Solved Problem 2 Assume That The Os Is Using A Memory Chegg
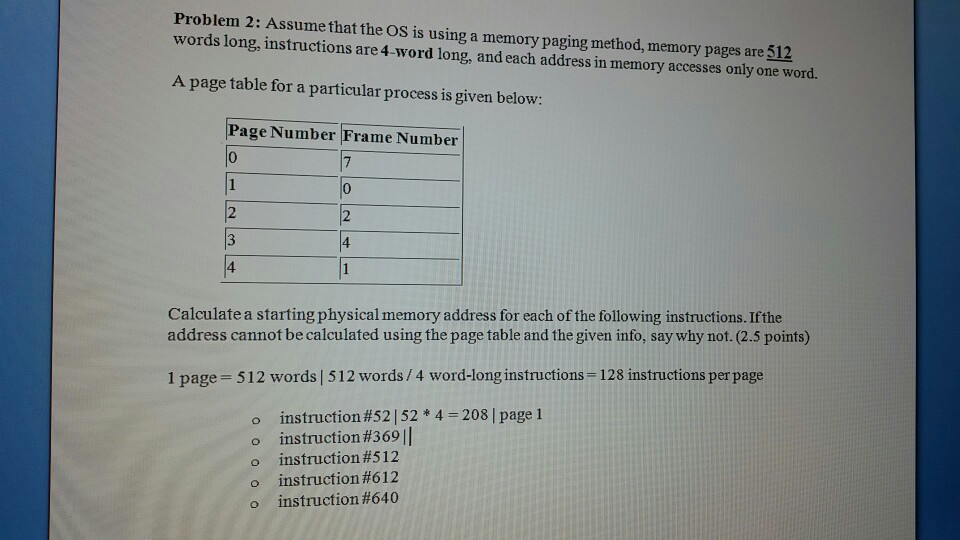
Solved Problem 2 Assume That The Os Is Using A Memory Chegg Problem 2: assume that the os is using a memory paging method, memory pages are 1024 words long, instructions are 8 word long, and each address in memory accesses only one word. A page fault occurs when an access to a page that has not been brought into main memory takes place. the operating system verifies the memory access, aborting the program if it is invalid. if it is valid a free frame is located and i o requested to read the needed page into the free frame.
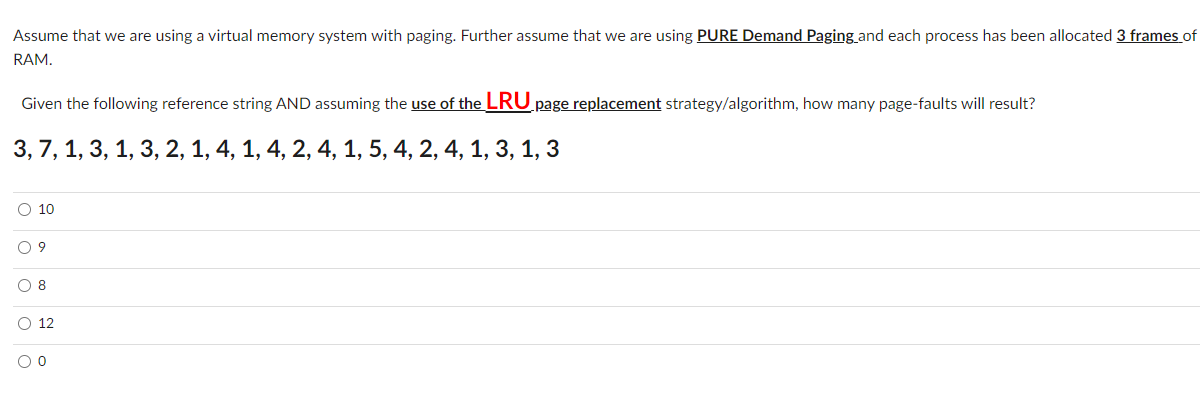
Solved Assume That We Are Using A Virtual Memory System With Chegg A) a fifo replacement algorithm associates with each page the time when that page was brought into memory. when a page must be replaced, the oldest page is chosen. Pages that have been requested by the user using mmap brk sbrk system calls, but have not yet been accessed by the user, and hence not allocated physical memory frames by the os. First, we need to determine the segment base address for each segment. the segment base address is the starting address of each segment. segment #0 has a starting address of 13,000. segment #1 has a starting address of 22,000. segment #2 has a starting address of 6,000. segment #3 has a starting address of 30,000. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 2: assume that the os is using a memory paging method, memory pages are 1024 words long, instructions are 8 word long, and each address in memory accesses only one word.
