Solved 7 10 Solve The Initial Value Problem Chegg
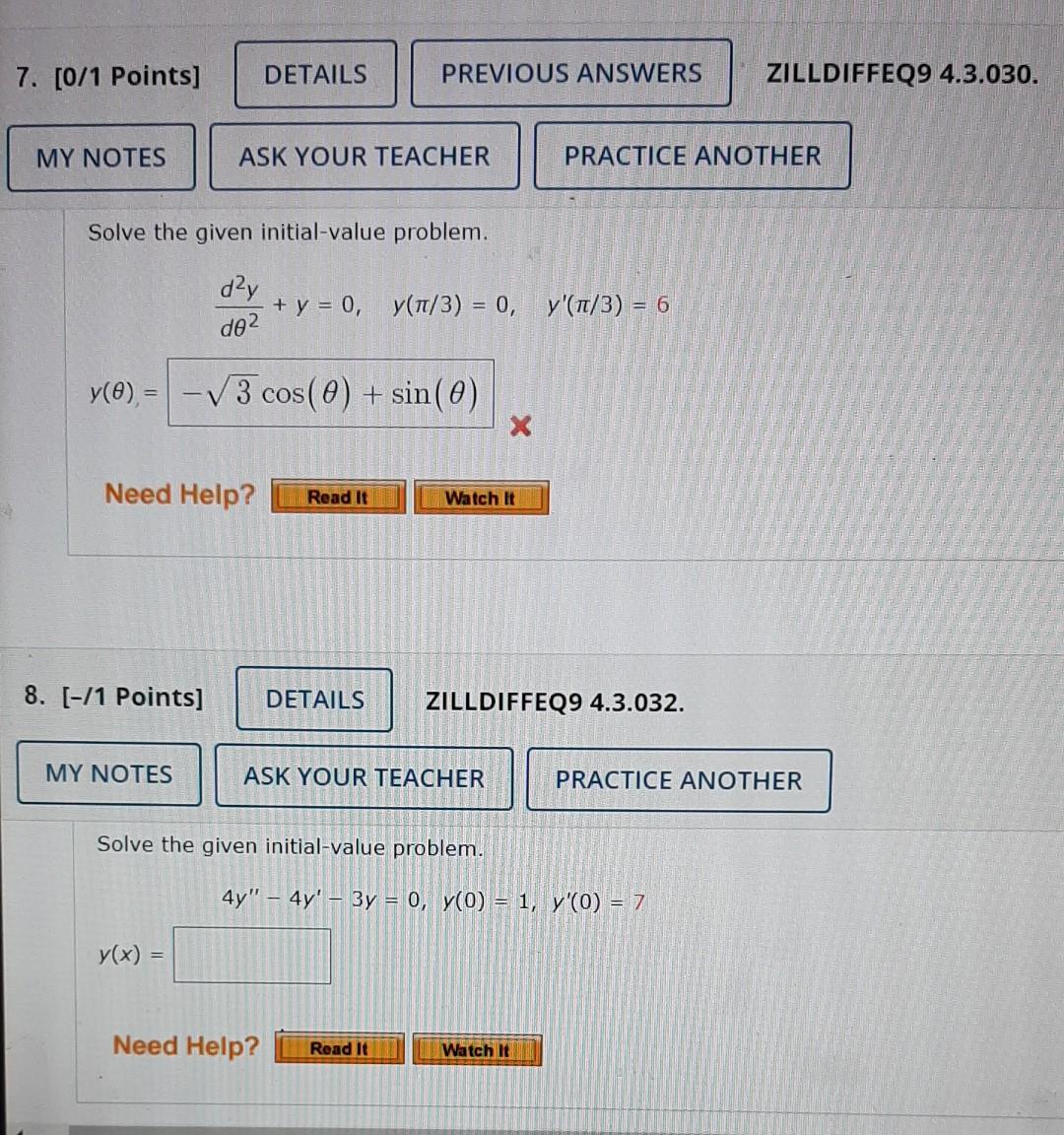
Solved 7 Solve The Given Initial Value Problem 8 Solve The Chegg Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 2 steps to solve this one. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. This calculus video tutorial explains how to solve the initial value problem as it relates to separable differential equations. more.
