Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360 It is very challenging for a computer to recognize an object if we change its features like angle or scale. this article will discuss an interesting technique known as scale invariant feature transform (sift) that helps overcome this problem. This article covers the concept of feature matching opencv using python with different techniques.

Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360 The speeded up robust features algorithm was developed by bay, h., tuytelaars, t. and van gool, l, from the motivation to overcome the limitations and shortcomings of the scale invariant feature transform. In this article, we will see the basics of surf and a brief about the feature extraction and description. In this article, we looked at what feature scaling is and how to do it in python with scikit learn using standardscaler for standardization and minmaxscaler for normalization. Sift stands for scale invariant feature transform and was first presented in 2004, by d.lowe, university of british columbia. sift is invariance to image scale and rotation.
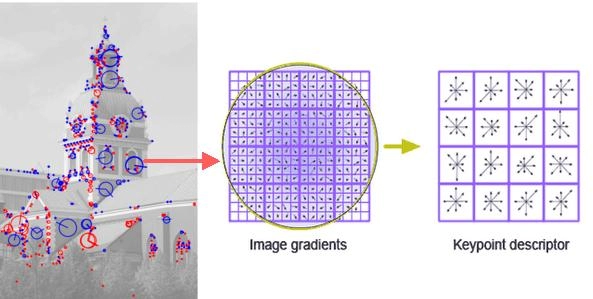
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360 In this article, we looked at what feature scaling is and how to do it in python with scikit learn using standardscaler for standardization and minmaxscaler for normalization. Sift stands for scale invariant feature transform and was first presented in 2004, by d.lowe, university of british columbia. sift is invariance to image scale and rotation. What is scale invariant feature transform (sift)? sift is a robust algorithm designed to identify and describe local features in images that are invariant to scale, rotation, and partially invariant to affine transformations and illumination changes. This is the problem with detecting features from images of different scales. now, sift comes in to help solve this problem. let’s walk through this algorithm. D.lowe proposed scale invariant feature transform (sift) in his paper, distinctive image features from scale invariant keypoints, which extracts keypoints and computes its descriptors. the paper also describes an approach to using these features for object recognition. Sift (scale invariant feature transform), surf(speeded up robust features), and brisk (binary robust invariant scalable keypoints) are some of the commonly used techniques for generating descriptors.
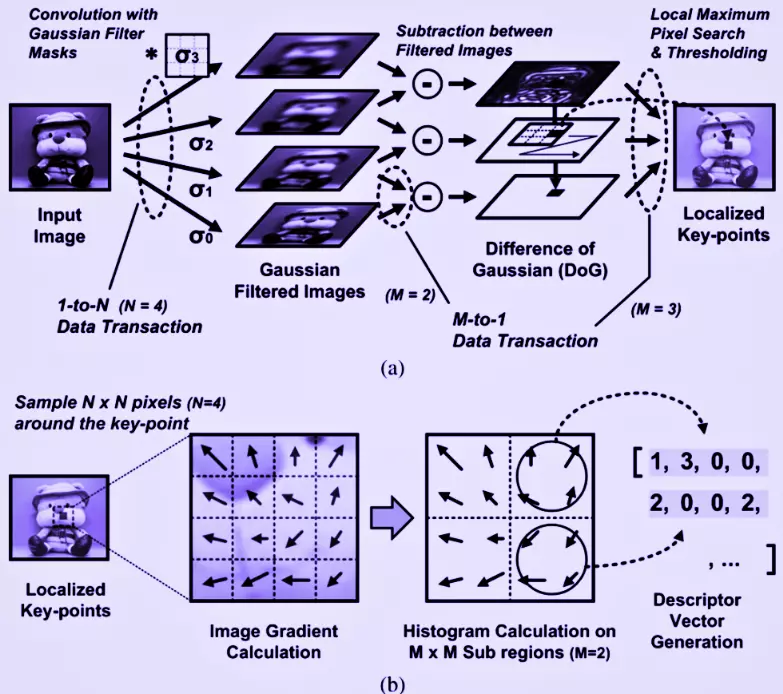
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360 What is scale invariant feature transform (sift)? sift is a robust algorithm designed to identify and describe local features in images that are invariant to scale, rotation, and partially invariant to affine transformations and illumination changes. This is the problem with detecting features from images of different scales. now, sift comes in to help solve this problem. let’s walk through this algorithm. D.lowe proposed scale invariant feature transform (sift) in his paper, distinctive image features from scale invariant keypoints, which extracts keypoints and computes its descriptors. the paper also describes an approach to using these features for object recognition. Sift (scale invariant feature transform), surf(speeded up robust features), and brisk (binary robust invariant scalable keypoints) are some of the commonly used techniques for generating descriptors.
