Solved 1 Point The Image Below Shows The Graph Of The Chegg
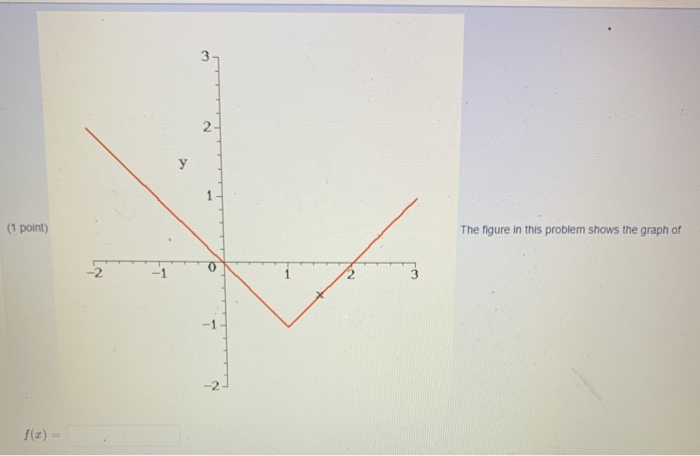
Solved 1 Point The Figure In This Problem Shows The Graph Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there are 2 steps to solve this one. given am image showing the graph of f (x). not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Spring 2022 problem set #1 the graph below shows supply and demand curves in black for apples. you can find a point where supply and demand curve intersect, indicating market equilibrium.
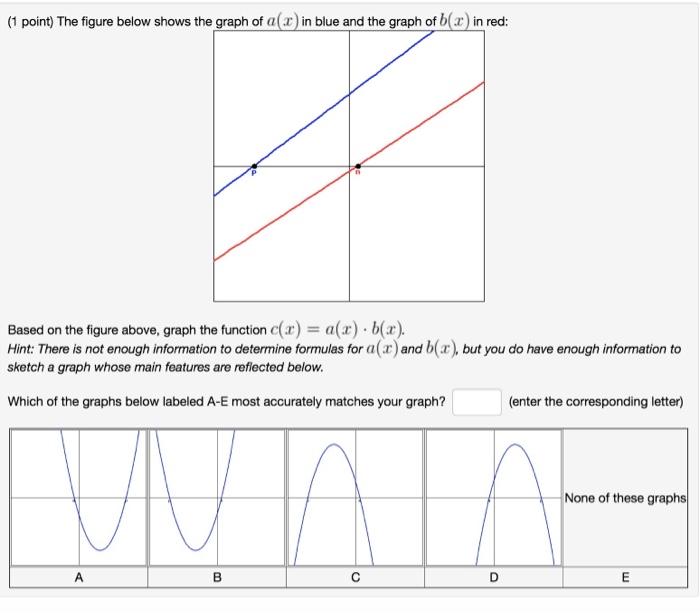
Solved 1 Point The Figure Below Shows The Graph Of A In Chegg The image contains two graphs with coca cola's data; the left pie chart shows unit case volume by region in 2000 with north america at 30.4%, europe at 20.5%, latin america at 25.7%, asia at 16.4%, and africa and middle east at 7.0%, totaling 17.1 billion. the right line graph displays share price, starting above $70 in 1996, dipping below $70 in 1997, peaking in 1998, fluctuating between $60. The following graph illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, marginal costs, average total costs, and average variable cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Solved which graph shows the solution set of the inequality chegg math algebra algebra questions and answers which graph shows the solution set of the inequality 2.9 (x 8)<26.1 ?. (1 point) the picture below shows the graph y = f ' (x) of the derivative of a function y = f (x). there are 3 steps to solve this one. we know that the function is increasing when f ′> 0 and the function is decreasing when f ′ <0. so here f ′> 0 (− ∞, a) u (c, e) and f ′ <0 on (a, c) u (e, ∞) not the question you’re looking for?.
