Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift

Introduction To Sift Scale Invariant Feature Transform By Deepanshu The scale invariant feature transform (sift) is a computer vision algorithm to detect, describe, and match local features in images, invented by david lowe in 1999. [1]. What is scale invariant feature transform (sift)? sift is a robust algorithm designed to identify and describe local features in images that are invariant to scale, rotation, and partially invariant to affine transformations and illumination changes.
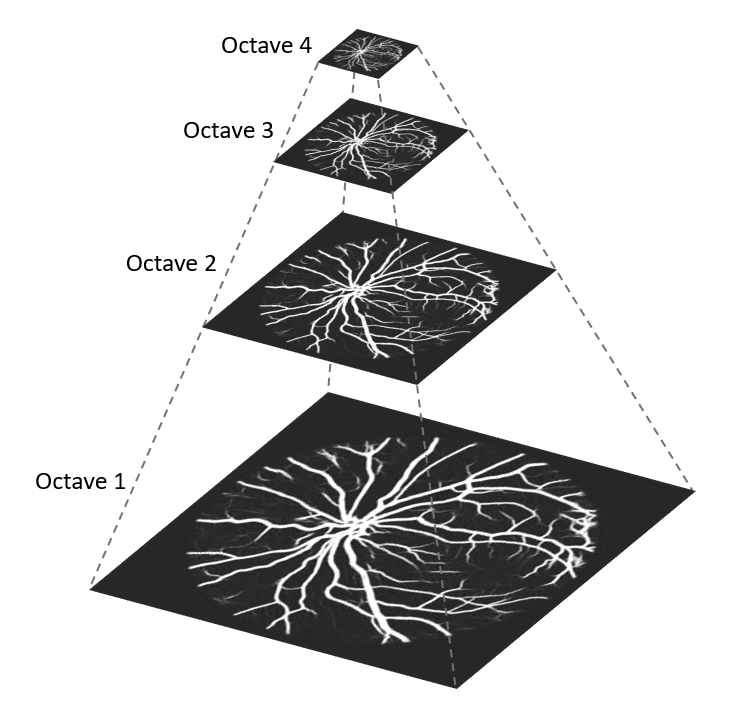
Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Sift stands for scale invariant feature transform and was first presented in 2004, by d.lowe, university of british columbia. sift is invariance to image scale and rotation. It is a technique for detecting salient, stable feature points in an image. for every such point, it also provides a set of “features” that “characterize describe” a small image region around the point. these features are invariant to rotation and scale. Scale invariant feature transform (sift) is an image descriptor for image based matching and recognition developed by david lowe (1999, 2004). For better image matching, lowe’s goal was to develop an interest operator that is invariant to scale and rotation. also, lowe aimed to create a descriptor that was robust to the variations corresponding to typical viewing conditions. the descriptor is the most used part of sift.

Lecture 05 Scale Invariant Feature Transform Sift Youtube Scale invariant feature transform (sift) is an image descriptor for image based matching and recognition developed by david lowe (1999, 2004). For better image matching, lowe’s goal was to develop an interest operator that is invariant to scale and rotation. also, lowe aimed to create a descriptor that was robust to the variations corresponding to typical viewing conditions. the descriptor is the most used part of sift. Orb: an efficient alternative to sift or surf. rublee et al., iccv, 2011. Learn what scale invariant feature transform (sift) is and how to use it with opencv. Many real applications require the localization of reference positions in one or more images, for example, for image alignment, removing distortions, object tracking, 3d reconstruction, etc. we have seen that corner points1 can be located quite reliably and independent of orientation. Sift, or the scale invariant feature transform, is a key technique in the sift scale invariant feature transform machine vision system. this method helps computers find and describe important parts of an image, even when the image changes in size, angle, or lighting.
Comments are closed.