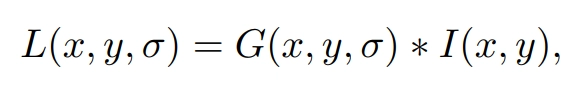
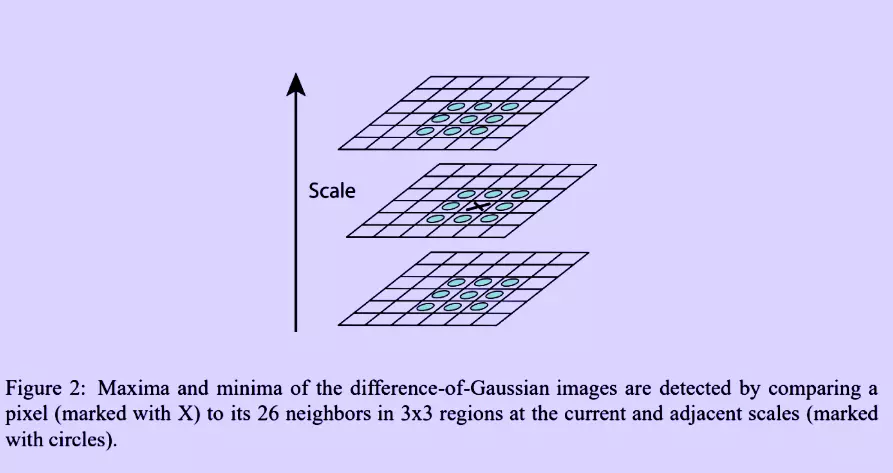
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360 D.lowe proposed scale invariant feature transform (sift) in his paper, distinctive image features from scale invariant keypoints, which extracts keypoints and computes its descriptors. the paper also describes an approach to using these features for object recognition. Sift (scale invariant feature transform), surf(speeded up robust features), and brisk (binary robust invariant scalable keypoints) are some of the commonly used techniques for generating descriptors.
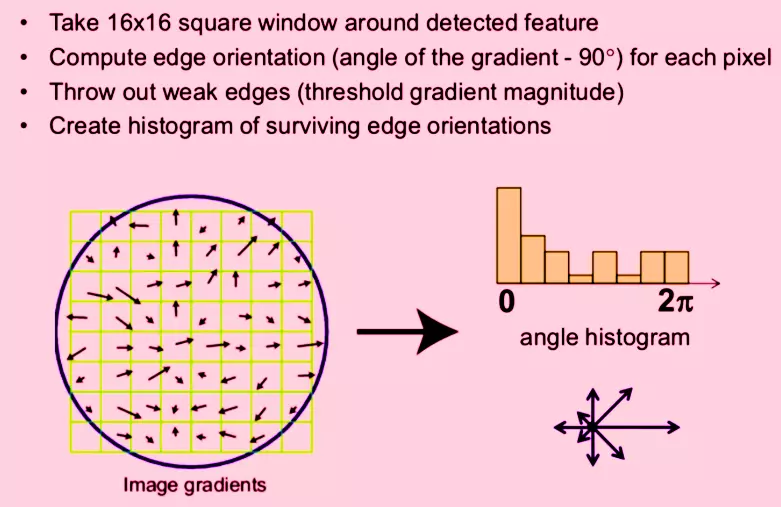
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Naukri Code360 Naukri Code 360
Comments are closed.