Solved Solve The Following Cauchy Euler Differential Chegg

Solved Cauchy Euler Solve The Following Differential Chegg Solve the following cauchy euler differential equations or initial value problems using the method of variation of parameters. note that prime denotes derivative with respect to x. The solutions of cauchy euler equations can be found using this characteristic equation. just like the constant coefficient differential equation, we have a quadratic equation and the nature of the roots again leads to three classes of solutions.

Solved Cauchy Euler2 ï Solve The Following Differential Chegg Our online calculator, based on the wolfram alpha system allows you to find a solution of cauchy problem for various types of differential equations. to get started, you need to enter your task's data (differential equation, initial conditions) in the calculator. Al section 4.7 cauchy euler equation goal of this section 1. study solution of a class of variable coefficient linear equations called cauchy euler equation. this section, we consider equations with variable coefficients of the form a(t)y00 b(t)y0 c(t)y = f(t):. Today’s goals learn how to solve cauchy euler equations. learn how to model spring mass systems with undamped motion. Crack the secrets of the cauchy euler equation in our in depth tutorial. discover methods, examples, and tips for tackling second order des.
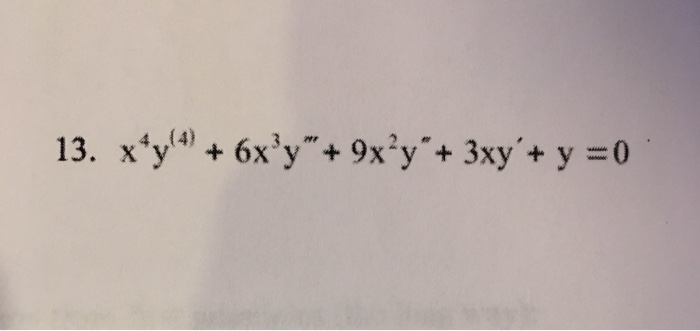
Solved Solve The Following Cauchy Euler Differential Chegg Today’s goals learn how to solve cauchy euler equations. learn how to model spring mass systems with undamped motion. Crack the secrets of the cauchy euler equation in our in depth tutorial. discover methods, examples, and tips for tackling second order des. Convert the above euler equation to a second order, constant coefficient differential equation using the substitution x = et. remember, this is equivalent to t = ln|x|. These types of equations can be solved using the technique described in the following theorem. theorem 4.14. the transformation x = et reduces the cauchy euler equation to a linear de with constant coefficients. note. by making the transformation x = et we are assuming x > 0. unless otherwise stated, this will be the assumption. In the grand tradition of mathematics, we will show how to solve a second order euler cauchy differential equation by transforming it into a differential equation that has been previously solved. Differential equations topic: cauchy euler equation solve the following differential equation using the cauchy euler equation's method also, fin the solution for the non homogeneus part of the equation.
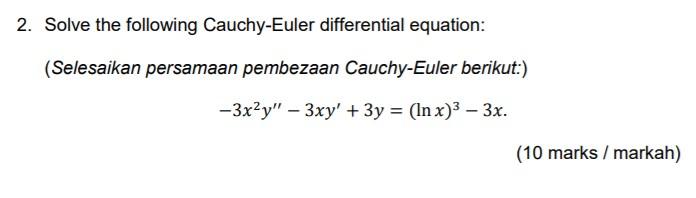
Solved 2 Solve The Following Cauchy Euler Differential Chegg Convert the above euler equation to a second order, constant coefficient differential equation using the substitution x = et. remember, this is equivalent to t = ln|x|. These types of equations can be solved using the technique described in the following theorem. theorem 4.14. the transformation x = et reduces the cauchy euler equation to a linear de with constant coefficients. note. by making the transformation x = et we are assuming x > 0. unless otherwise stated, this will be the assumption. In the grand tradition of mathematics, we will show how to solve a second order euler cauchy differential equation by transforming it into a differential equation that has been previously solved. Differential equations topic: cauchy euler equation solve the following differential equation using the cauchy euler equation's method also, fin the solution for the non homogeneus part of the equation.
Comments are closed.