Solved The Dimensional Formula Of Angular Velocity Is

Solved The Dimensional Formula Of Angular Velocity Is Angular velocity = angular displacement × [time] 1. or, v = [m 0 l 0 t 0] × [m 0 l 0 t 1] 1 = [m 0 l 0 t 1] therefore, the angular velocity is dimensionally represented as [m0 l0 t 1]. put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few mcqs. click ‘start quiz’ to begin!. To find the dimensional formula of angular velocity, we can follow these steps: angular velocity (ω) is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement (θ) with respect to time (t). mathematically, it can be expressed as: angular displacement (θ) is a measure of rotation and is considered dimensionless. therefore, its dimensional formula is:.

Angular Velocity Formula Definition Best Example More Get Angular velocity (ω) is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement (θ). explanation: ∴ dimensional formula of angular velocity = [m0l0t 1]. this are some of the useful dimensions of basic physical quantity, here m, l, t & i represents mass, length, time and current respectively. To derive the dimensional formula for angular velocity, we start with the definition of angular velocity itself. angular velocity (\omega ω) is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement with respect to time. Now, we need to put the dimensions of angular rotation and time in the equation of angular velocity. hence, option (d), i.e. m 0 l 0 t − 1 is the correct choice of the given question. note: we should know that the unit of the angular rotation θ is radian but it is a dimensionless quantity. Dimensional formula – each quantity can be expressed by means of power (fundamental units) to each unit for derived quantity. the expression can be simply written as, a= mplqtr. where a, p, q and r are constants, and their values differ with each measure.
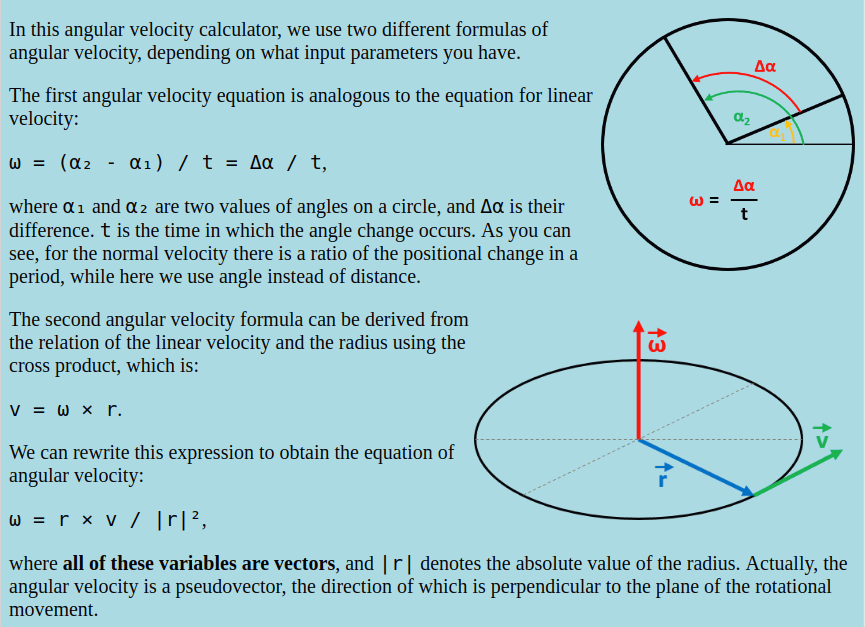
Angular Velocity Formula Now, we need to put the dimensions of angular rotation and time in the equation of angular velocity. hence, option (d), i.e. m 0 l 0 t − 1 is the correct choice of the given question. note: we should know that the unit of the angular rotation θ is radian but it is a dimensionless quantity. Dimensional formula – each quantity can be expressed by means of power (fundamental units) to each unit for derived quantity. the expression can be simply written as, a= mplqtr. where a, p, q and r are constants, and their values differ with each measure. The orbital angular velocity vector encodes the time rate of change of angular position, as well as the instantaneous plane of angular displacement. in this case (counter clockwise circular motion) the vector points up. in three dimensional space, we again have the position vector r of a moving particle. here, orbital angular velocity is a pseudovector whose magnitude is the rate at which r. Here in this article, we will be discussing the definition of angular speed and the dimensional formula of angular speed along with its derivation. dimensional formula is the formula which represents a physical quantity in the terms of fundamental physical quantities. It is generally denoted by ω (omega) and its unit is radians per second (denoted by rad.s − 1). its dimensional formula is [m 0 l 0 t − 1]. the angular velocity (ω) formula is. ω = angle traced time taken. i.e. ω = Δ θ Δ t ≈ d θ d t. consider a point object moving along a circular path, with a center (i.e., axis of rotation) at o. Angular speed = 2π × [time] 1. or, ω = [m 0 l 0 t 1] 1. therefore, angular speed is dimensionally represented as m0 l0 t 1. put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few mcqs. click ‘start quiz’ to begin!.
