Solved Find F 3 I Given That Chegg
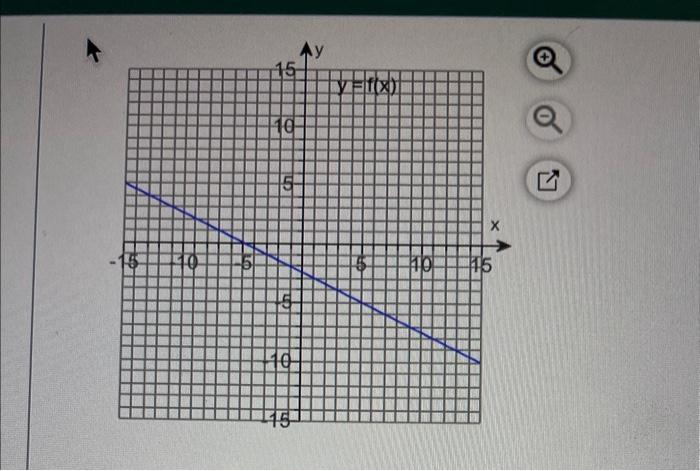
Solved For The Given Function Find A F 1 B F 3 A Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. This problem has been solved! you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.

Solved Given The Following Function Find F 3 F 0 ï And Chegg How exactly does this method of finding f (3) given the derivative and a point work? i understand solving for c to create the equation for f (x), but how does this method using an integral work?. A fourier series ( ˈfʊrieɪ, iər [1]) is an expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. the fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. [2] by expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. for example, fourier series were. I 3. given f (x) = ** find f" (x) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Get the free "find f (x) for a given x" widget for your website, blog, wordpress, blogger, or igoogle. find more widget gallery widgets in wolfram|alpha.
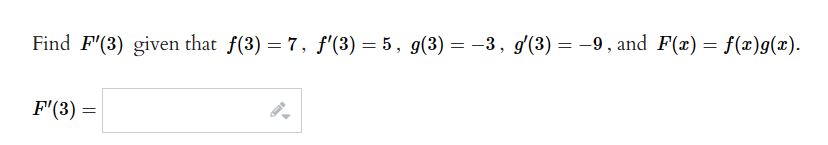
Solved Find F 3 ï Given That Chegg I 3. given f (x) = ** find f" (x) your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Get the free "find f (x) for a given x" widget for your website, blog, wordpress, blogger, or igoogle. find more widget gallery widgets in wolfram|alpha. This is an alternate isbn. view the primary isbn for: intermediate algebra (with cengagenow, tle labs, personal tutor printed access card) 8th edition textbook solutions intermediate algebra(8th edition) edit edition solutions for chapter 6.1problem 6e: given , find f (−3).…. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. use the given information to find f ' (3). here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Use the chain rule of differentiation to find derivatives of functions; examples with detailed solutions are presented. (a) find the solution u (x, y) of laplace's equation in the semi infinite strip 0 < x < 3, y > 0, that satisfies the boundary conditions u (0, y) = u (a, y), u (x, 0) = f (x), and the additional condition that u (x, y) = Σ cn sin (nÏ€x a) where cn = ∫ f (x)sin (nÏ€x a) dx.

Solved 7 Given F X 3 X Find F 4 Chegg This is an alternate isbn. view the primary isbn for: intermediate algebra (with cengagenow, tle labs, personal tutor printed access card) 8th edition textbook solutions intermediate algebra(8th edition) edit edition solutions for chapter 6.1problem 6e: given , find f (−3).…. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. use the given information to find f ' (3). here’s the best way to solve it. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Use the chain rule of differentiation to find derivatives of functions; examples with detailed solutions are presented. (a) find the solution u (x, y) of laplace's equation in the semi infinite strip 0 < x < 3, y > 0, that satisfies the boundary conditions u (0, y) = u (a, y), u (x, 0) = f (x), and the additional condition that u (x, y) = Σ cn sin (nÏ€x a) where cn = ∫ f (x)sin (nÏ€x a) dx.

Solved Given F 7 3 F 1 3 Chegg Use the chain rule of differentiation to find derivatives of functions; examples with detailed solutions are presented. (a) find the solution u (x, y) of laplace's equation in the semi infinite strip 0 < x < 3, y > 0, that satisfies the boundary conditions u (0, y) = u (a, y), u (x, 0) = f (x), and the additional condition that u (x, y) = Σ cn sin (nπx a) where cn = ∫ f (x)sin (nπx a) dx.
Comments are closed.