Solved Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation Aim To Understand Chegg

Solved Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation Aim To Understand Chegg With this scheme, the "1" is called the mark frequency and the "0" is called the space frequency. in binary fsk system, symbol 1 & 0 are distinguished from each other by transmitting one of the two sinusoidal waves that differ in frequency by a fixed amount. Frequency modulation (fm) is a nonlinear modulation technique where the modulating signal varies the instantaneous frequency of the carrier wave. in this experiment you will generate fm signals and study their frequency domain characteristics.
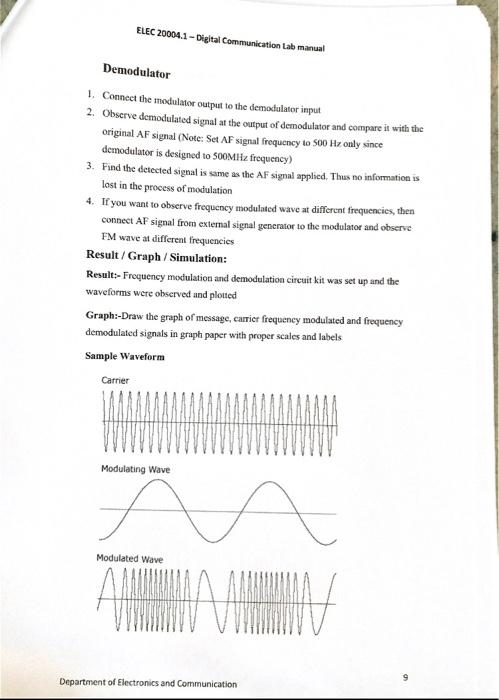
Solved Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation Aim To Understand Chegg Now observe the frequency modulation output on the 1st channel of on cro and adjust the amplitude of the af signal to get clear frequency modulated wave form. vary the modulating frequency (a signal) and amplitude and observe the effects on the modulated waveform. Introduction to frequency modulation and demodulation. the most obvious modulation method is to vary the carrier amplitude with the instantaneous message signal value. however, the amplitude is not the only quantity the carrier that can be used to carry the message. Given the 3 circuits with their corresponding output waveforms, please give and write some observation of each. also, give and write some comparison needed. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Special cases of angle modulation include schemes such as phase modulation (pm) and frequency modulation (fm). more details on these modulation schemes are found in the class notes.

Solved Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation Aim To Understand Chegg Given the 3 circuits with their corresponding output waveforms, please give and write some observation of each. also, give and write some comparison needed. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Special cases of angle modulation include schemes such as phase modulation (pm) and frequency modulation (fm). more details on these modulation schemes are found in the class notes. This document describes an experiment on frequency modulation and demodulation. the objectives are to introduce frequency modulation, where the frequency of a carrier signal is varied according to an input message signal. The frequency modulation is a non linear modulation process. each spectral component of the base band signal gives rise to one or two spectral components in the modulated signal. these components are separated from the carrier by a frequency difference equal to the frequency of base band component. In this lab you will concentrate on understanding what goes on in the frequency domain for a sine wave message modulating a sinusoidal carrier. make sure your frequency domain display gives you a good picture. There are 3 steps to solve this one. 1. fm modulation, or frequency modulation, is a method of encoding information on a carrier wave by.
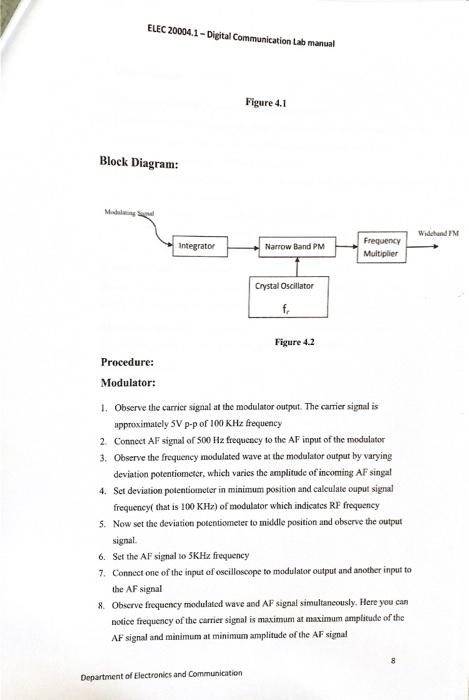
Solved Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation Aim To Understand Chegg This document describes an experiment on frequency modulation and demodulation. the objectives are to introduce frequency modulation, where the frequency of a carrier signal is varied according to an input message signal. The frequency modulation is a non linear modulation process. each spectral component of the base band signal gives rise to one or two spectral components in the modulated signal. these components are separated from the carrier by a frequency difference equal to the frequency of base band component. In this lab you will concentrate on understanding what goes on in the frequency domain for a sine wave message modulating a sinusoidal carrier. make sure your frequency domain display gives you a good picture. There are 3 steps to solve this one. 1. fm modulation, or frequency modulation, is a method of encoding information on a carrier wave by.
Comments are closed.