Solved Etermine The Position Vector Of A Point Relative To Chegg
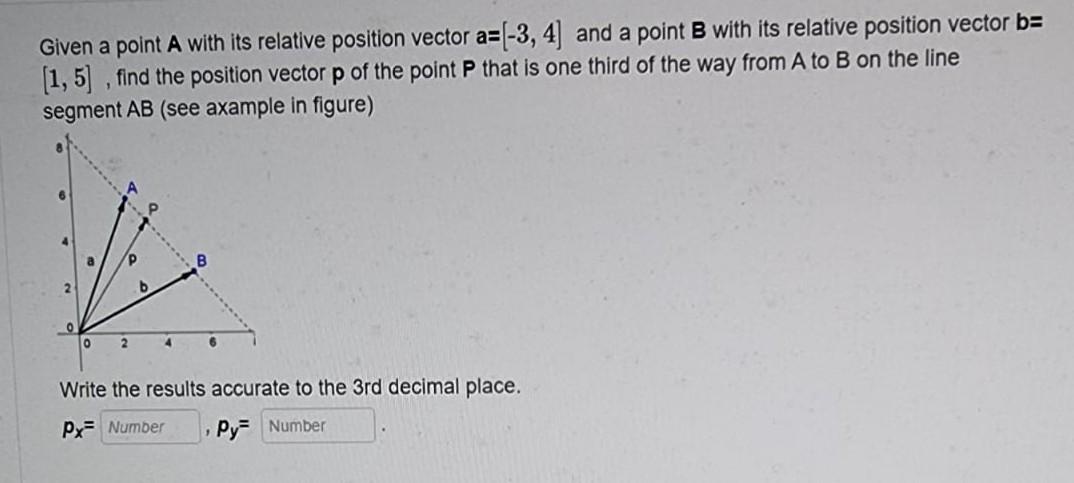
Solved Given A Point A With Its Relative Position Vector Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. etermine the position vector of a point relative to nother point, and calculate the corresponding unit ector. lthough vectors are often constructed from points, oints are not vectors. It's essential to first determine the coordinates of a point, before finding the position vector of that point. consider two points, a and b, where a = (x 1, y 1) and b = (x 2, y 2). next, we will find the position vector from point a to point b, the vector ab.
Solved The Position Vector Of A Point Relative To Another Chegg Before determining the position vector of a point, we first need to determine the coordinates of that point. let’s suppose we have two points, m and n, where m = (x1, y1) and n = (x2, y2). next, we want to find the position vector from point m to point n, the vector mn. What is a position vector and how to find a position vector for a vector between two points, find the length of the vector, position vectors on the coordinate plane, with video lessons, examples and step by step solutions. How far and at what angle is the person's final position from his her initial position? in what direction would the person have to head to return to his her initial position?. Instead of a and b let's discuss the position vector between two points as a general case. the position vector of a point is a vector that represents the position of that point in space relative to the origin.

Solved Given A Point A With Its Relative Position Vector Chegg How far and at what angle is the person's final position from his her initial position? in what direction would the person have to head to return to his her initial position?. Instead of a and b let's discuss the position vector between two points as a general case. the position vector of a point is a vector that represents the position of that point in space relative to the origin. Learn what position vectors are for your a level maths exam. this revision note covers the key concept and worked examples. Consider a point whose location in space is specified with cartesian coordinates (e.g., p(x,y,z)). now consider the directed distance (a vector quantity!) extending from the origin to this point. Here’s the best way to solve it. a position vector is defined as a fixed vector that locates a point in space relative to another point. (28 32) (a consider two points, a and b, in 3 d space. let their coordinates be (xa, ya, za) and (xb, yb, zb), respectively. Determine the position, velocity, and acceleration of e relative to point n. use transport thm. for vector differentiation and addition thm. for angular velocity when necessary.
Comments are closed.