Solved Simple Random Sampling Systematic Sarnpling Convenience

Systematic Random Sampling Pdf This video lecture on sampling: sampling & its types | simple random, convenience, systematic, cluster, stratified | examples | definition with examples |. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like objective:, simple random sample, sample of convenience and more.

In Systematic Random Sampling Method Pdf Sampling Statistics You don't have a complete list, so simple random sampling doesn't apply, and the bulbs are already in boxes, so you can't order them to use systematic. and all the bulbs are essentially the same, so there aren't any characteristics with which to stratify them. These two designs highlight a trade‐offs inherent in selecting a sampling design: to select sample units at random to minimize the risk of introducing biases into the sample or to select samples systematically to ensure that sample units are well‐distributed throughout the population. Besides simple random sampling, there are other forms of sampling that involve a chance process for getting the sample. other well known random sampling methods are the stratified sample, the cluster sample, and the systematic sample. Answer the correct term for the sampling method described is stratified sample. explanation in a stratified sample: the population is divided into homogeneous groups (called strata). each element in the population belongs to one and only one stratum, ensuring that the groups are non overlapping.

Simple Random Sampling Pdf Confidence Interval Estimator Besides simple random sampling, there are other forms of sampling that involve a chance process for getting the sample. other well known random sampling methods are the stratified sample, the cluster sample, and the systematic sample. Answer the correct term for the sampling method described is stratified sample. explanation in a stratified sample: the population is divided into homogeneous groups (called strata). each element in the population belongs to one and only one stratum, ensuring that the groups are non overlapping. Systematic sampling involves choosing your sample based on a regular interval, rather than a fully random selection. it can also be used when you don’t have a complete list of the population. The core types of sampling (with visual intuition) sampling gets thrown around like it’s one size fits all, but it’s not. depending on your context, data shape, and what you’re trying to learn, the “right” approach to sampling can look very different. Identify the sampling method (simple random sampling, systematic sampling, convenience sampling, cluster sampling, or stratified sampling) in the following study. It explained probability based methods (e.g., simple random, stratified, cluster) and non probability methods (e.g., convenience, purposive, snowball) with practical examples demonstrating their applications.
Solved Simple Random Sampling Systematic Sarnpling Convenience Systematic sampling involves choosing your sample based on a regular interval, rather than a fully random selection. it can also be used when you don’t have a complete list of the population. The core types of sampling (with visual intuition) sampling gets thrown around like it’s one size fits all, but it’s not. depending on your context, data shape, and what you’re trying to learn, the “right” approach to sampling can look very different. Identify the sampling method (simple random sampling, systematic sampling, convenience sampling, cluster sampling, or stratified sampling) in the following study. It explained probability based methods (e.g., simple random, stratified, cluster) and non probability methods (e.g., convenience, purposive, snowball) with practical examples demonstrating their applications.

Sampling Its Types Simple Random Convenience Systematic Cluster Identify the sampling method (simple random sampling, systematic sampling, convenience sampling, cluster sampling, or stratified sampling) in the following study. It explained probability based methods (e.g., simple random, stratified, cluster) and non probability methods (e.g., convenience, purposive, snowball) with practical examples demonstrating their applications.
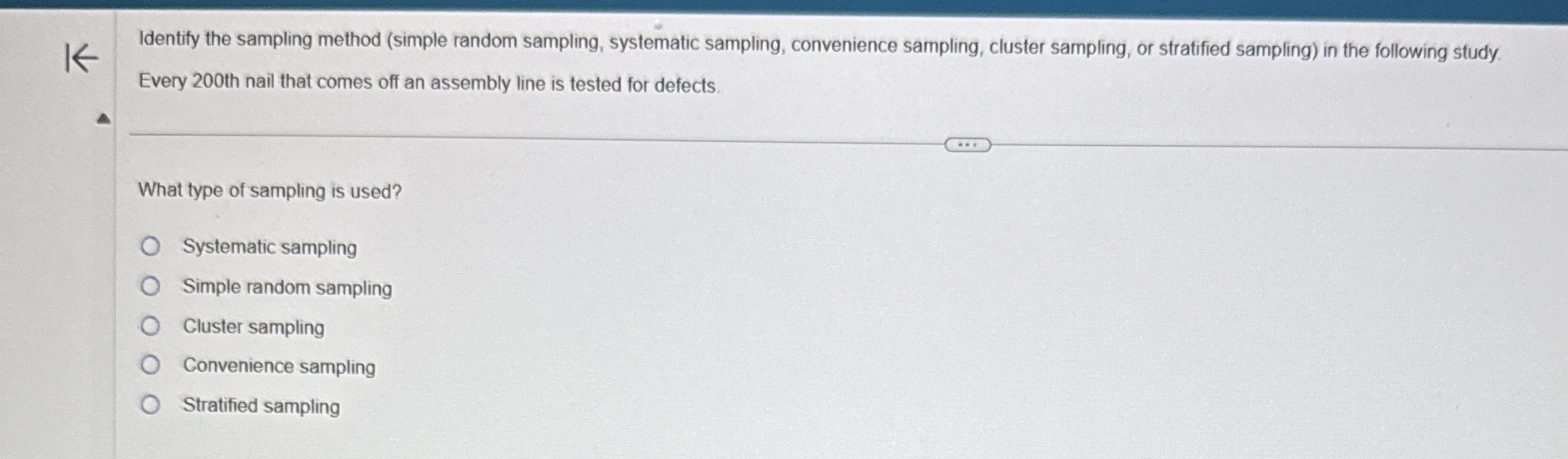
Identify The Sampling Method Simple Random Sampling Chegg
Comments are closed.