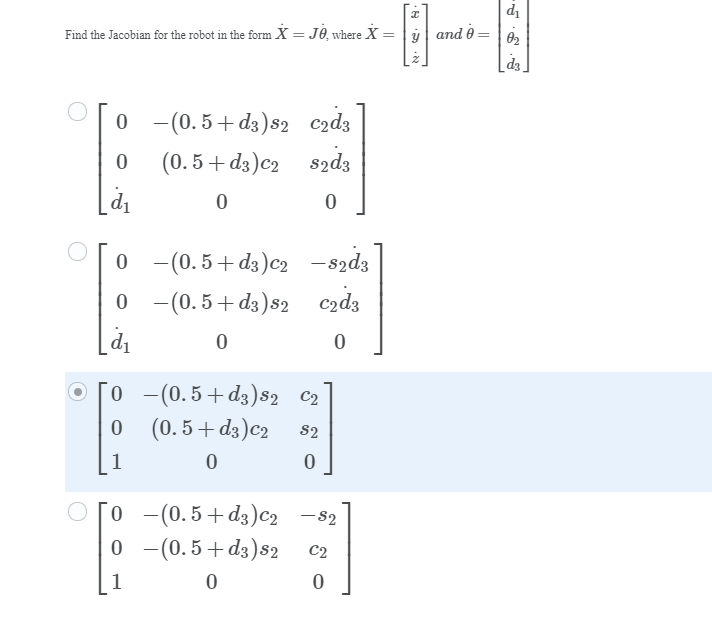
Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. the robot's joint classification is prp, where p stands for prismatic joint and r sta … the robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m, l2 = 0.2 m. Consider the simplified robot shown in figure 33. suppose the robot’s cartesian coordinates are known at all times, as are those of its goal location. however, the locations of the obstacles are unknown. the robot can sense obstacles in its immediate proximity, as illustrated in this figure. For simplicity, let us assume the robot's motion is noise free, and the state space is discrete. figure 25.33 is only one example; in this exercise you are required to address all possible grid worlds with a valid path from the start to the goal location. The robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m. l2 = 0.2 m. l3 = 0.3 m 20,21,22 oe 16 13 which of the following joint values correspond to the robot's singularities? di=o di = 1 d = 1 ♡ ez=0 02 = 1 62 = 1 2 62 = 1 2 v d3=0 d3 = 0.5 d3=0.5.

Solved The Robot Shown Is A Simplified Version Of This Chegg For simplicity, let us assume the robot's motion is noise free, and the state space is discrete. figure 25.33 is only one example; in this exercise you are required to address all possible grid worlds with a valid path from the start to the goal location. The robot shown is a simplified version of this crane. all the following problems refer to this robot. given: l1 = 1 m. l2 = 0.2 m. l3 = 0.3 m 20,21,22 oe 16 13 which of the following joint values correspond to the robot's singularities? di=o di = 1 d = 1 ♡ ez=0 02 = 1 62 = 1 2 62 = 1 2 v d3=0 d3 = 0.5 d3=0.5.
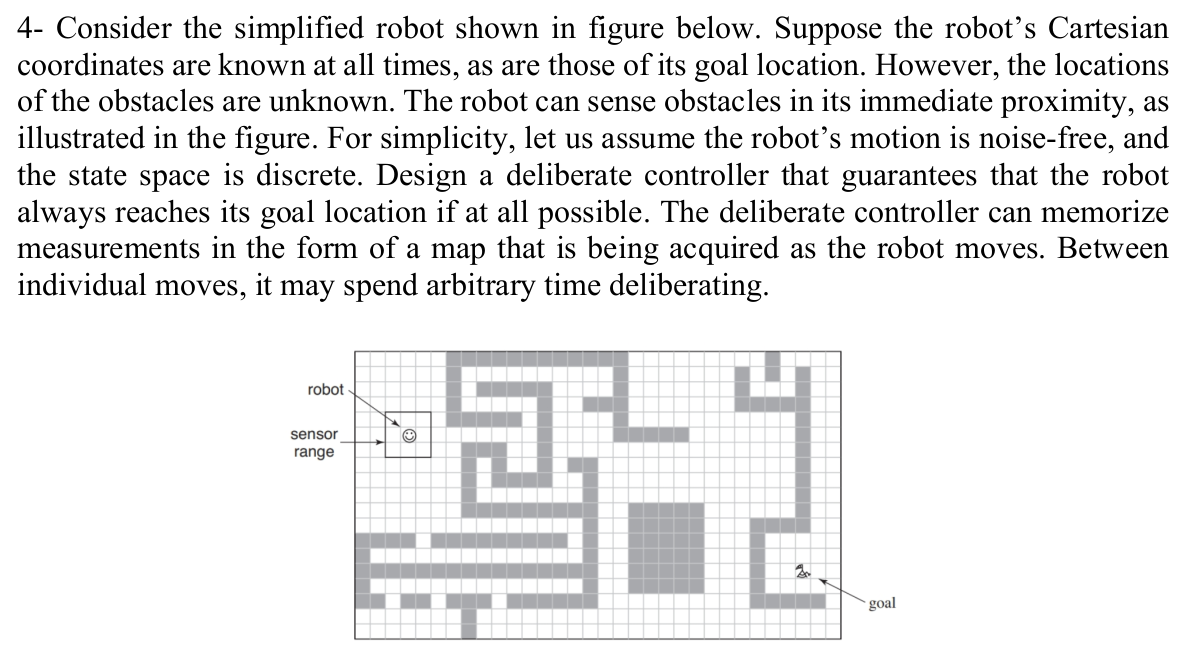
Solved 4 Consider The Simplified Robot Shown In Figure Chegg
Comments are closed.