Solved 2 Identify The Configuration Of The Robot Given In Chegg

7 Robot Configuration Pdf Identify the configuration of the robot given in fig.2 and solve for inverse kinematics using the dh convention. (3 points) fig. 2. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 2. The configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot. since a robot’s links are rigid and of a known shape, only a few variables (coordinates in a general sense) are needed to represent its configuration.
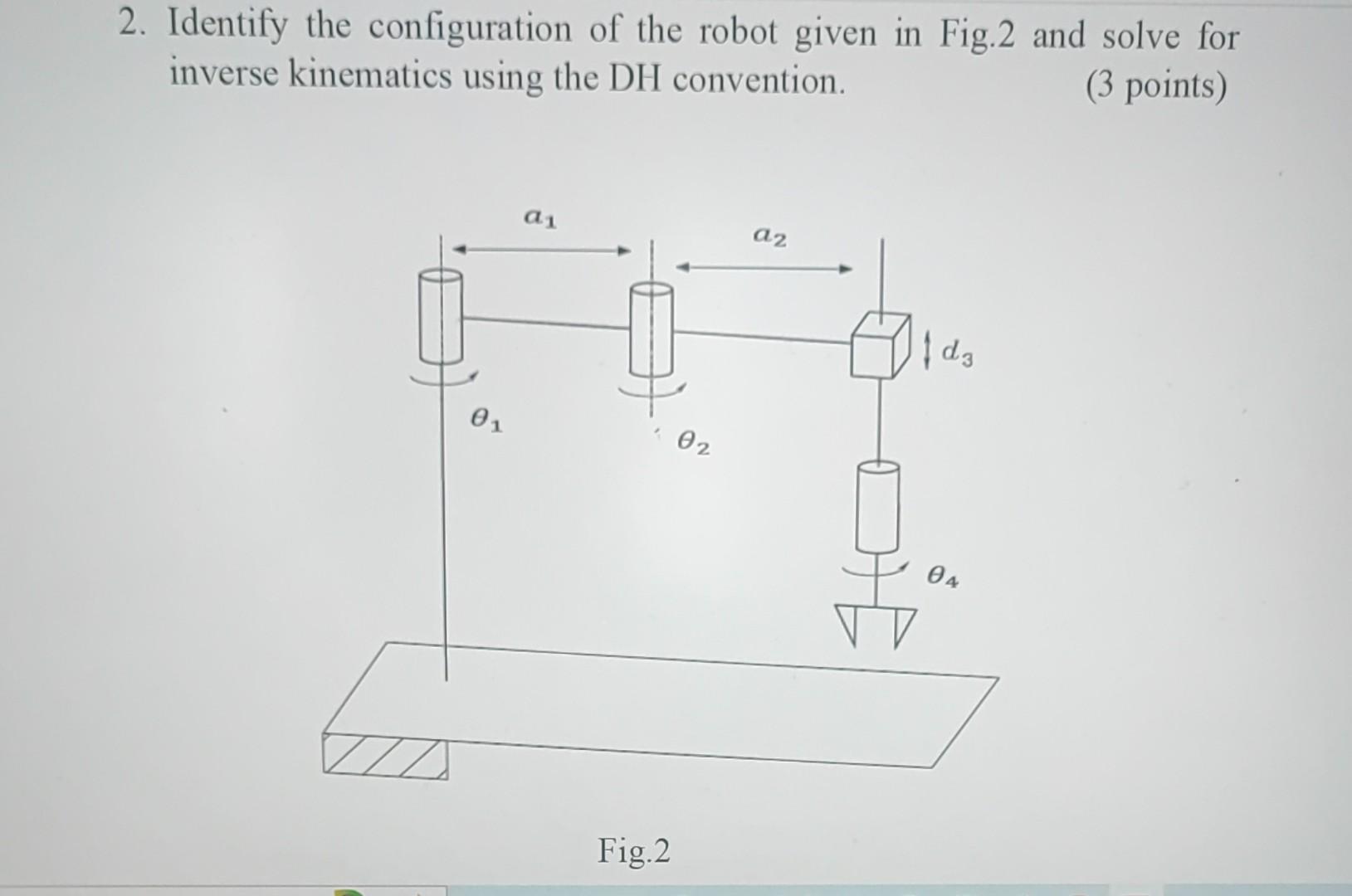
Solved 2 Identify The Configuration Of The Robot Given In Chegg Solution for 2. identify the configuration of the robot given in fig.2 and solve for inverse kinematics using the dh convention (3 points) fig.2. Please note that the specific steps and calculations may vary depending on the robot configuration and dh convention used. it is important to refer to the specific dh convention and equations for your robot to accurately solve for inverse kinematics. 1) body and arm: for positioning of objects in the robot's work volume 2) wrist assembly: for orientation of objects. Before diving into the quesitons, some of the most handy notes and equations will be summarized in this section. definition 2.1. the configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot.
