Solved Figure Interpreting Short Run Cost Curves I Given Chegg
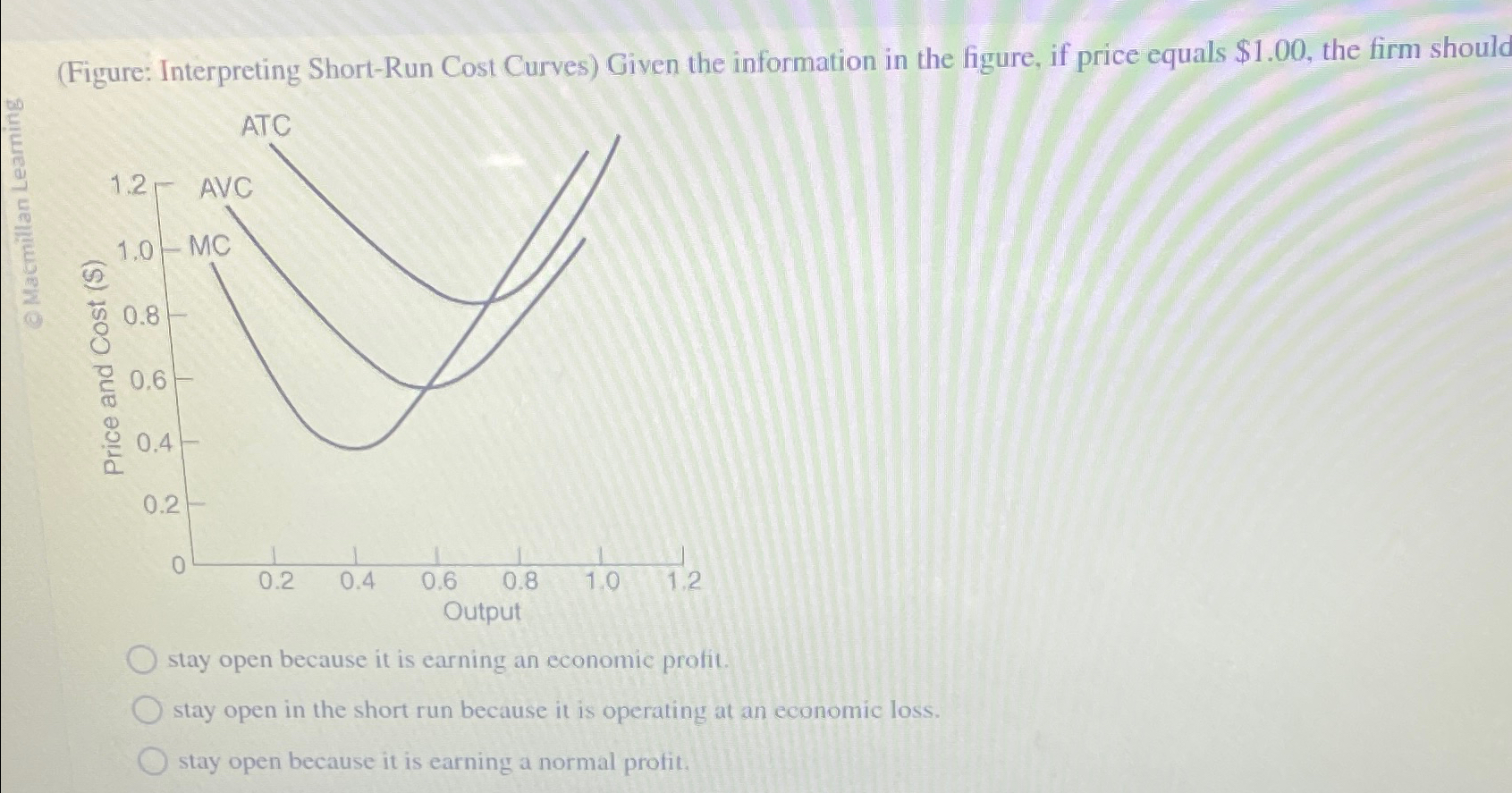
Solved Figure Interpreting Short Run Cost Curves ï Given Chegg (figure: interpreting short run cost curves) given the information in the figure, if price equals $0.70, the firm should:a linear graph plots total output against price and cost in dollars. (figure: interpreting short run cost curves) using information from the figure, if price equals $1.50, the firm should:.

