Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Chegg

Solved 3 Given The Initial Value Problem I Solve The Chegg Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. This calculus video tutorial explains how to solve the initial value problem as it relates to separable differential equations. more.
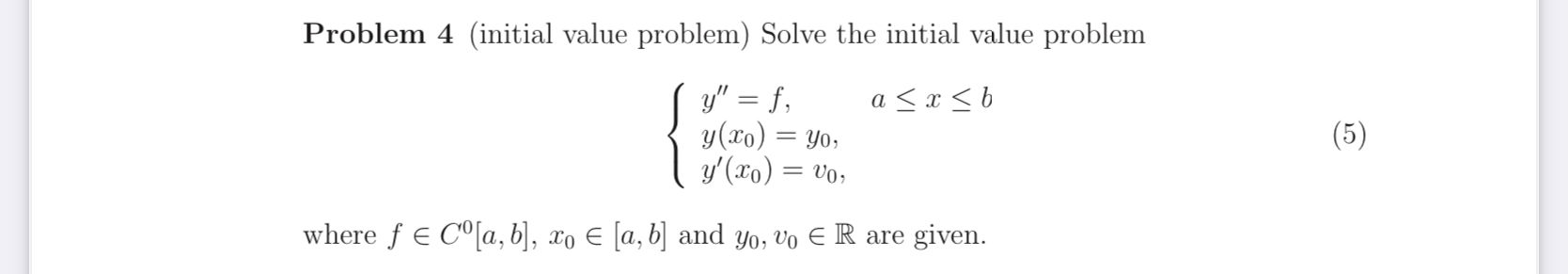
Solved Problem 4 Initial Value Problem Solve The Initial Chegg In this article, we’ll talk about initial value problems and what they are. we’ll also look at the steps you can take to solve them, along with some examples to show how it’s done in practice. Ask a question for free get a free answer to a quick problem. most questions answered within 4 hours. An initial value problem specific solution is a differential equation that comes with extra conditions. these additional conditions, known as "initial values," specify the function's value and sometimes its derivatives at a particular point. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: solve the initial value problem (ivp): x˙ (t)=t2−x with x (0)=2. the true solution to this equation is x (t)=2−2t t2. we will use this true solution to calculate the error of our approximations.
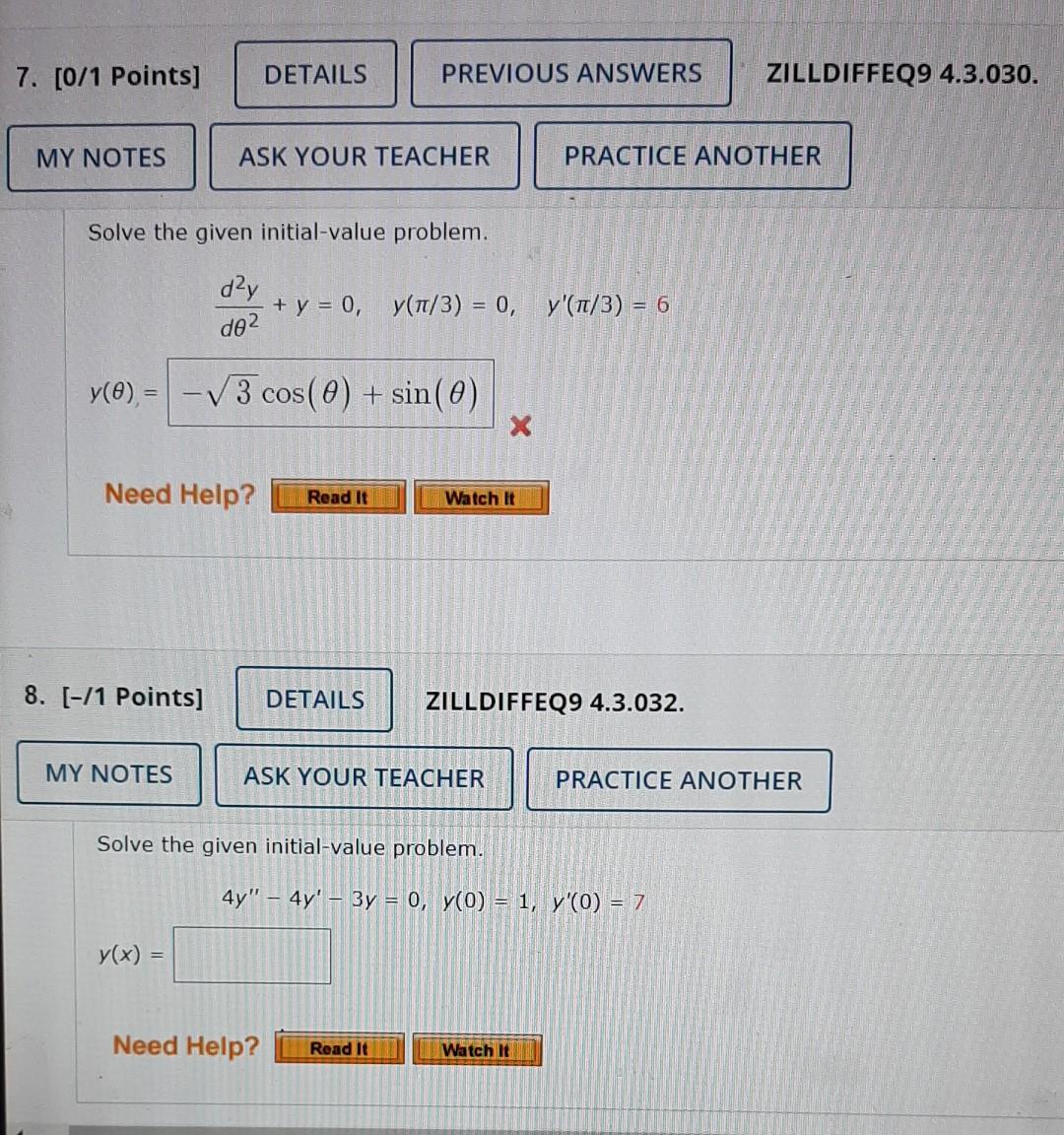
Solved 7 Solve The Given Initial Value Problem 8 Solve The Chegg An initial value problem specific solution is a differential equation that comes with extra conditions. these additional conditions, known as "initial values," specify the function's value and sometimes its derivatives at a particular point. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: solve the initial value problem (ivp): x˙ (t)=t2−x with x (0)=2. the true solution to this equation is x (t)=2−2t t2. we will use this true solution to calculate the error of our approximations. The approach will be as mentioned by d.f. in comments, we are going to solve for the lower interval and use