Solved 1 Cauchy Euler Differential Equations A Linear Chegg
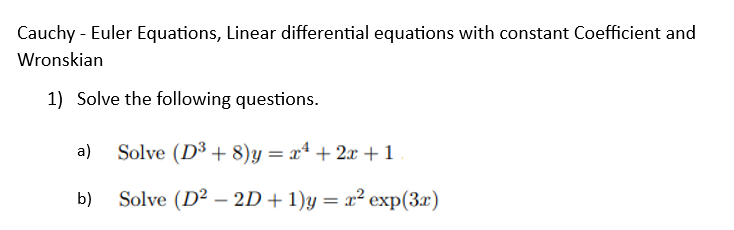
Cauchy Euler Equations Linear Differential Chegg The observable characteristic of this type of equation is that the degree of the power function of each term matches the degree of the derivative of that term. to find a solution we try a solution of the form y=x" where m is a constant. Another class of solvable linear differential equations that is of interest are the cauchy euler type of equations, also referred to in some books as euler’s equation.

Solved 1 Cauchy Euler Differential Equations A Linear Chegg Convert the above euler equation to a second order, constant coefficient differential equation using the substitution x = et. remember, this is equivalent to t = ln|x|. In the grand tradition of mathematics, we will show how to solve a second order euler cauchy differential equation by transforming it into a differential equation that has been previously solved. Solve the characteristic equation: similar to the equations with constant coefficients, we solve the quadratic equation for r, and depending on the nature of the roots, the solution will have different forms. Crack the secrets of the cauchy euler equation in our in depth tutorial. discover methods, examples, and tips for tackling second order des.
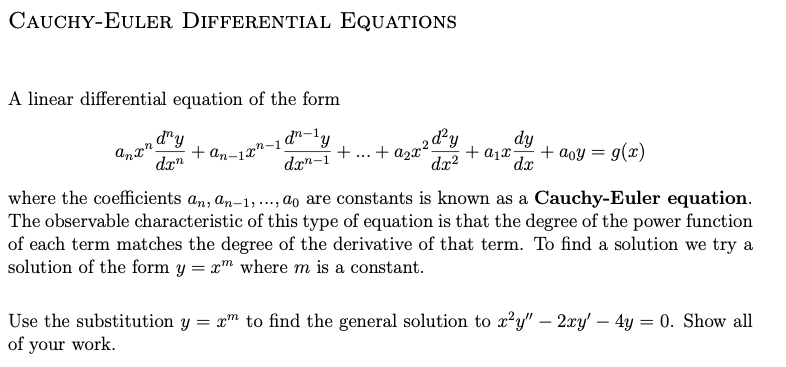
Solved Cauchy Euler Differential Equations A Linear Chegg Solve the characteristic equation: similar to the equations with constant coefficients, we solve the quadratic equation for r, and depending on the nature of the roots, the solution will have different forms. Crack the secrets of the cauchy euler equation in our in depth tutorial. discover methods, examples, and tips for tackling second order des. Second order homogeneous cauchy euler differential equations are easy to solve. the keys to solving these equations are knowing how to determine the indicial equation, how to find its roots, and knowing which of the three forms for the solutions to use. Al section 4.7 cauchy euler equation goal of this section 1. study solution of a class of variable coefficient linear equations called cauchy euler equation. this section, we consider equations with variable coefficients of the form a(t)y00 b(t)y0 c(t)y = f(t):. There’s just one step to solve this. 1. the euler cauchy equation is a linear, second order variable coefficient differential equation of the form aty" bty' cy = 0, t > 0 where a, b, c e r and a # 0. So we use the general solution form corresponding to case 1 with r1 = 1, r2 = 2 and since the initial condition was given for positive t (i.e. at t = 1) we want the solution to be valid for t > 0.
Comments are closed.