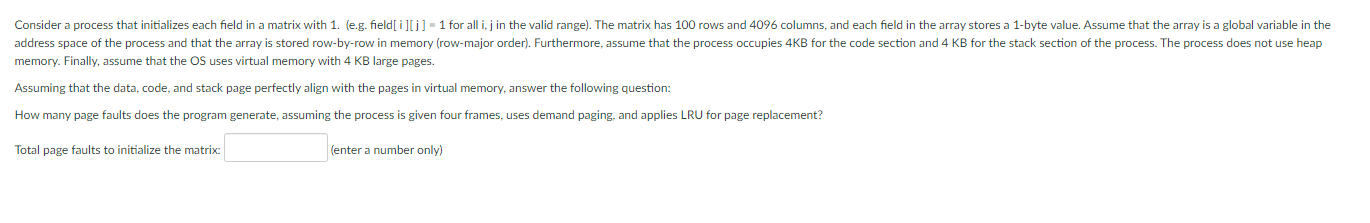
Solved Memory Finally Assume That The Os Uses Virtual Chegg First, we need to determine the segment base address for each segment. the segment base address is the starting address of each segment. segment #0 has a starting address of 13,000. segment #1 has a starting address of 22,000. segment #2 has a starting address of 6,000. segment #3 has a starting address of 30,000. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 2: assume that the os is using a memory paging method, memory pages are 1024 words long, instructions are 8 word long, and each address in memory accesses only one word. Assume a system comprises 16 gb physical memory with 8 kb page frame size, and the instruction set comprises instruction that may need access to one (ret), two (push a), or three (mov a, b) memory locations to fetch the op code and operands. The operating system verifies the memory access, aborting the program if it is invalid. if it is valid, a free frame is located and i o is requested to read the needed page into the free frame. Internal fragmentation is when there is unused memory space within the allocation to a specific process (e.g., rounding up to the page size), and cannot be used by anyone else. Since the virtual address space is of the same size as the physical address space, the operating system designers decide to get rid of the virtual memory entirely.
