Solved Game Theory Consider The Following Problem In Its Chegg

Game Theory Problem Set Pdf Banks Algorithms Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. Game theory provides a formal language for the representation and analysis of interactive situations, that is, situations where several “entities”, called players, take actions that affect each other.

Solved Problem 3 Game Theory 80 Points Consider The Chegg 17.1 games equivalent to the prisoner’s dilemma the game in the left panel differs from the pr. soner’s dilemma in both players’ pref erences. player 1 prefers (y, x) to (x, x) to (x, y) to (y, y), for example, which differs from her preference in the prisoner’s dilemma, which is (f, q) to (q, q) . An army can capture the island either by attacking when its opponent does not or by attacking when its rival does if it is strong and its rival is weak. if two armies of equal strength both attack, neither captures the island. Consider the following ‘brooklyn bridge’ game, except that this time, player 1 chooses her location (brooklyn or manhattan) before player 2 does, so player 2 observes player 1’s choice before choosing his own. Game theory chapter 5 hat is proposed to be shown is obviously false. what should be shown is that the sum of marginal ra es of substitution which equals not k but 1=k.] if the allocation is pareto e cient, then it must maximize a weighted sum of individual utilities subject to the constraints given by t n x max iui(xi; y) x n = 1 i 1.

Solved Problem 3 Game Theory 80 Points Consider The Chegg Consider the following ‘brooklyn bridge’ game, except that this time, player 1 chooses her location (brooklyn or manhattan) before player 2 does, so player 2 observes player 1’s choice before choosing his own. Game theory chapter 5 hat is proposed to be shown is obviously false. what should be shown is that the sum of marginal ra es of substitution which equals not k but 1=k.] if the allocation is pareto e cient, then it must maximize a weighted sum of individual utilities subject to the constraints given by t n x max iui(xi; y) x n = 1 i 1. Section 2 consider the following game between sony, a manufacturer of video cassettes players, and columbia pictures, a movie studio. each firm must decide whether to use the vhs or beta format sony to make video players, columbia to release its movies for rental or purchase. Solved exercises game theory free download as word doc (.doc .docx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. This question is from 'game theory' an introduction by steven tadelis book chapter 16 (signaling), problem 16.3 (more limit pricing). an incumbent firm, player 1, is either a low cost type or a high cost type, each with equal probability. Finally, note that extending this problem to allowing for mixed strategies is straight forward; if we, given some beliefs, have multiple optimal pure strategies, then any mix of those strategies is also optimal.

