Solved Robot Modelling 1 I Identify The Configuration Of The Chegg

7 Robot Configuration Pdf Identify the configuration of the robot given in fig.2 and solve for inverse kinematics using the dh convention. (3 points) fig.23. for the cylindrical robot with spherical wrist given in fig.3, robot modelling 1. The configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot. since a robot’s links are rigid and of a known shape, only a few variables (coordinates in a general sense) are needed to represent its configuration.
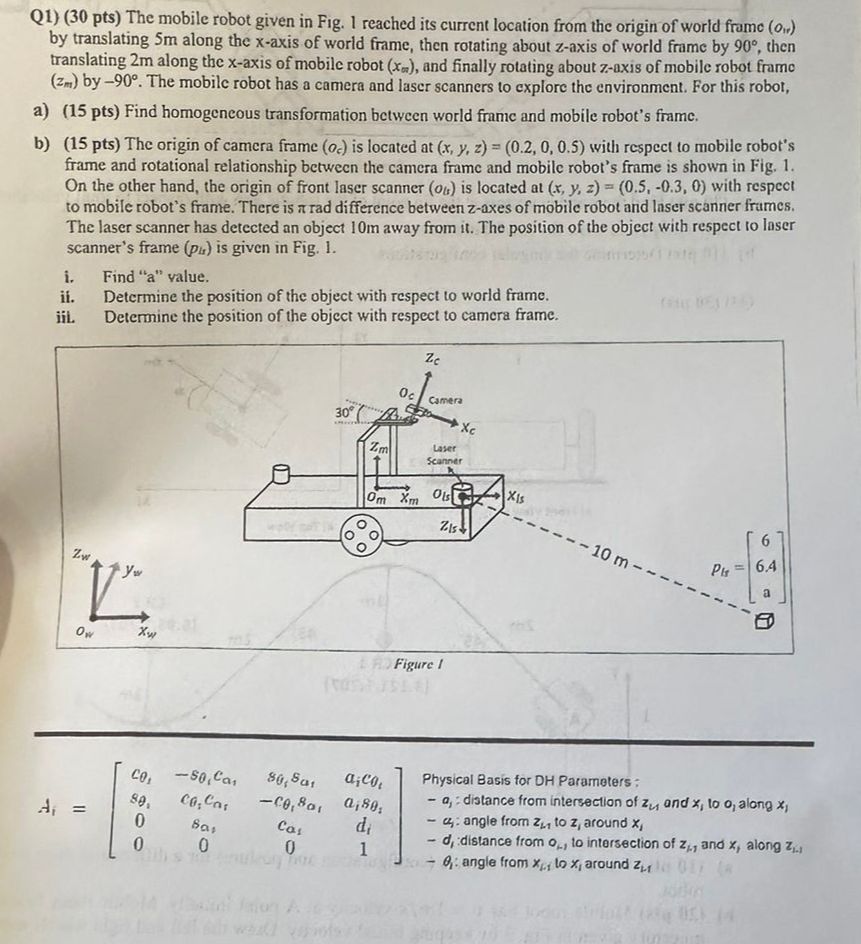
Solved Robot Modelling 1 ï Identify The Configuration Of The Chegg The type of program used when a work cycle is taught to robot by moving the manipulator through the required motion cycle and simultaneously entering the program into controller memory for later playback. Given two frames of reference, transformations convert configurations (position orientation) from one to the other. a robot sees a thing. where is the thing in the world? there’s a thing in the world. where is it wrt. the robot? a robot moves around. where is it in the world?. The configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot. the minimum number n of real valued coordinates needed to represent the configuration is the number of degrees of freedom (dof) of the robot. However, we can still discuss the types of motions involved in three different configurations: (i), (iii), and (ix). (i) in configuration (i), the robot configuration could be a cartesian configuration, where the robot has three linear joints that allow it to move in the x, y, and z directions.
