Solved Problem 3 Ray Tracing For Concave Mirrors An Object Chegg
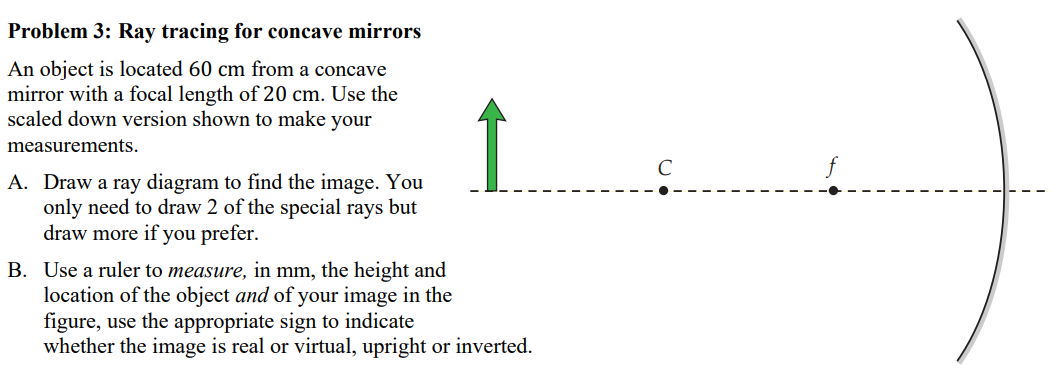
Solved Problem 3 Ray Tracing For Concave Mirrors An Object Chegg Problem 3: ray tracing for concave mirrors an object is located 60 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 20 cm. use the scaled down version shown to make your measurements. In this section of lesson 3, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a concave mirror. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection.

Solved Problem 3 Ray Tracing For Concave Mirrors An Object Chegg How to: ray tracing for a concave mirror and an object between the focus and the mirror. Step 1: draw a ray diagram draw a vertical line to represent the object, 3 cm high, located 72 cm from the concave mirror. draw a line from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis, and then reflect it through the focal point on the same side of the mirror. For concave mirrors, when the object is outside c, the image will be between c and f and the image will be inverted and diminished (smaller than the object). for concave mirrors, when the object is between c and f, the image will be beyond c and will be enlarged and inverted. The mirror equation relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length of a mirror. it is expressed as 1 f = 1 do 1 di, where f is the focal length, do is the object distance, and di is the image distance.

Solved Problem 3 Ray Tracing For Concave Mirrors An Object Chegg For concave mirrors, when the object is outside c, the image will be between c and f and the image will be inverted and diminished (smaller than the object). for concave mirrors, when the object is between c and f, the image will be beyond c and will be enlarged and inverted. The mirror equation relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length of a mirror. it is expressed as 1 f = 1 do 1 di, where f is the focal length, do is the object distance, and di is the image distance. In a ray diagram for a mirror, drawing any tworays from a point on the object reflecting off the mirror determines the location of its image (they intersect at the location of the image). Study the image from the practice problem above carefully. notice how parallel rays enter the piece of glass and emerge bent, eventually crossing paths at a single location. Solved problem (submit sketches and computations in the following question) ray tracing concave mirror find and describe the image of the object in the diagram below. use ray tracing and the mirror equation. Follow the steps above to solve the problem: an object is 18.0 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 7.5 cm. use ray tracing to determine the location of the image.

Solved Problem 3 Ray Tracing For Concave Mirrors An Object Chegg In a ray diagram for a mirror, drawing any tworays from a point on the object reflecting off the mirror determines the location of its image (they intersect at the location of the image). Study the image from the practice problem above carefully. notice how parallel rays enter the piece of glass and emerge bent, eventually crossing paths at a single location. Solved problem (submit sketches and computations in the following question) ray tracing concave mirror find and describe the image of the object in the diagram below. use ray tracing and the mirror equation. Follow the steps above to solve the problem: an object is 18.0 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 7.5 cm. use ray tracing to determine the location of the image.
Comments are closed.