Remote Sensing Gis Maps Vector Data Vs Raster Data
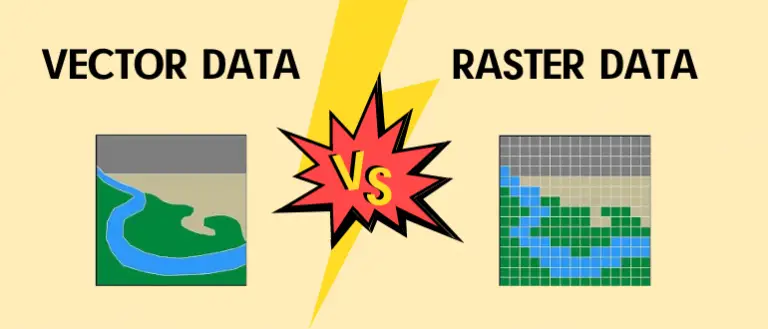
Vector Data Vs Raster Data Which One Should I Choose The spatial data further divided into two types; raster data and vector data. while on the other hand non spatial data are those representing a set of information that is systematically organized and computing against spatial data. At the core of gis lie two fundamental data types: raster and vector. each has unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. understanding their differences is essential for anyone.

Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Explore the key differences between vector and raster mapping data: precision vs. continuity, storage needs, processing speed, and ideal use cases in digital cartography and gis. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. In gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. understanding the differences between these data types and when to use them is essential for effective gis analysis. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific climate change applications. before diving into data models, it’s important to distinguish between entities and features.
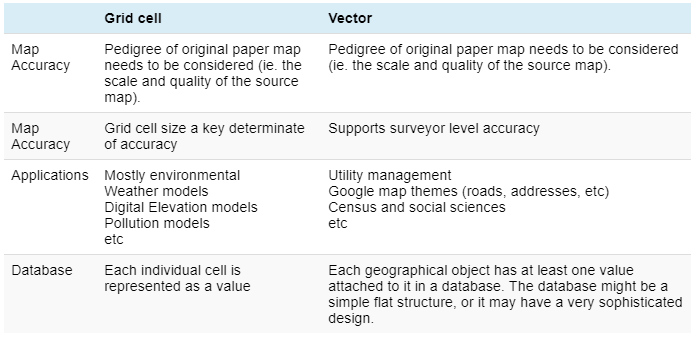
Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis In gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. understanding the differences between these data types and when to use them is essential for effective gis analysis. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific climate change applications. before diving into data models, it’s important to distinguish between entities and features. Choosing between raster and vector data depends largely on the type of geographic information you're working with and the purpose of your analysis. vector data is best suited for. Mastering raster and vector data in gis requires understanding their unique characteristics, applications, and analytical techniques. raster data excels in continuous surface analysis and remote sensing applications, while vector data is ideal for precise spatial representation and network analysis. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the two primary types of geospatial data raster and vector and delve into essential tools and formats used in the field. raster data represents spatial information as a grid of cells or pixels. Vector vs. raster data – this classification differentiates between data that represents precise geographic features using geometric shapes (vector) and data that captures continuous spatial information in a grid format (raster).

Raster Vs Vector Gis Gis University Raster Vs Vector Gis Choosing between raster and vector data depends largely on the type of geographic information you're working with and the purpose of your analysis. vector data is best suited for. Mastering raster and vector data in gis requires understanding their unique characteristics, applications, and analytical techniques. raster data excels in continuous surface analysis and remote sensing applications, while vector data is ideal for precise spatial representation and network analysis. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the two primary types of geospatial data raster and vector and delve into essential tools and formats used in the field. raster data represents spatial information as a grid of cells or pixels. Vector vs. raster data – this classification differentiates between data that represents precise geographic features using geometric shapes (vector) and data that captures continuous spatial information in a grid format (raster).

12 Raster Vs Vector Gis Images Vector And Raster Data Gis Vector And In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the two primary types of geospatial data raster and vector and delve into essential tools and formats used in the field. raster data represents spatial information as a grid of cells or pixels. Vector vs. raster data – this classification differentiates between data that represents precise geographic features using geometric shapes (vector) and data that captures continuous spatial information in a grid format (raster).
Comments are closed.