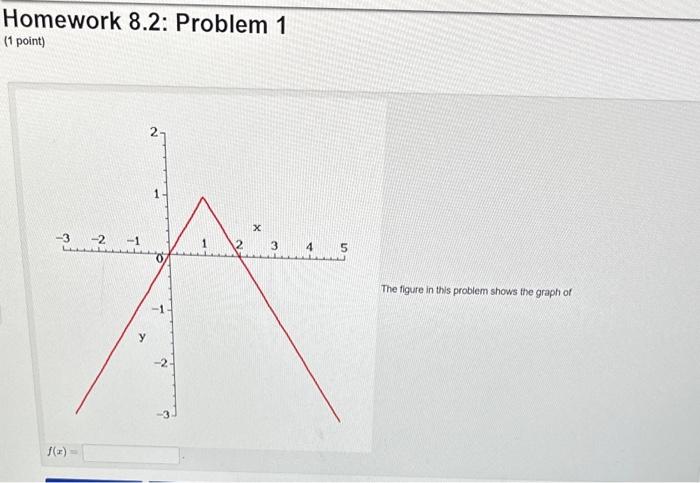
Solved Homework 8 2 Problem 1 1 Point The Figure In This Chegg Solved which graph shows the solution set of the inequality chegg math algebra algebra questions and answers which graph shows the solution set of the inequality 2.9 (x 8)<26.1 ?. (1 point) the picture below shows the graph y = f ' (x) of the derivative of a function y = f (x). there are 3 steps to solve this one. we know that the function is increasing when f ′> 0 and the function is decreasing when f ′ <0. so here f ′> 0 (− ∞, a) u (c, e) and f ′ <0 on (a, c) u (e, ∞) not the question you’re looking for?. The image shows a stock chart for xauusd (gold vs. us dollar). it displays the price fluctuations over time, with the x axis representing time (august 20) and the y axis representing the price. The following screenshot shows the structure of a typical solution along with the possible labeling of data objects. the contents of the screenshot have been deliberately blurred. The graph of the dirac delta is usually thought of as following the whole x axis and the positive y axis. [5] the dirac delta is used to model a tall narrow spike function (an impulse), and other similar abstractions such as a point charge or point mass. [6][7] for example, to calculate the dynamics of a billiard ball being struck, one can approximate the force of the impact by a dirac delta. Question 44 1 point the below graph shows the demand and cost curves for a natural monopoly market structure with a single monopoly supplying electricity to a town.
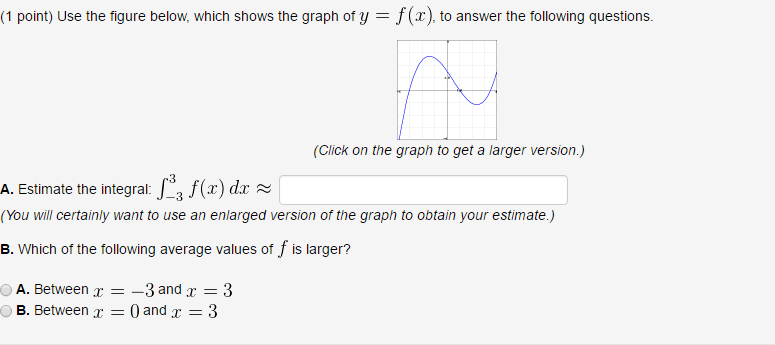
Solved 1 Point Use The Figure Below Which Shows The Graph Chegg The image shows a stock chart for xauusd (gold vs. us dollar). it displays the price fluctuations over time, with the x axis representing time (august 20) and the y axis representing the price. The following screenshot shows the structure of a typical solution along with the possible labeling of data objects. the contents of the screenshot have been deliberately blurred. The graph of the dirac delta is usually thought of as following the whole x axis and the positive y axis. [5] the dirac delta is used to model a tall narrow spike function (an impulse), and other similar abstractions such as a point charge or point mass. [6][7] for example, to calculate the dynamics of a billiard ball being struck, one can approximate the force of the impact by a dirac delta. Question 44 1 point the below graph shows the demand and cost curves for a natural monopoly market structure with a single monopoly supplying electricity to a town.
Comments are closed.