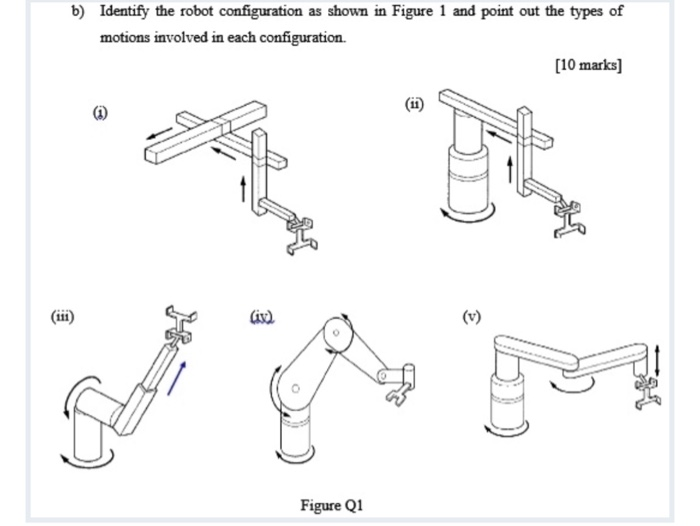
Solved B Identify The Robot Configuration As Shown In Chegg The configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot. the minimum number n of real valued coordinates needed to represent the configuration is the number of degrees of freedom (dof) of the robot. However, we can still discuss the types of motions involved in three different configurations: (i), (iii), and (ix). (i) in configuration (i), the robot configuration could be a cartesian configuration, where the robot has three linear joints that allow it to move in the x, y, and z directions. Here’s the best way to solve it. identify the scara manipulator by noting the parallel configuration of the z axes (z 0, z 1, z 2) and the rrp (revolute revolute prismatic) joint structure. This is the second lesson on fundamentals of robotics, and it will be your guide to know everything you have ever needed to know about the configuration and configuration space (its topology and representation) of a robot. in this lesson, we will talk about the configuration of the robot. Except for some special cases, these actuators uniquely determine the end effecter position and orientation as well as the configuration of the entire robot mechanism. Understand that the configuration of a robot refers to the specification of its position and orientation in space, as well as the positions of its joints or other movable parts.
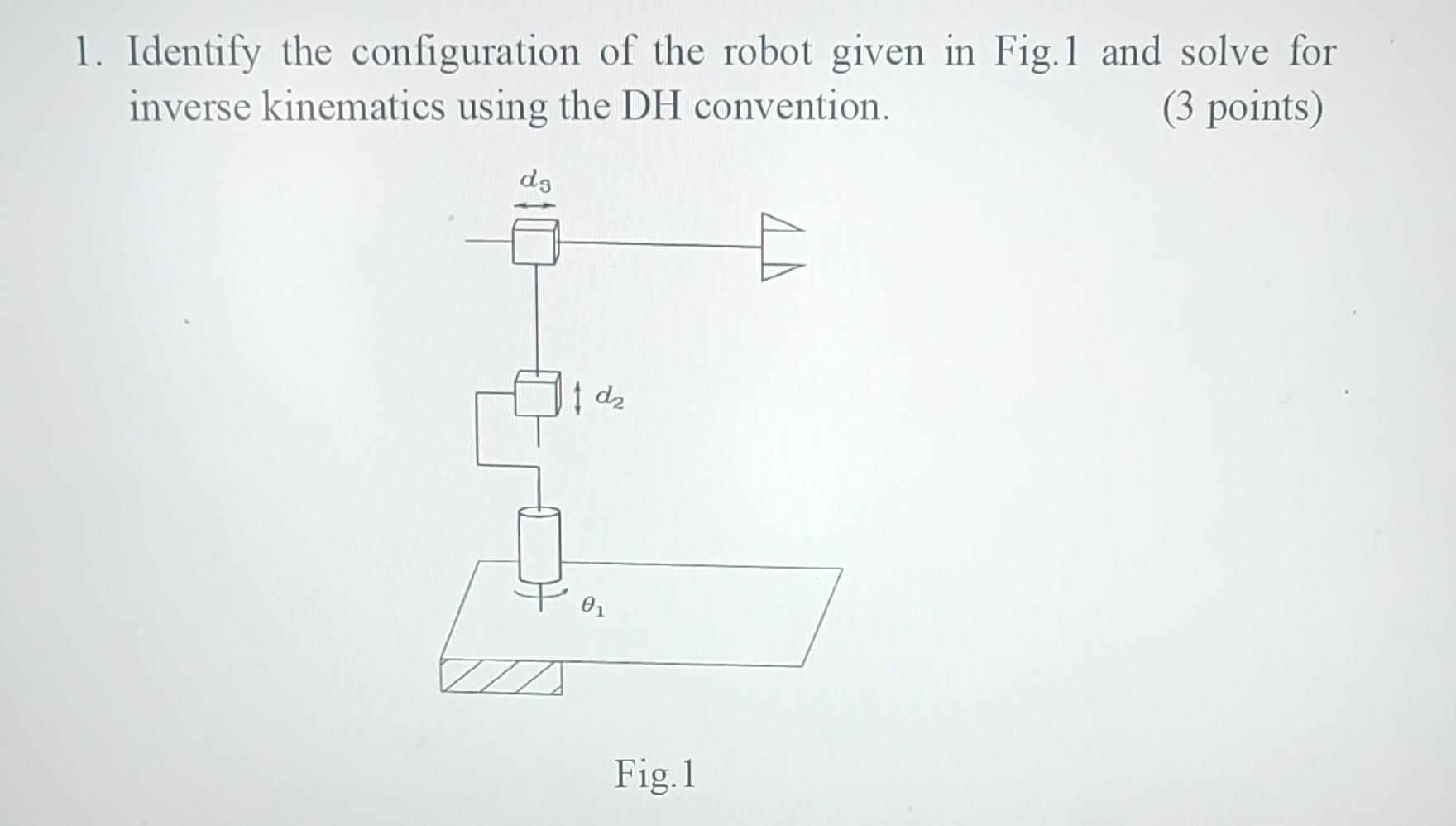
Solved 1 Identify The Configuration Of The Robot Given In Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. identify the scara manipulator by noting the parallel configuration of the z axes (z 0, z 1, z 2) and the rrp (revolute revolute prismatic) joint structure. This is the second lesson on fundamentals of robotics, and it will be your guide to know everything you have ever needed to know about the configuration and configuration space (its topology and representation) of a robot. in this lesson, we will talk about the configuration of the robot. Except for some special cases, these actuators uniquely determine the end effecter position and orientation as well as the configuration of the entire robot mechanism. Understand that the configuration of a robot refers to the specification of its position and orientation in space, as well as the positions of its joints or other movable parts.
