Solved If A And B Are Constants Then E Ax B Ae X Chegg

Solved From The Formula E Ax B Ae X B Setting B 0 We Chegg There are 3 steps to solve this one. e (a x b) = ∑ [(a x b) × p (x = x)] if a and b are constants, then e [ax b] = ae [x] b. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. The expectation operator, e, for a random variable x, adheres to the linearity property. this means that for any constants a and b, the expectation of ax b is indeed ae [x] b.
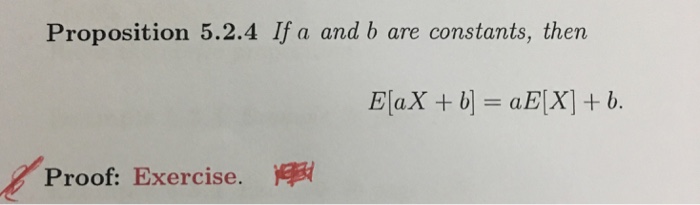
Solved If A And B Are Constants Then E Ax B Ae X Chegg This proof shows that the expectation of a linear transformation of a random variable x is equal to the linear transformation of the expectation of x. note: this property holds for any random variable x and constants a and b. This seems rather simple. i know that the expected value of a constant is just the constant. but i feel like i'm missing something. any help would be appreciated, thanks. E h(z) = z2 or h(z) = log(5z)? it turns out we can't just say e z2 = e [z]2 or e log(5z) = log(5e[z]) this is actually almost never true! let's see if we can't derive a nice formula for e [g(x)] for. Step by step video & image solution for prove that e (ax b)=ae (x) b where a and b are constants by maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in class 12 exams.

Solved Show That 1 E Ax B Ae X B 2 V Ax B Chegg E h(z) = z2 or h(z) = log(5z)? it turns out we can't just say e z2 = e [z]2 or e log(5z) = log(5e[z]) this is actually almost never true! let's see if we can't derive a nice formula for e [g(x)] for. Step by step video & image solution for prove that e (ax b)=ae (x) b where a and b are constants by maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in class 12 exams. Consider the random variable y = ax b, where 'a' and 'b' are constants. we want to find e (y) the expected value of y is:. Prove that e (ax b) =ae (x) b? recall: if x is a discrete random variable with probability function p (x = x i) = p (x i), then the expected value of the random variable x is given by: μ x = e (x) = ∑ x i • p (x i) so, e (ax b) = ∑ (ax i b) • p (x i) = a ∑x i •p (x i) b ∑ p (x i) i i. Statistics and probability questions and answers a.) prove that if x is a discrete random variable, and a and b are constants, then the e [ax b]=ae [x] b. (hint: use the definition of e [h (x)]) b.) prove that if x is a continuous random variable, and a and b are constants, then the var (ax b)=a2var (x). (hint: var (h (x))=e [h (x)2]−e [h (x)]2). Solution for show that if a and b are constants, then e [ax b] = ae [x] b.

Solved If A And B Are Constants Then E Ax B A E X Chegg Consider the random variable y = ax b, where 'a' and 'b' are constants. we want to find e (y) the expected value of y is:. Prove that e (ax b) =ae (x) b? recall: if x is a discrete random variable with probability function p (x = x i) = p (x i), then the expected value of the random variable x is given by: μ x = e (x) = ∑ x i • p (x i) so, e (ax b) = ∑ (ax i b) • p (x i) = a ∑x i •p (x i) b ∑ p (x i) i i. Statistics and probability questions and answers a.) prove that if x is a discrete random variable, and a and b are constants, then the e [ax b]=ae [x] b. (hint: use the definition of e [h (x)]) b.) prove that if x is a continuous random variable, and a and b are constants, then the var (ax b)=a2var (x). (hint: var (h (x))=e [h (x)2]−e [h (x)]2). Solution for show that if a and b are constants, then e [ax b] = ae [x] b.
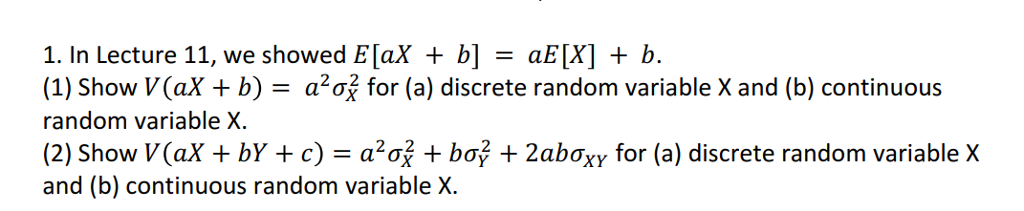
Solved 1 In Lecture 11 We Showed E Ax B Ae X B Chegg Statistics and probability questions and answers a.) prove that if x is a discrete random variable, and a and b are constants, then the e [ax b]=ae [x] b. (hint: use the definition of e [h (x)]) b.) prove that if x is a continuous random variable, and a and b are constants, then the var (ax b)=a2var (x). (hint: var (h (x))=e [h (x)2]−e [h (x)]2). Solution for show that if a and b are constants, then e [ax b] = ae [x] b.
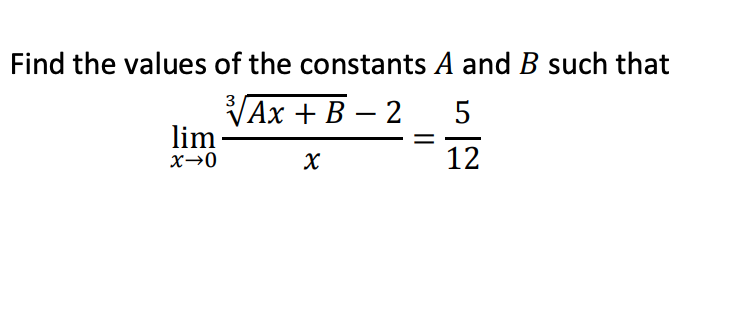
Solved Find The Values Of The Constants A And B Such That 3 Chegg
Comments are closed.