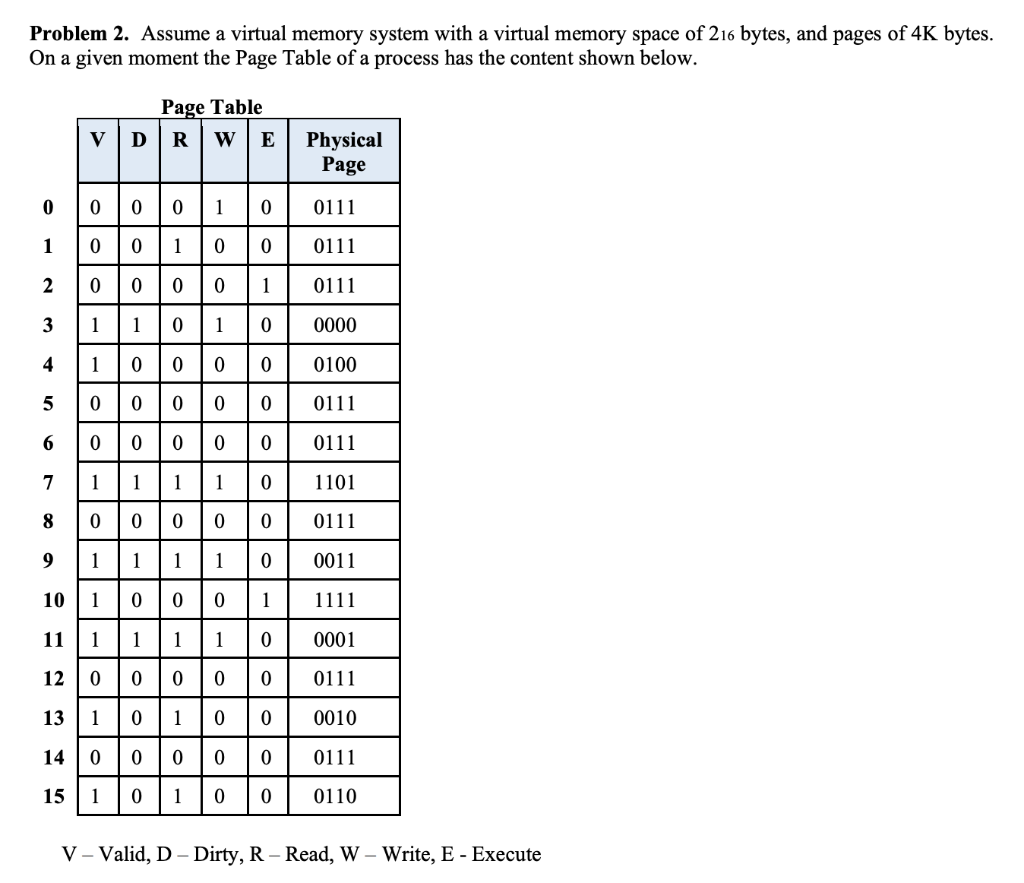
Problem 2 Assume A Virtual Memory System With A Chegg Assume a system comprises 16 gb physical memory with 8 kb page frame size, and the instruction set comprises instruction that may need access to one (ret), two (push a), or three (mov a, b) memory locations to fetch the op code and operands. The operating system verifies the memory access, aborting the program if it is invalid. if it is valid, a free frame is located and i o is requested to read the needed page into the free frame. Internal fragmentation is when there is unused memory space within the allocation to a specific process (e.g., rounding up to the page size), and cannot be used by anyone else. Since the virtual address space is of the same size as the physical address space, the operating system designers decide to get rid of the virtual memory entirely.
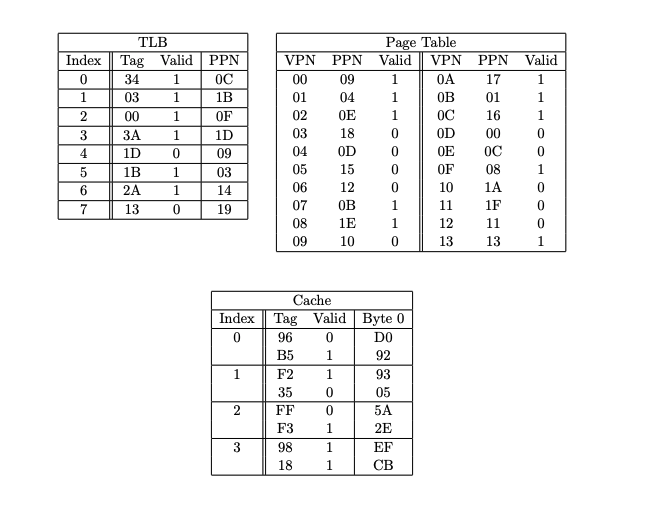
Solved Sample Problem 2 Assume The Following Setup Of Chegg Internal fragmentation is when there is unused memory space within the allocation to a specific process (e.g., rounding up to the page size), and cannot be used by anyone else. Since the virtual address space is of the same size as the physical address space, the operating system designers decide to get rid of the virtual memory entirely.
Comments are closed.