Solved Problem 5 9 Points Find The Net Electric Flux Chegg
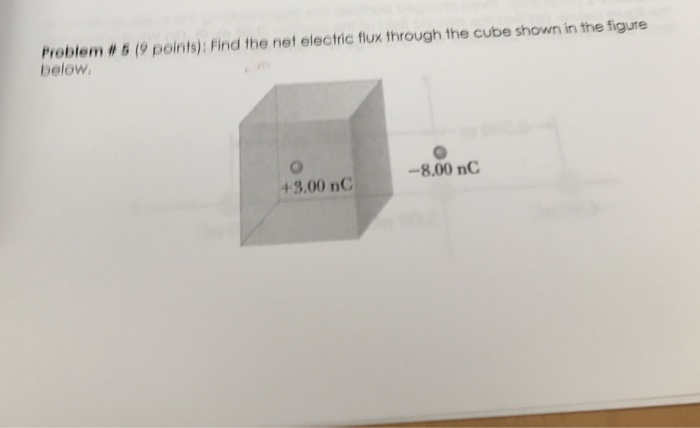
Solved Problem 5 9 Points Find The Net Electric Flux Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. What is the net electric flux through the surface? solution: in this problem, computing the electric flux through the cube's surface using its direct definition as Φ e = e a Φe = e ⋅ a is a challenging and time consuming task. gauss's law provides an alternative method for finding the electric flux.

Solved Find The Net Electric Flux Through The Closed Chegg Determine the electric flux that penetrates the plane of the carton when the carton is in position: (a) horizontal, (b) vertical and (c) sloping at an angle π 6 rad towards the north. (ii) in figure (b), the net charge inside the cube is 3q and the total electric flux in the cube is therefore Φe = 3q ε . note that the charge 10 q lies outside the cube and it will not contribute the total flux through the surface of the cube. There is a connection between magnitude of net enclosed charge and strength of net “flow” of e. the net electric flux through the surface of a box is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net charge enclosed by the box. 1. a uniform electric field e = 8000 n c passing through a flat square area a = 10 m2. determine the electric flux.

Solved Problem4 15 Points Find The Net Electric Flux Chegg There is a connection between magnitude of net enclosed charge and strength of net “flow” of e. the net electric flux through the surface of a box is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net charge enclosed by the box. 1. a uniform electric field e = 8000 n c passing through a flat square area a = 10 m2. determine the electric flux. The cube lies in a region where the electric field vector is given by e→ = 2.8 î 3.2 y^2ĵ 2.6 k̂ n c, with y in meters. what is the net charge contained by the cube? x and z are constants, only y (y^2) is not. net flux on z and x are zero. so we're just doing the left and right faces. There are 3 steps to solve this one. find the net electric flux passing through the surface s2 express your in newton meters squared per coulomb to two significant figures. figure 1) shows cross sections of five closed surfaces s1, s2 and so on. To calculate the net electric flux through a cube with uniform electric fields on its faces, use the formula electric flux = electric field * area. consider the direction of the electric fields, assigning positive values to flux leaving the cube and negative values to flux entering. Problems on electric flux with detailed solutions are provided for uniform and non uniform electric fields over arbitrary surfaces.

Solved 5 Bonus Points Find The Net Electric Flux Through Chegg The cube lies in a region where the electric field vector is given by e→ = 2.8 î 3.2 y^2ĵ 2.6 k̂ n c, with y in meters. what is the net charge contained by the cube? x and z are constants, only y (y^2) is not. net flux on z and x are zero. so we're just doing the left and right faces. There are 3 steps to solve this one. find the net electric flux passing through the surface s2 express your in newton meters squared per coulomb to two significant figures. figure 1) shows cross sections of five closed surfaces s1, s2 and so on. To calculate the net electric flux through a cube with uniform electric fields on its faces, use the formula electric flux = electric field * area. consider the direction of the electric fields, assigning positive values to flux leaving the cube and negative values to flux entering. Problems on electric flux with detailed solutions are provided for uniform and non uniform electric fields over arbitrary surfaces.
Comments are closed.