Solved Part Game Theory Exercise Consider The Following Chegg
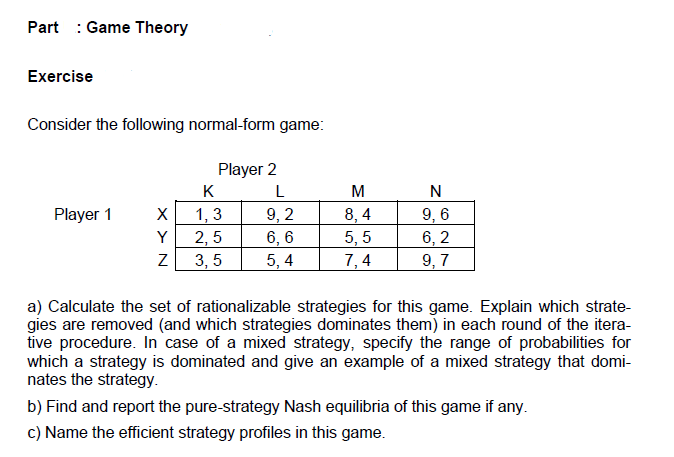
Solved Part Game Theory Exercise Consider The Following Chegg Game theory consider the following game in normal form: a. if the game is played simultaneously by both players, find the nash equilibrium or equilibria. b. if the game is played sequentially, solve this game. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Introduction 1 exercise 5.3 (altruistic preferences) 1 exercise 6.1 (alternative representations of preferences) 1 nash equilibrium 3.

Solved Part A Game Theory 12 Points 1 Consider The Chegg In game theory, as in mathematics in general, it is essential to test one’s understanding of the material by attempting to solve exercises and problems. indeed the reader is encouraged to attempt solving exercises after the introduction of every new concept. Consider three neighboring municipalities, a, b, and c, who can supply themselves with municipal water either by building separate facilities or by building a joint water supply facility. Consider the following game in matrix form with two players. payoffs for the row player shelia are indicated first in each cell, and payoffs for the column player thomas are second. If the goalie jumps in the same direction as the kick, then the goalie wins and the kicker loses. if the goalie jumps in the opposite direction of the kick then the kicker wins and the goalie loses. model this as a normal form game and write down the matrix that represents the game you modeled.

Solved Part 2 Game Theory 3 Consider The Following Games Chegg Consider the following game in matrix form with two players. payoffs for the row player shelia are indicated first in each cell, and payoffs for the column player thomas are second. If the goalie jumps in the same direction as the kick, then the goalie wins and the kicker loses. if the goalie jumps in the opposite direction of the kick then the kicker wins and the goalie loses. model this as a normal form game and write down the matrix that represents the game you modeled. Game theory chapter 5 hat is proposed to be shown is obviously false. what should be shown is that the sum of marginal ra es of substitution which equals not k but 1=k.] if the allocation is pareto e cient, then it must maximize a weighted sum of individual utilities subject to the constraints given by t n x max iui(xi; y) x n = 1 i 1. Solutions to game theory exercises involving game trees, decision nodes, and rollback equilibrium. examples include hansel & gretel, scarecrow & tinman. The low cost type of player 1 earns 20 in the bayesiannash equilibrium and 20. in the full information game, so would prefer to signal its type if it could. similar calculations show that the high cost player would like to hide its type. (a) in solving such problems, it is advisable to start the investigation with simpler positions and work up to the more difficult ones. here are the simplest p positions. the last position shows that chomping at (3,1) is a winning move for the first player.

Solved Game Theory Example Consider The Following Chegg Game theory chapter 5 hat is proposed to be shown is obviously false. what should be shown is that the sum of marginal ra es of substitution which equals not k but 1=k.] if the allocation is pareto e cient, then it must maximize a weighted sum of individual utilities subject to the constraints given by t n x max iui(xi; y) x n = 1 i 1. Solutions to game theory exercises involving game trees, decision nodes, and rollback equilibrium. examples include hansel & gretel, scarecrow & tinman. The low cost type of player 1 earns 20 in the bayesiannash equilibrium and 20. in the full information game, so would prefer to signal its type if it could. similar calculations show that the high cost player would like to hide its type. (a) in solving such problems, it is advisable to start the investigation with simpler positions and work up to the more difficult ones. here are the simplest p positions. the last position shows that chomping at (3,1) is a winning move for the first player.

Solved Game Theory Consider The Following Game Player 1 C Chegg The low cost type of player 1 earns 20 in the bayesiannash equilibrium and 20. in the full information game, so would prefer to signal its type if it could. similar calculations show that the high cost player would like to hide its type. (a) in solving such problems, it is advisable to start the investigation with simpler positions and work up to the more difficult ones. here are the simplest p positions. the last position shows that chomping at (3,1) is a winning move for the first player.
Comments are closed.