that result to solve the upper interval (in essence, we are solving two odes). We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. In this chapter we will use the forward and backward finite difference formulae to solve the initial value problem. the accuracy and stability of the techniques will be briefly discussed. Thankfully there are many solver packages that have been created for use on personal computers that deal quite well with solving initial value problems. these solver packages fall into two groups: symbolic solvers, and numerical solvers.
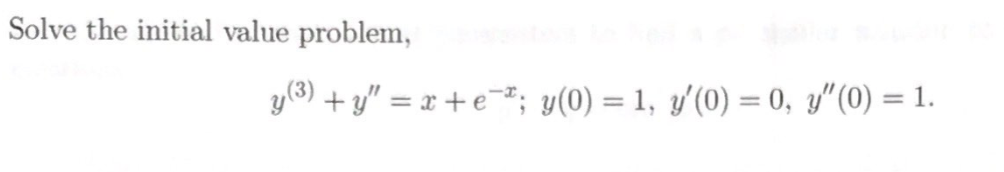
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Chegg The approach will be as mentioned by d.f. in comments, we are going to solve for the lower interval and use that result to solve the upper interval (in essence, we are solving two odes). We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. In this chapter we will use the forward and backward finite difference formulae to solve the initial value problem. the accuracy and stability of the techniques will be briefly discussed. Thankfully there are many solver packages that have been created for use on personal computers that deal quite well with solving initial value problems. these solver packages fall into two groups: symbolic solvers, and numerical solvers.
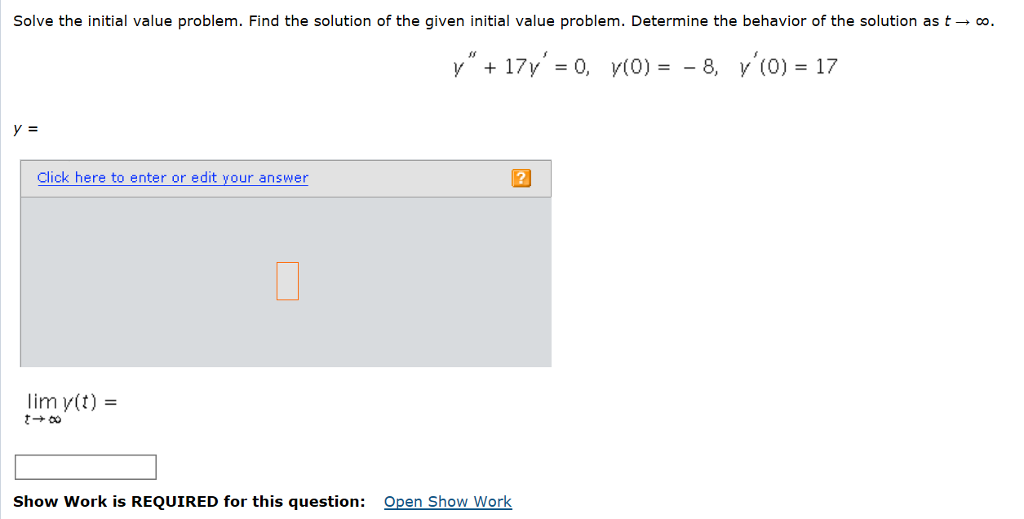
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Find The Solution Of Chegg In this chapter we will use the forward and backward finite difference formulae to solve the initial value problem. the accuracy and stability of the techniques will be briefly discussed. Thankfully there are many solver packages that have been created for use on personal computers that deal quite well with solving initial value problems. these solver packages fall into two groups: symbolic solvers, and numerical solvers.
Comments are closed.