Solved Identify The Different Structures Of A Neuron By M Chegg
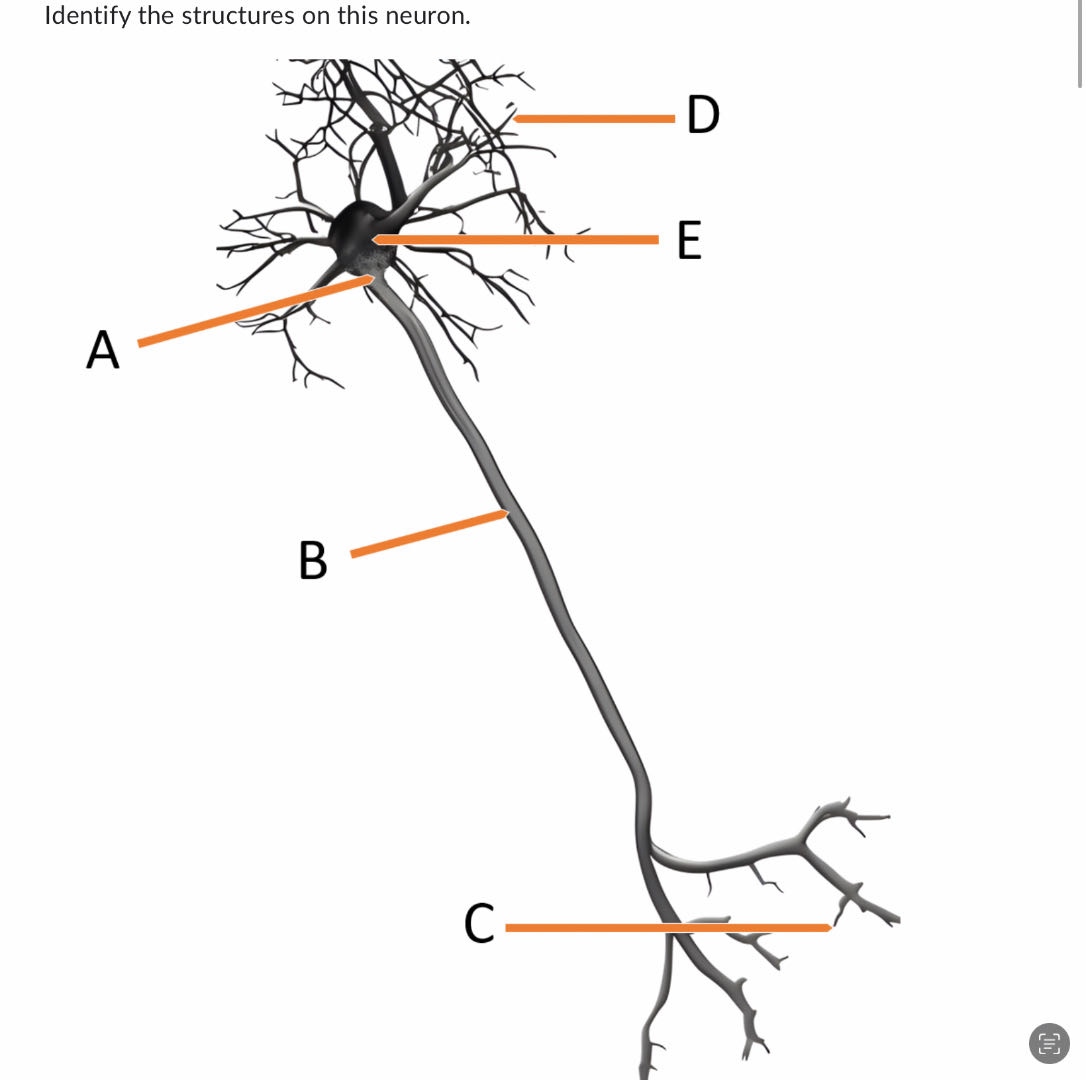
Solved Identify The Structures On This Neuron Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. 1. structure of neuron a dendrite b soma c node of ranvier d axon terminal e nucleus f axon g myelin sheath h schwann cell 2. brachial nerve structure of neuron a. epineurium b. perineurium c. endoneurium d. myelinated sheath … 1. identify the different structures of the neuron. Drag the labels to identify the structural components of a typical neuron. look at pic.
