Solved Consider The Following Search Problem With Initial Chegg
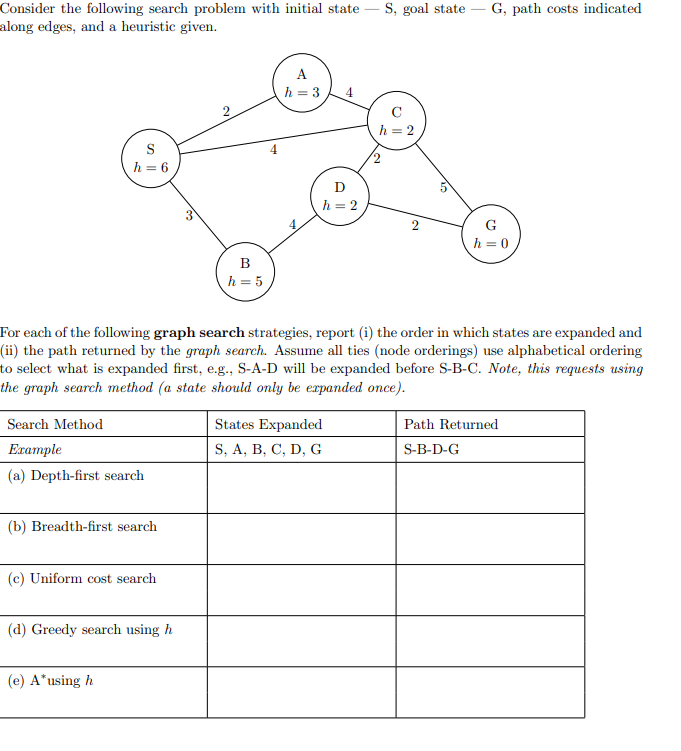
Solved Consider The Following Search Problem With Initial Chegg Consider the following search problem with initial state −s, goal state −g, path costs indicated along edges, and a heuristic given. for each of the following graph search strategies, report (i) the order in which states are expanded and (ii) the path returned by the graph search. Consider the search space depicted above for a hypothetical search problem. s is the initial state and t is the goal state. the cost of each edge has been labeled on the graph. a (4 points): compute the shortest path and its cost using uniform cost search (djikstra's algorithm).

Solved Assume You Have The Following Search Problem Initial Chegg We can perform a depth first search on state space (set of all configurations of a given problem i.e. all states that can be reached from the initial state) tree. Note that the following questions variously reference both tree search and graph search. for questions that require a heuristic, use the one given in the figure. If a strategy gets lost on an infinite path and never finds the goal, show the search tree with a few steps and then states a “fail” under the tree. i) hill climbing with heuristic h2. Explain how this online search problem can be viewed as an offline search in belief state space, where the initial belief state includes all possible environment configurations.

Solved Consider The Following Search Problem The Starting Chegg If a strategy gets lost on an infinite path and never finds the goal, show the search tree with a few steps and then states a “fail” under the tree. i) hill climbing with heuristic h2. Explain how this online search problem can be viewed as an offline search in belief state space, where the initial belief state includes all possible environment configurations. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: consider the following search problem. Graph search algorithm: augment tree search to store expanded nodes in a set called explored set (or closed set) and only add new nodes not in the explored set to the fringe. Find a heuristic for use with a* search in this problem which is admissible and which does not require extensive mathematical calculation. explain clearly why your heuristic is admissible. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: consider the following search problem. initial state is a. the goal state is d. the following graph outlines states and transitions, transition cost, and simple heuristic estimates from the states a, b, and c to the goal d. 1.
Comments are closed.