Solved 2 Consider A Direct Mapped Cache Memory Hierarchy Chegg
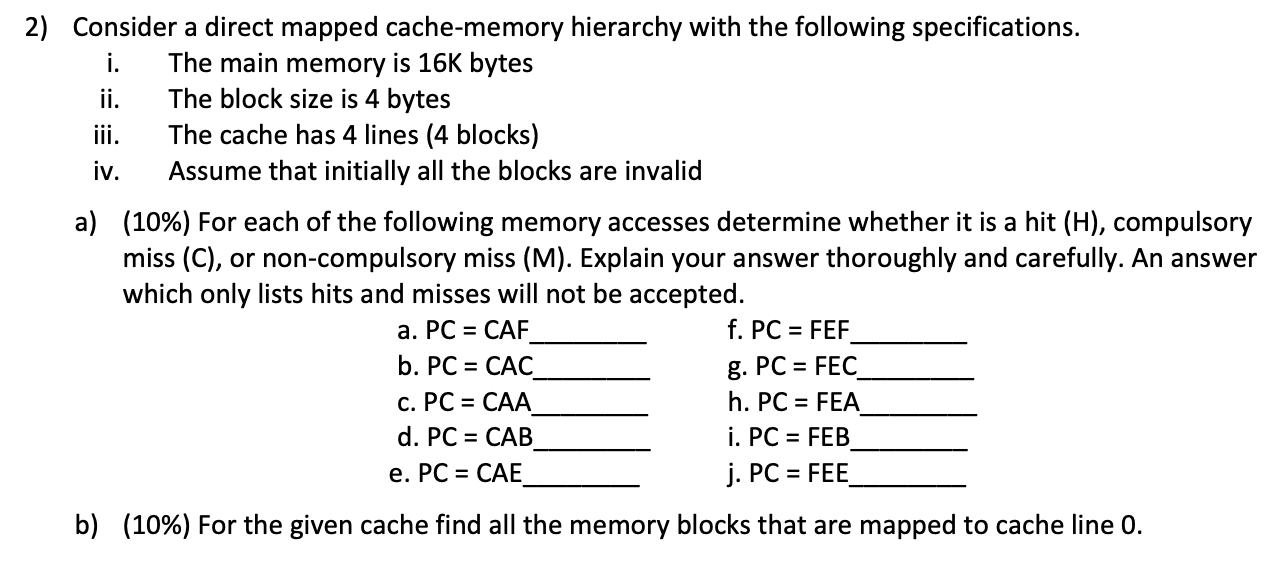
Solved 2 Consider A Direct Mapped Cache Memory Hierarchy Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 2) consider a direct mapped cache memory hierarchy with the following specifications. i. the main memory is 16k bytes ii. the block size is 4 bytes iii. the cache has 4 lines (4 blocks) iv. Always write the data into both the cache block and the next level in the memory hierarchy (write through). writes run at the speed of the next level in the memory hierarchy – slow – or can use a write buffer and stall only if the write buffer is full.
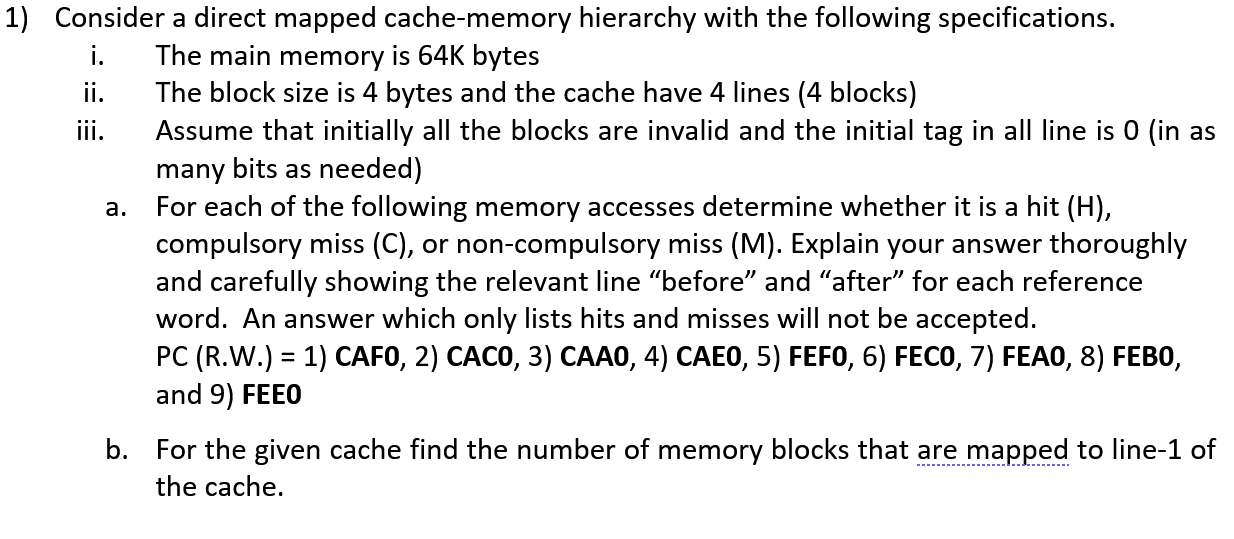
Solved 1 Consider A Direct Mapped Cache Memory Hierarchy Chegg Refer to the cache structure from 2.1b. for each of the following, identify whether it might increase or decrease (or it's impossible to tell) the hit rate for the instruction cache and data cache. Direct mapping problems consider direct mapped cache of size 16 kb with block size 256 tes. the size of main memory is 128 kb. find1. number of bits in tag tag. Consider a direct mapped cache with 64 total data words with 1 word cache line, which uses a lru replacement strategy and a write back write strategy. this cache architecture is used for parts (c) through (f). Since the cache is direct mapped, the block address modulo the number of cache lines will give us the cache line number. block address ca maps to cache line 2.

Solved Problem 3 Memory Hierarchy Or A Direct Mapped Cache Chegg Consider a direct mapped cache with 64 total data words with 1 word cache line, which uses a lru replacement strategy and a write back write strategy. this cache architecture is used for parts (c) through (f). Since the cache is direct mapped, the block address modulo the number of cache lines will give us the cache line number. block address ca maps to cache line 2. A particular block of main memory can be mapped to one particular cache line only. block ‘j’ of main memory will map to line number (j mod number of cache lines) of the cache. there is no need of any replacement algorithm. in this article, we will discuss practice problems based on direct mapping. For each reference identify the index bits, the tag bits, the block offset bits, and if it is a hit or a miss caches are important to providing a high performance memory hierarchy to processors. For a cache that has a power of two blocks (suppose 2m blocks), finding the position is a direct mapped cache is trivial: position (index) is indicated by the last (the least significant) log2m bits of the block frame address. Consider a machine with a byte addressable main memory of 2^20 bytes, blocksize of 16 bytes and a direct mapped cache having 2^12 lines. what are the tagaddress, cache index address and block offset address?.
Comments are closed.