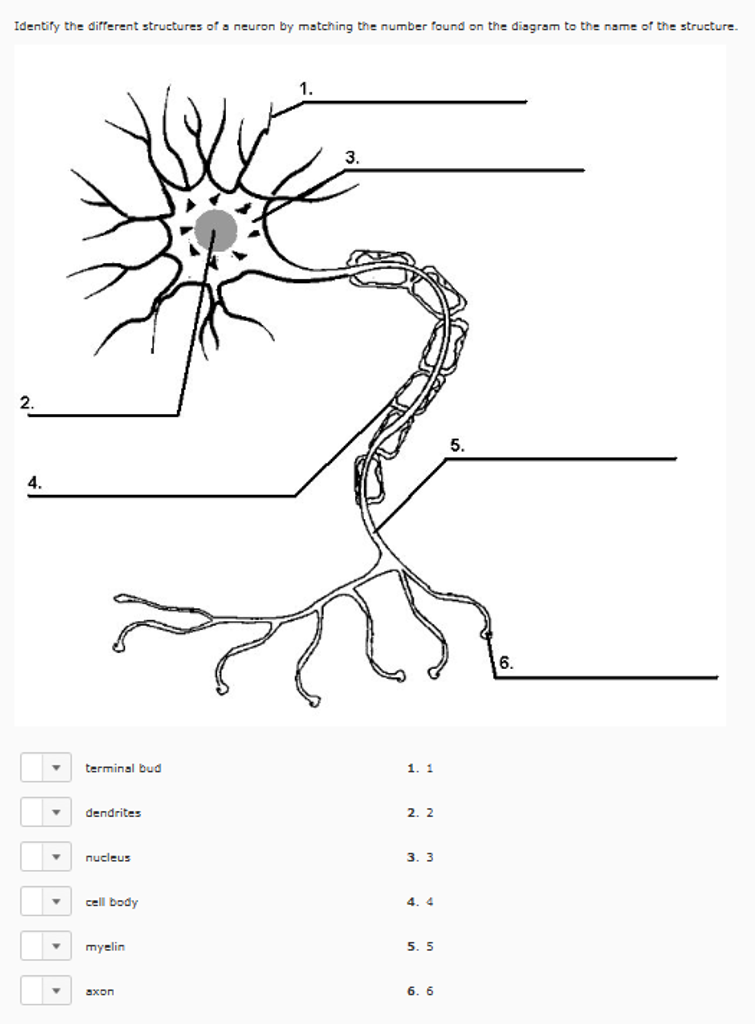
Solved Identify The Different Structures Of A Neuron By M Chegg Arrow a indicates the chromatophilic substance, also known as nissl bodies, which are clusters of rough endoplasmic reticulum found in the cell body of a neuron. Compare the number of processes (axon and dendrites) emerging from the cell body to identify each type of neuron. on the structural basis , neurons are classified as 1) multipolar neuron they are found more ab … identify the neurons based on their structure. Identify each major neuron structure and describe the major function (s) of each. learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Then, you’ll look at two different neurons in rat brain (found at histologyguide): purkinje cells, which are found in the cerebellum, and pyramidal cells, which are found in the cerebral cortex.

Solved 1 Identify The Different Structures Of The Neuron A Chegg Identify each major neuron structure and describe the major function (s) of each. learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Then, you’ll look at two different neurons in rat brain (found at histologyguide): purkinje cells, which are found in the cerebellum, and pyramidal cells, which are found in the cerebral cortex. Neuron structure activity answers free download as pdf file (.pdf) or read online for free. very nice. To describe the structure of a neuron, start by explaining that neurons consist of three main parts: dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. neurons are cells that make up the nervous system. their major function is to receive information from and transmit these signals to different parts of our body. Distinguish between sensory neurons, motor neurons, and association neurons in terms of structure, location, and function. sensory (afferent) neurons: conducts afferent impulses to cns. Distinguish the characteristics of the neuron structural types by clicking and dragging the labels to the correct location. unipolar neuron that is functionally a sensory neuron: begins at a sensory receptor, such as a touch receptor, and sends information toward the central nervous system.
Comments are closed.