Sampling Methods Techniques Probability Vs Non Probability Sampling Images
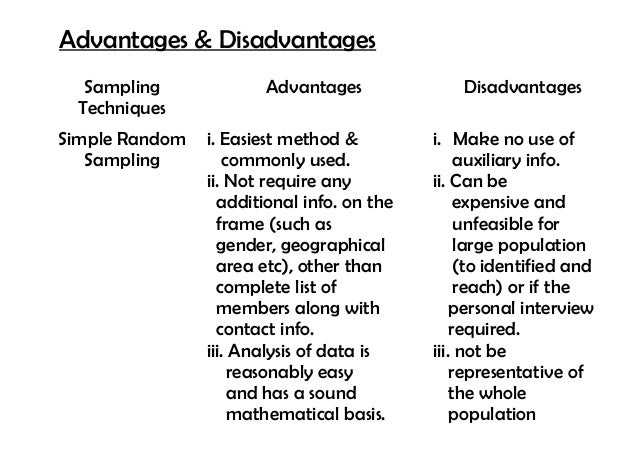
Sampling Methods Techniques Probability Vs Nonprobability Sampling To draw valid conclusions from your results, you have to carefully decide how you will select a sample that is representative of the group as a whole. this is called a sampling method. there are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research:. In this statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population.

Sampling Methods Techniques Probability Vs Nonprobability Sampling Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. What is sampling? sampling is a statistical technique for efficiently analyzing large datasets by selecting a representative subset. There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. these are known as sampling methods. in this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in statistics, including the benefits and drawbacks of the various methods. Explore sampling methods: familiarize yourself with different sampling methods, including probability sampling (e.g., random, stratified, cluster) and non probability sampling (e.g., convenience, purposive, quota).
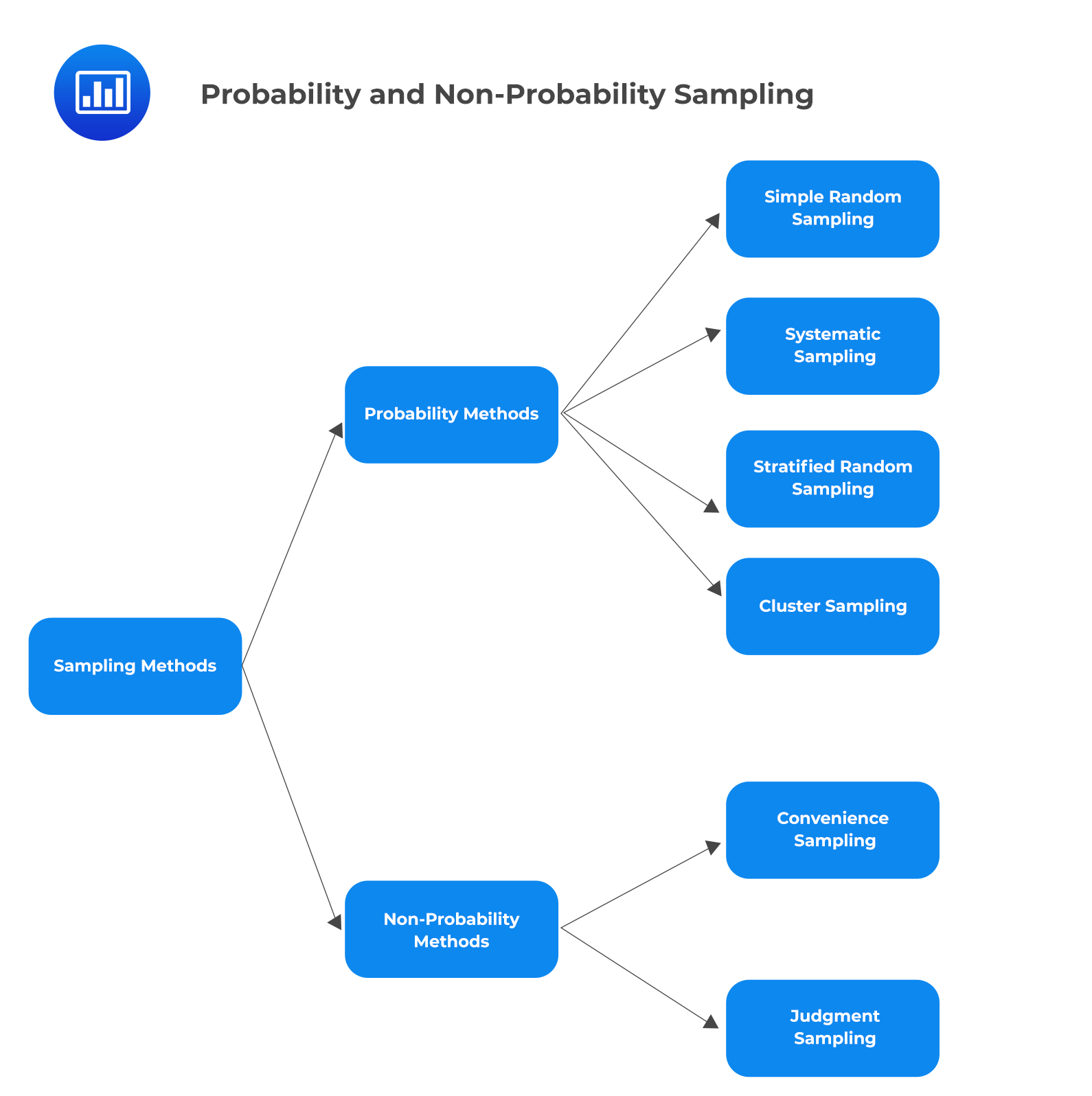
Sampling Methods Techniques Probability Vs Non Probability Sampling There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. these are known as sampling methods. in this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in statistics, including the benefits and drawbacks of the various methods. Explore sampling methods: familiarize yourself with different sampling methods, including probability sampling (e.g., random, stratified, cluster) and non probability sampling (e.g., convenience, purposive, quota). Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. when performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Sampling methods can be categorized as probability or non probability. in probability sampling, every individual in the population has a known or equal chance of being studied, which helps create a more representative sample. probability sampling includes simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. As a subject, sampling considers the different methodologies one could use to survey a portion of the population and seeks to find a sample that is most indicative of the overall population. Even if response is complete, some sampling designs tend to be biased. the best way to keep bias to a minimum is to use random sampling, which deliberately introduces chance into the selection of the sample from the population.

Sampling Methods Techniques Probability Vs Non Probability Sampling Images Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. when performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Sampling methods can be categorized as probability or non probability. in probability sampling, every individual in the population has a known or equal chance of being studied, which helps create a more representative sample. probability sampling includes simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. As a subject, sampling considers the different methodologies one could use to survey a portion of the population and seeks to find a sample that is most indicative of the overall population. Even if response is complete, some sampling designs tend to be biased. the best way to keep bias to a minimum is to use random sampling, which deliberately introduces chance into the selection of the sample from the population.
Comments are closed.