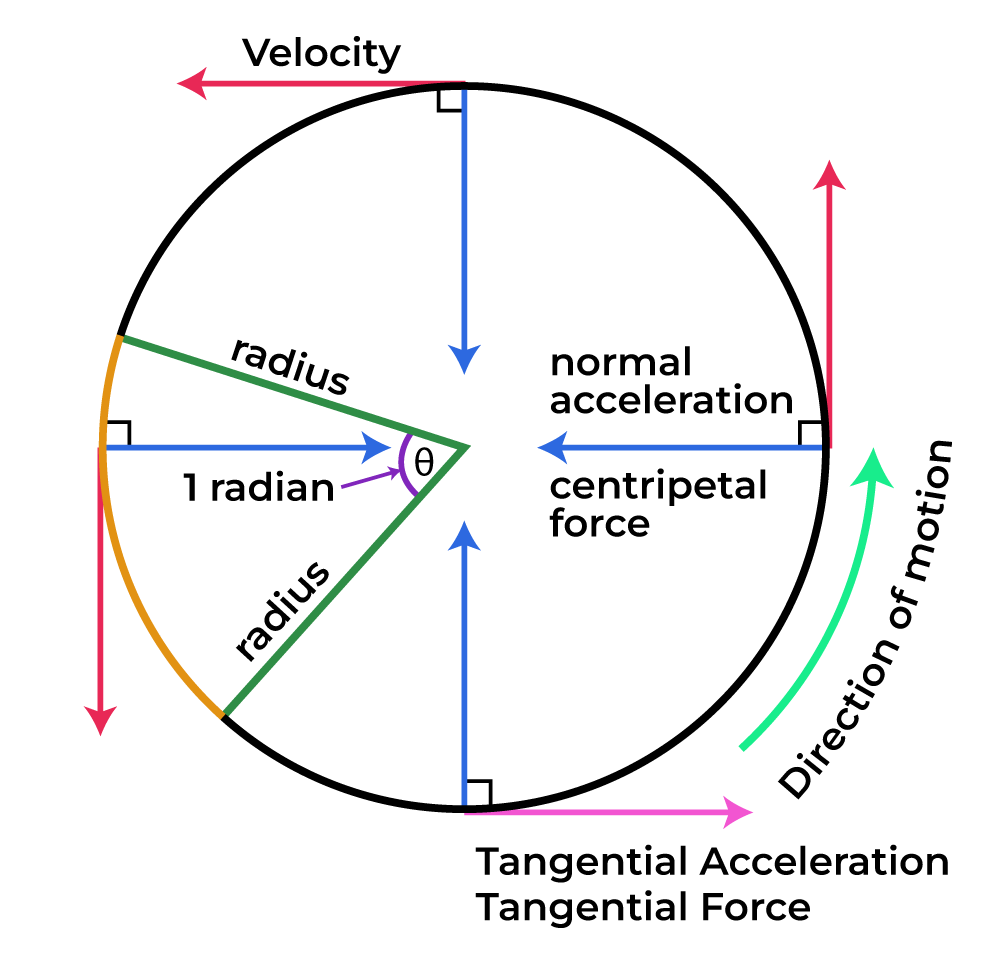
Angular Velocity Formula The orbital angular velocity vector encodes the time rate of change of angular position, as well as the instantaneous plane of angular displacement. in this case (counter clockwise circular motion) the vector points up. in three dimensional space, we again have the position vector r of a moving particle. here, orbital angular velocity is a pseudovector whose magnitude is the rate at which r. Here in this article, we will be discussing the definition of angular speed and the dimensional formula of angular speed along with its derivation. dimensional formula is the formula which represents a physical quantity in the terms of fundamental physical quantities. It is generally denoted by ω (omega) and its unit is radians per second (denoted by rad.s − 1). its dimensional formula is [m 0 l 0 t − 1]. the angular velocity (ω) formula is. ω = angle traced time taken. i.e. ω = Δ θ Δ t ≈ d θ d t. consider a point object moving along a circular path, with a center (i.e., axis of rotation) at o. Angular speed = 2π × [time] 1. or, ω = [m 0 l 0 t 1] 1. therefore, angular speed is dimensionally represented as m0 l0 t 1. put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few mcqs. click ‘start quiz’ to begin!.
Comments are closed.