Solved B Use Initial Conditions To Determine The Current Chegg
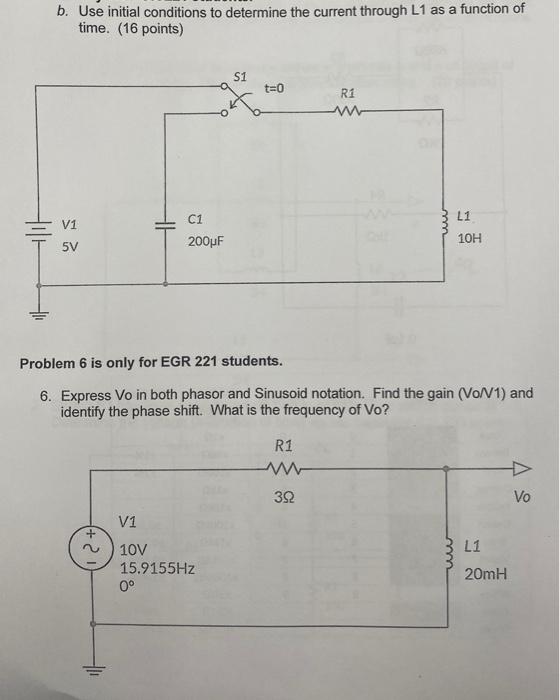
Solved B Use Initial Conditions To Determine The Current Chegg B. use initial conditions to determine the current through l1 as a function of time. (16 points) problem 6 is only for egr 221 students. 6. express vo in both phasor and sinusoid notation. find the gain ( von11) and identify the phase shift. what is the frequency of vo?. Zero initial conditions it is very common to have zero initial conditions simply replace components with their laplace domain impedances.

Solved 4 From The Circuit Below Determine These Following Chegg Write down the equations of motion of the ball in the vertical plane. I know that the initial condition for the voltage in the capacitor is v1 (0.01). i solved the exercise exactly the same way but with a different initial condition and got the wrong answer. When solving second order differential equation problems, it's crucial to determine two initial conditions. in the context of circuit problems, these initial conditions represent the voltage across a component and its derivative at a specific point in time, usually at t = 0. First, we are given the differential equation: d 2 d t 2 = 2 we need to solve this equation to find the expression for the current in terms of t. this is a second order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients. to solve it, we can assume a solution of the form: t = e r t where r is a constant.
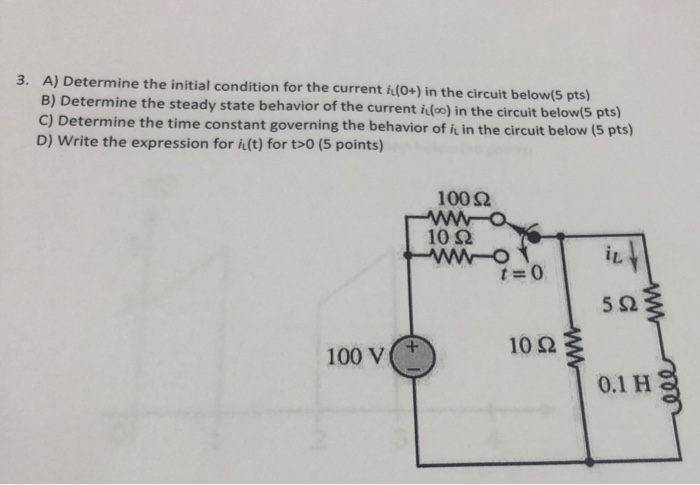
Solved 3 A Determine The Initial Condition For The Current Chegg When solving second order differential equation problems, it's crucial to determine two initial conditions. in the context of circuit problems, these initial conditions represent the voltage across a component and its derivative at a specific point in time, usually at t = 0. First, we are given the differential equation: d 2 d t 2 = 2 we need to solve this equation to find the expression for the current in terms of t. this is a second order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients. to solve it, we can assume a solution of the form: t = e r t where r is a constant. For subcircuit b the voltage and current correspond to the passive sign convention (i.e. the current arrow in the opposite direction to the voltage arrow) and so the power absorbed by b is given by. Determine the current through the capacitor. the current through the capacitor is 13.060 ± sin(377t) a. explanation: 60 x 10 = 333333.3 cos2(377t) v(t) = ±577.4 cos(377t) v assume that v(t) = 577.4 cos(377t) v. Simplify first order circuits with solved problems to excel in your exams and grasp key concepts easily. Determine the initial condition for the current | chegg . 1. determine the initial condition for the current through the inductor in the switched circuit shown in fig. 1. [25\%] 2. sketch the \ ( s \) domain circuit that corresponds to that in fig. 1, taking into account the initial condition. [25\%] 3.
Comments are closed.