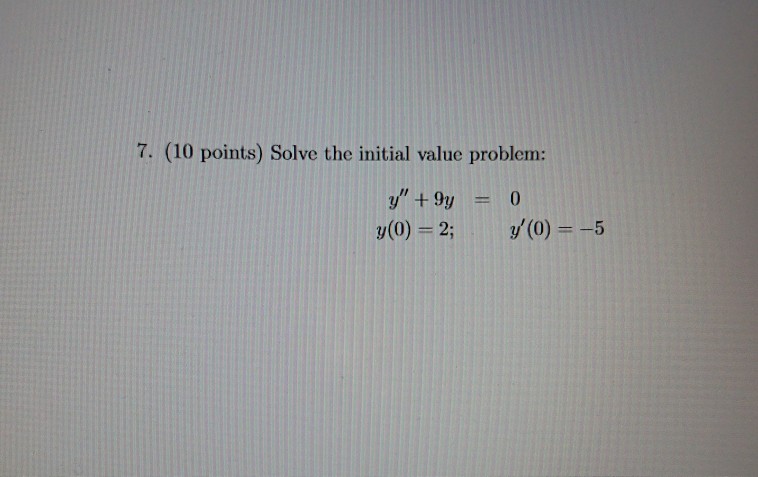
Solved 7 10 Points Solve The Initial Value Problem Chegg Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. for math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…. We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. Ask a question for free get a free answer to a quick problem. most questions answered within 4 hours. A differential equation together with one or more initial values is called an initial value problem. the general rule is that the number of initial values needed for an initial value problem is equal to the order of the differential equation.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem 10 7 6 7 Chegg Ask a question for free get a free answer to a quick problem. most questions answered within 4 hours. A differential equation together with one or more initial values is called an initial value problem. the general rule is that the number of initial values needed for an initial value problem is equal to the order of the differential equation. Initial value problems 1 euler’s explicit method (section 10.2.1) definition . by a first order initial value problem, we mean a problem such as dy = f (x;y) dx. Enter the differential equation, initial conditions, and target time into the calculator to solve the initial value problem. An initial value problem is a differential equation (i.e., an equation involving f ′) combined with an initial condition (i.e., f (a) = b). the goal of an initial value problem is to find the unique function that satisfies the differential equation and the initial condition. Goals the goal of this section is to use laplace transform to solve initial value problems, second order linear equations (as in §3.1, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6). this way, the methods may become more algebraic. two theorem that follows would be instrumental for this method.
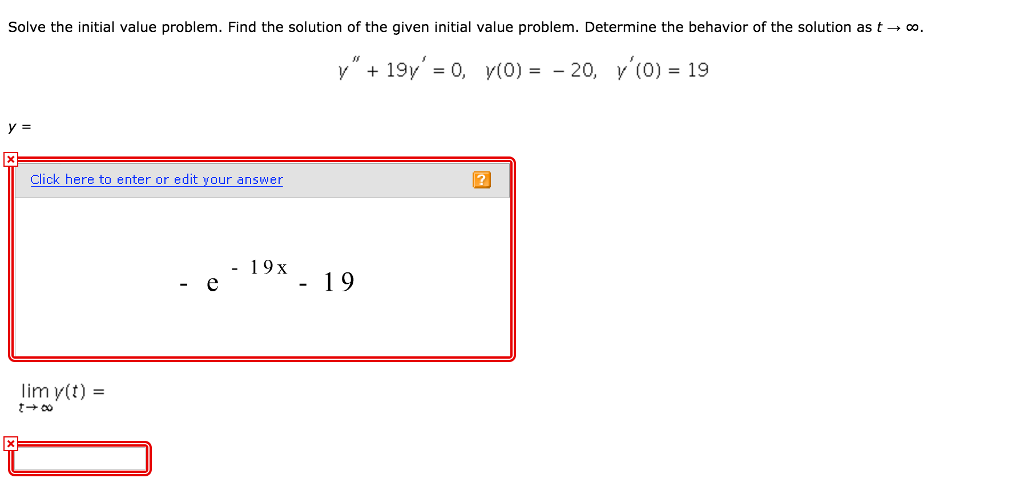
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Find The Solution Of Chegg Initial value problems 1 euler’s explicit method (section 10.2.1) definition . by a first order initial value problem, we mean a problem such as dy = f (x;y) dx. Enter the differential equation, initial conditions, and target time into the calculator to solve the initial value problem. An initial value problem is a differential equation (i.e., an equation involving f ′) combined with an initial condition (i.e., f (a) = b). the goal of an initial value problem is to find the unique function that satisfies the differential equation and the initial condition. Goals the goal of this section is to use laplace transform to solve initial value problems, second order linear equations (as in §3.1, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6). this way, the methods may become more algebraic. two theorem that follows would be instrumental for this method.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Find The Solution Of Chegg An initial value problem is a differential equation (i.e., an equation involving f ′) combined with an initial condition (i.e., f (a) = b). the goal of an initial value problem is to find the unique function that satisfies the differential equation and the initial condition. Goals the goal of this section is to use laplace transform to solve initial value problems, second order linear equations (as in §3.1, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6). this way, the methods may become more algebraic. two theorem that follows would be instrumental for this method.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Find The Solution Of Chegg
Comments are closed.