Solved Problem 1 Game Theory Consider A Game With The Chegg Section 2 consider the following game between sony, a manufacturer of video cassettes players, and columbia pictures, a movie studio. each firm must decide whether to use the vhs or beta format sony to make video players, columbia to release its movies for rental or purchase. Solved exercises game theory free download as word doc (.doc .docx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. This question is from 'game theory' an introduction by steven tadelis book chapter 16 (signaling), problem 16.3 (more limit pricing). an incumbent firm, player 1, is either a low cost type or a high cost type, each with equal probability. Finally, note that extending this problem to allowing for mixed strategies is straight forward; if we, given some beliefs, have multiple optimal pure strategies, then any mix of those strategies is also optimal.
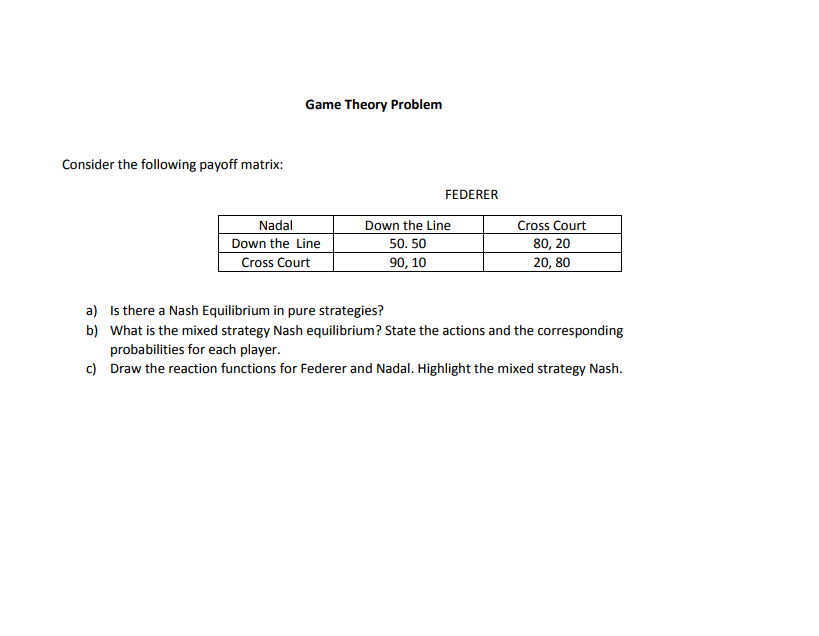
Solved Game Theory Problem Consider The Following Payoff Chegg This question is from 'game theory' an introduction by steven tadelis book chapter 16 (signaling), problem 16.3 (more limit pricing). an incumbent firm, player 1, is either a low cost type or a high cost type, each with equal probability. Finally, note that extending this problem to allowing for mixed strategies is straight forward; if we, given some beliefs, have multiple optimal pure strategies, then any mix of those strategies is also optimal.
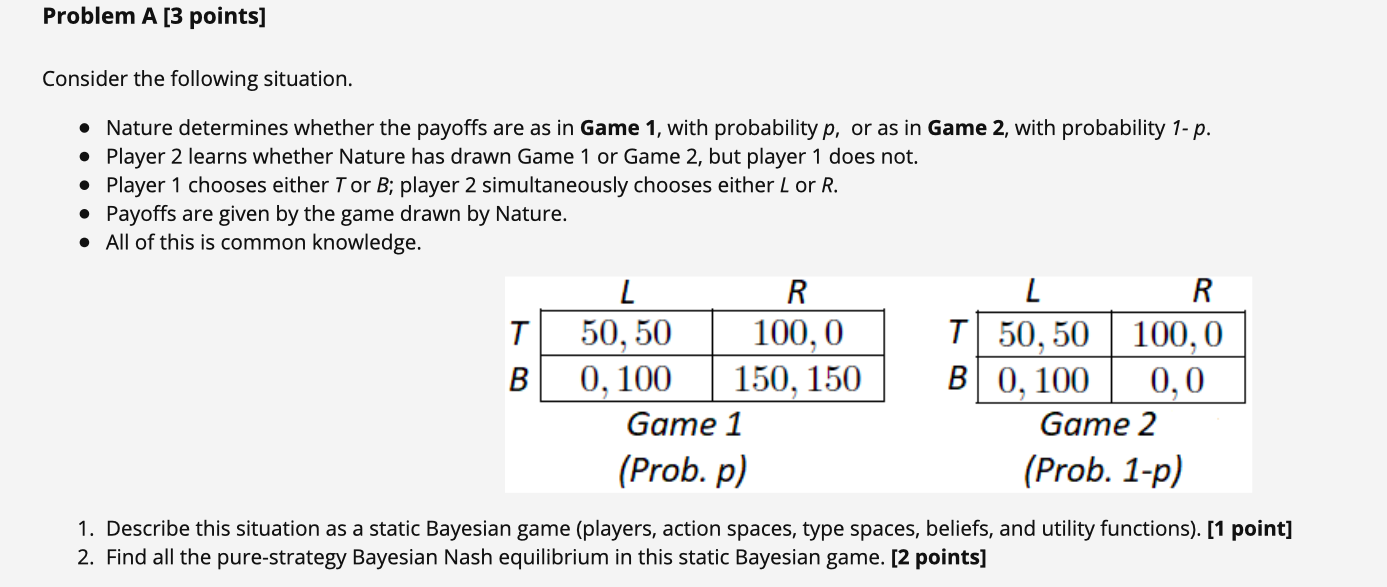
Solved Problem A 3 Points Consider The Following Chegg
Comments are closed.