Solved In Problems 1 Through 8 Assuming General Initial Chegg
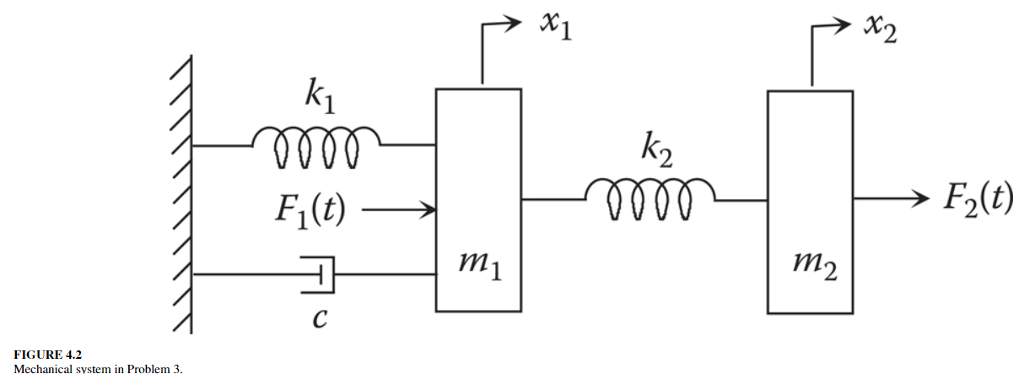
Solved In Problems 1 Through 8 Assuming General Initial Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: in problems 1 through 8, assuming general initial conditions, express the system model in a. For mass (m1), the motion is influenced by the force applied by the spring (k1), damping from (c1), and the interaction between (m1) and (m2) through the second spring and damper (k2) and (c2).

Solved In Problems 1 Through 8 Assuming General Initial Chegg I started my carrier as an online tutor on chegg as a subject matter expert and since then i am enjoying my work, i have helped thousands of students with my skills. A car is initially at x=0 and its velocity is u=5ms−1. it begins to accelerate and its acceleration changes with its x coordinate as a=2x, where a is in ms−2 and x is in m. In each of problems 5 through 8 find the solution of the given initial value problem. sketch the graph of the solution and describe its behaviour as increases. In problems 1 through 8, assuming general initial conditions, express the system model in a. configuration form. b. standard, second order matrix form.

Solved In Problems 1 Through 8 Assuming General Initial Chegg In each of problems 5 through 8 find the solution of the given initial value problem. sketch the graph of the solution and describe its behaviour as increases. In problems 1 through 8, assuming general initial conditions, express the system model in a. configuration form. b. standard, second order matrix form. Transform the given system into a single equation of second order: x'1 = 4x1 9x2 x'2 = 9x1 4x2. then find x1 and x2 that also satisfy the initial conditions: x1 (0) = 8 x2 (0) = 5. In problems 1 through 8, assuming general initial conditions, express the system model in a. configuration form. b. standard, second order matrix form. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. C 4.2.28 for the system below first calculate the operational determinant to c in a general solution. then attempt to solve the system explicitly so as to find s 2 ( 2— d d)x. The steps outlined for solving the initial value problem are standard procedures in differential equations, particularly involving the combination of complementary and particular solutions.

Solved Problem Set 4 1 In Problems 1 Through 8 Assuming Chegg Transform the given system into a single equation of second order: x'1 = 4x1 9x2 x'2 = 9x1 4x2. then find x1 and x2 that also satisfy the initial conditions: x1 (0) = 8 x2 (0) = 5. In problems 1 through 8, assuming general initial conditions, express the system model in a. configuration form. b. standard, second order matrix form. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. C 4.2.28 for the system below first calculate the operational determinant to c in a general solution. then attempt to solve the system explicitly so as to find s 2 ( 2— d d)x. The steps outlined for solving the initial value problem are standard procedures in differential equations, particularly involving the combination of complementary and particular solutions.

Solved 12 Determine The General Solution If Initial Chegg C 4.2.28 for the system below first calculate the operational determinant to c in a general solution. then attempt to solve the system explicitly so as to find s 2 ( 2— d d)x. The steps outlined for solving the initial value problem are standard procedures in differential equations, particularly involving the combination of complementary and particular solutions.
Comments are closed.