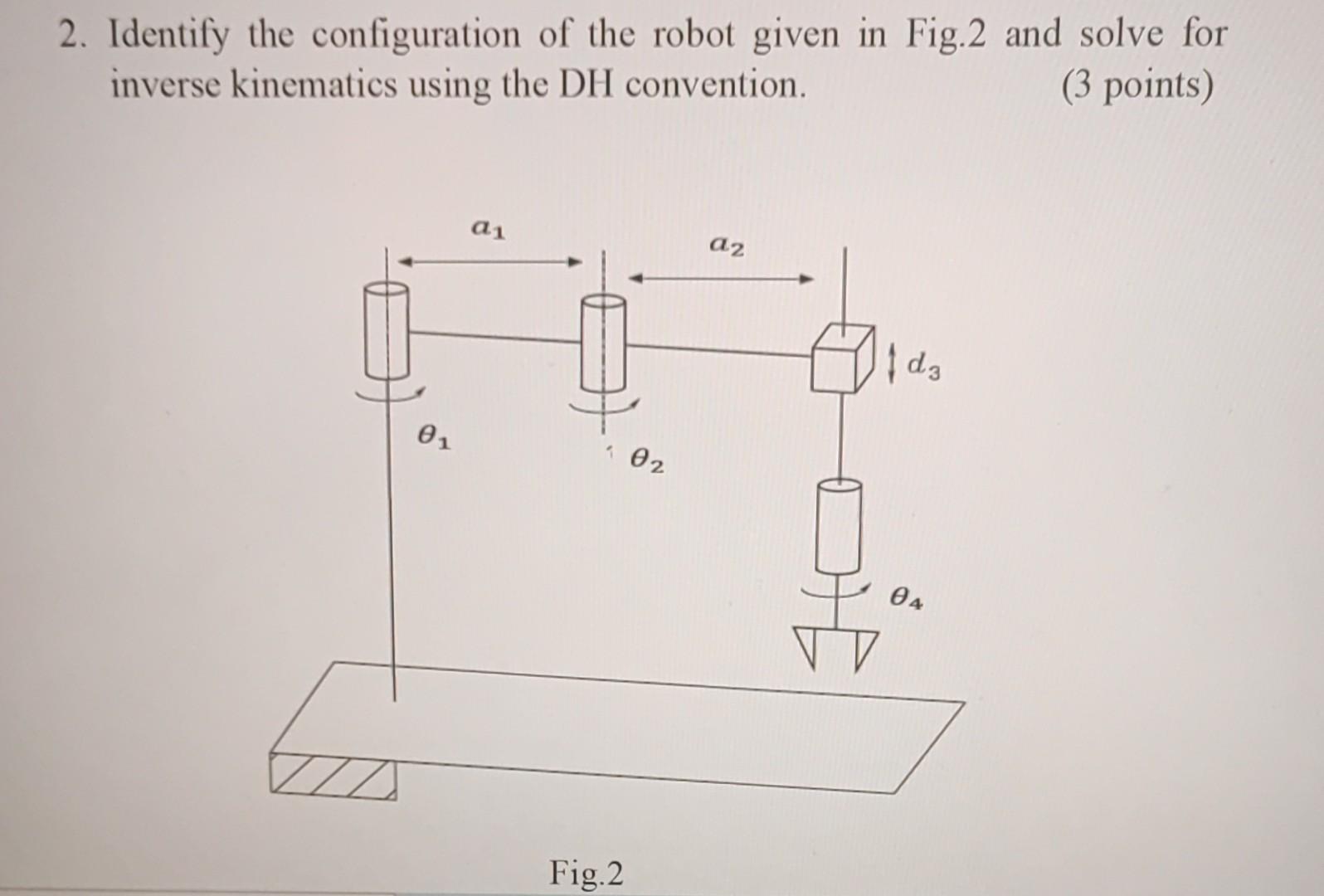
Solved 1 Identify The Configuration Of The Robot Given In Chegg Except for some special cases, these actuators uniquely determine the end effecter position and orientation as well as the configuration of the entire robot mechanism. Understand that the configuration of a robot refers to the specification of its position and orientation in space, as well as the positions of its joints or other movable parts.
Comments are closed.