Solved Bytes Chegg

Chegg Solutions Pdf Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: bytes): ptr1=malloc (500);ptr2=malloc (200);ptr3=malloc (800);ptr4=malloc (1500). assume that the header added by the allocator is less than 10 bytes in size. You are asked to optimize a cache capable of storing 8 bytes total for the given references. there are three direct mapped cache designs possible by varying the block size: c1 has one byte blocks, c2 has two byte blocks, and c3 has four byte blocks.
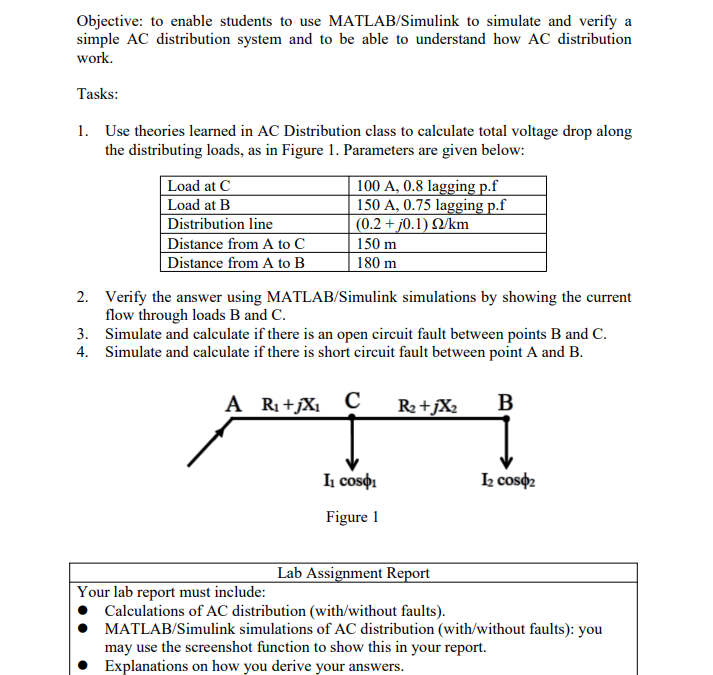
Solved Question Chegg Consider a computer using byte addressable memory accessing different types of cache. each cache consists of 8 blocks with one 32 bit word per block. specify how many bits are used for the tag, index or set, and byte offset for each type of cache listed in the table below. First, we are given that the address length is 32 bits and the memory is byte addressable. the cache has 256 blocks and each block has one 32 bit word. since we don't know the word size, we assume that 1 word = 1 byte, so the block size is 4 bytes (32 bits). What is the programming problem you're trying to solve? this sounds more like homework from a computer architecture class. ok, but this isn't about programming, which is what stack overflow is for. maybe cs.stackexchange would be better. a byte is 8 bits. Consider a byte addressable computer with 24 bit addresses, a cache capable of storing a total of 64k bytes of data, and blocks of 32 bytes. show the format of a 24 bit memory address if the computer uses direct mapping.