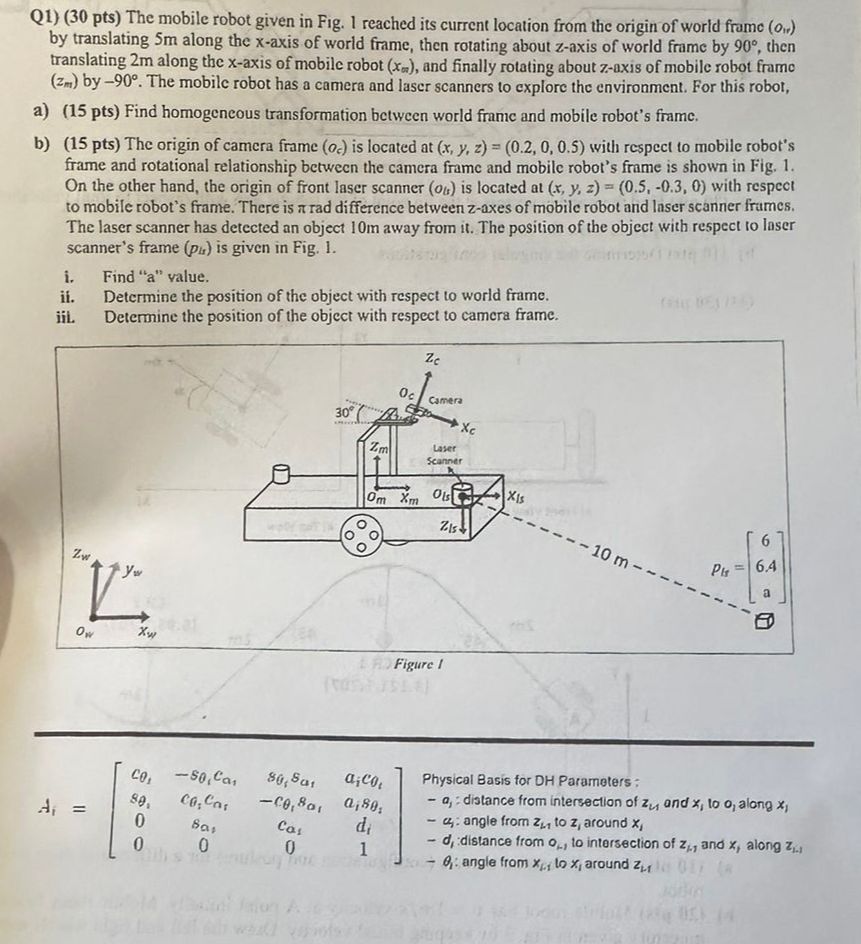
Solved Robot Modelling 1 ï Identify The Configuration Of The Chegg 1) body and arm: for positioning of objects in the robot's work volume 2) wrist assembly: for orientation of objects. Before diving into the quesitons, some of the most handy notes and equations will be summarized in this section. definition 2.1. the configuration of a robot is a complete specification of the position of every point of the robot. Mit robotics problem set focusing on kinematic equations, inverse kinematics, and workspace analysis for robot arm configurations. The robot arm is placed in front of the furnace opening in the same line of action but at a particular distance away from it, such that the robot arm is not affect by the heat source. The forward kinematics of a robot determines the con guration of the end e ector (the gripper or tool mounted on the end of the robot) given the relative con gurations of each pair of adjacent links of the robot. As opposed to forward kinematics, which computes the workspace coordinates of the robot given a configuration as input, inverse kinematics (ik) is essentially the reverse operation: computing configuration (s) to reach a desired workspace coordinate.
Comments are closed.