Solved Figure Interpreting Short Run Cost Curves Given Chegg The question asks for the price at which a firm will break even and the price at which the firm will shut down in the short run. to answer this question, we need to understand the relationship between price, cost curves, and profit in a perfectly competitive market. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. in the short run, capital is fixed. after a certain point, increasing extra workers leads to declining productivity. therefore, as you employ more workers the marginal cost increases. Figure 10 2 shows demand and short run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. at its profit maximizing level of output, the firm's short run tc is represented by area. Figure 9.1.1: three short run cost curves – fixed, variable and total costs. figure 9.1.1 also shows variable and total cost curves plotted from data in table 9.1.1.
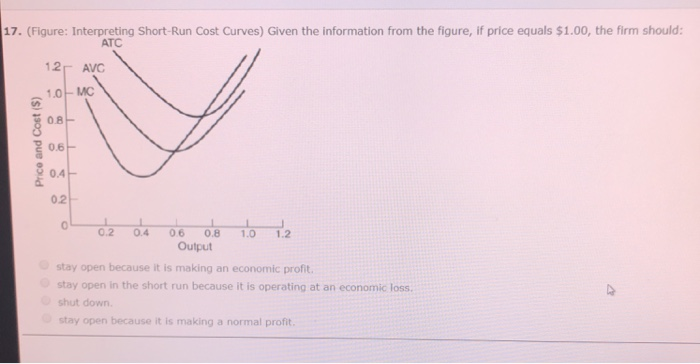
Solved 17 Figure Interpreting Short Run Cost Curves Chegg Figure 10 2 shows demand and short run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. at its profit maximizing level of output, the firm's short run tc is represented by area. Figure 9.1.1: three short run cost curves – fixed, variable and total costs. figure 9.1.1 also shows variable and total cost curves plotted from data in table 9.1.1. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 2 steps to solve this one. a perfectly competitive firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve beca. In a short run with a fixed amount of at least one input, the law of diminishing (marginal) returns must apply, causing the firm’s average variable cost of production to increase eventually. The difference between the money collected from the selling of commodities and the costs of the inputs required, as well as any opportunity costs, is known as an economic profit or loss. opportunity expenses and explicit costs are removed from revenue gained while computing economic profit. Part 1 of 2 suppose the figure illustrates the short run cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. let mc be the marginal cost curve, atc be the short run average total cost curve, and avc be the average variable cost curve.
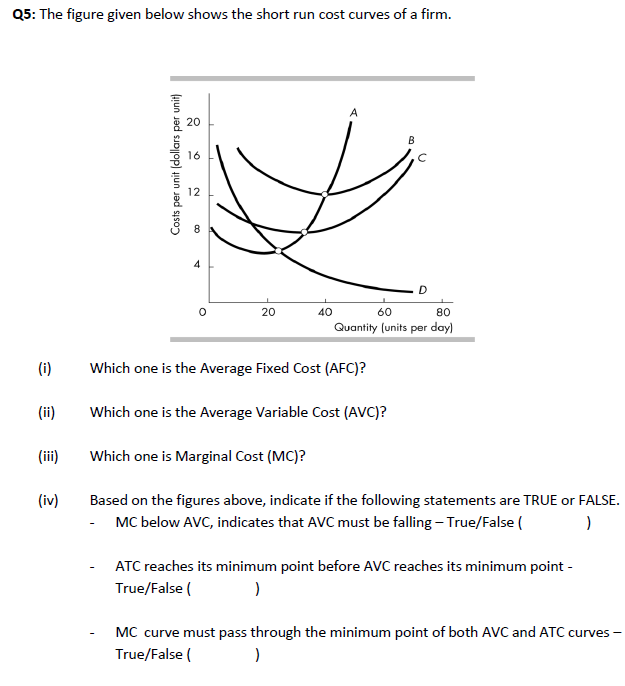
Solved Q5 The Figure Given Below Shows The Short Run Cost Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 2 steps to solve this one. a perfectly competitive firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve beca. In a short run with a fixed amount of at least one input, the law of diminishing (marginal) returns must apply, causing the firm’s average variable cost of production to increase eventually. The difference between the money collected from the selling of commodities and the costs of the inputs required, as well as any opportunity costs, is known as an economic profit or loss. opportunity expenses and explicit costs are removed from revenue gained while computing economic profit. Part 1 of 2 suppose the figure illustrates the short run cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. let mc be the marginal cost curve, atc be the short run average total cost curve, and avc be the average variable cost curve.
Comments are closed.