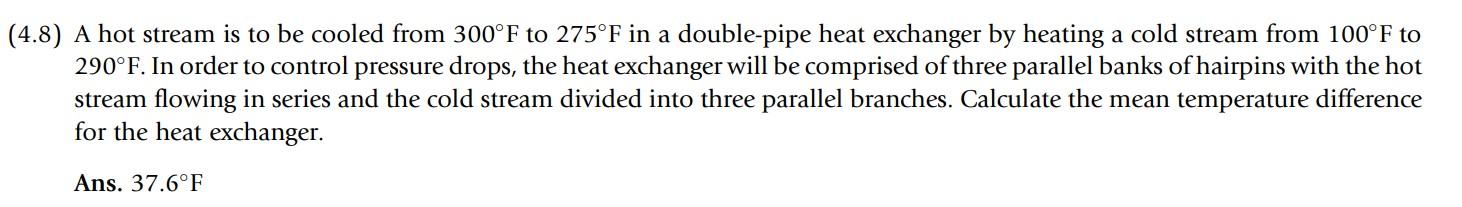
Solved 5 This Have Been Solved On Chegg Already Chegg What is the programming problem you're trying to solve? this sounds more like homework from a computer architecture class. ok, but this isn't about programming, which is what stack overflow is for. maybe cs.stackexchange would be better. a byte is 8 bits. Consider a byte addressable computer with 24 bit addresses, a cache capable of storing a total of 64k bytes of data, and blocks of 32 bytes. show the format of a 24 bit memory address if the computer uses direct mapping. Question: bytes exercises 9 and 10 refer to computer bytes. a computer byte is a string of eight digits, where each digit is either a zero or a one. two examples are 01001001 and 11001101. 9. how many bytes have exactly five ones? 10. in how many of the bytes with exactly five ones are no two zeroes next to each other? hw23 further counting. Question uppose a byte addressable computer using set associative cache has suppose a byte addressable computer using set associative cache has 221 bytes of main memory and a cache of 64 blocks, where each cache block contains 4 bytes. Sakshi ojha . Since the memory is byte addressable, we have 32 bits 4 bits (index) 2 bits (set selection) = 26 bits for the tag. for a fully associative cache: the cache consists of 16 blocks, so we don't need any bits for the index or set.
Github Hbohra98 Chegg Solutions All The Solutions To Chegg Questions Question: bytes exercises 9 and 10 refer to computer bytes. a computer byte is a string of eight digits, where each digit is either a zero or a one. two examples are 01001001 and 11001101. 9. how many bytes have exactly five ones? 10. in how many of the bytes with exactly five ones are no two zeroes next to each other? hw23 further counting. Question uppose a byte addressable computer using set associative cache has suppose a byte addressable computer using set associative cache has 221 bytes of main memory and a cache of 64 blocks, where each cache block contains 4 bytes. Sakshi ojha . Since the memory is byte addressable, we have 32 bits 4 bits (index) 2 bits (set selection) = 26 bits for the tag. for a fully associative cache: the cache consists of 16 blocks, so we don't need any bits for the index or set.
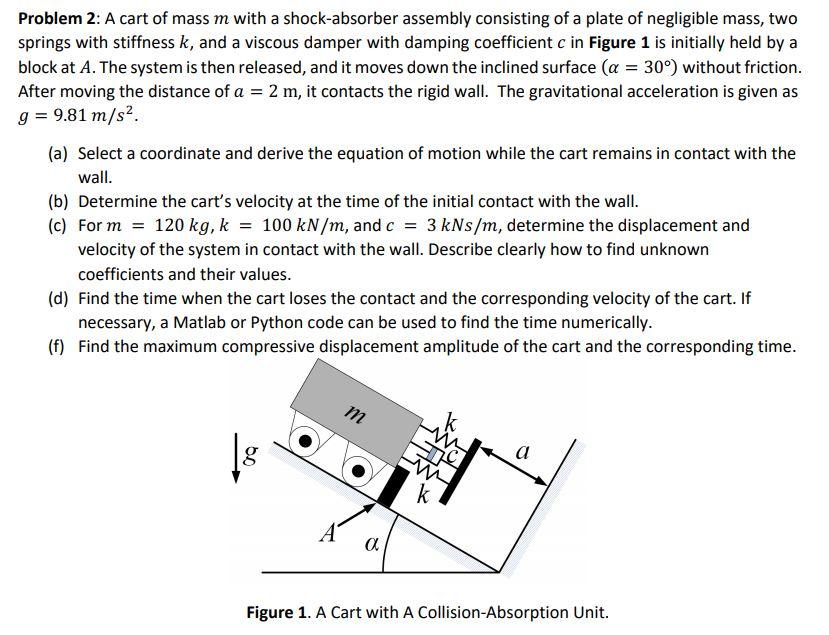
Solved I Already Checked Uploaded Chegg Solution But It Is Chegg Sakshi ojha . Since the memory is byte addressable, we have 32 bits 4 bits (index) 2 bits (set selection) = 26 bits for the tag. for a fully associative cache: the cache consists of 16 blocks, so we don't need any bits for the index or set.

Chegg
Comments are closed.