Raster And Vector Data Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Geographic

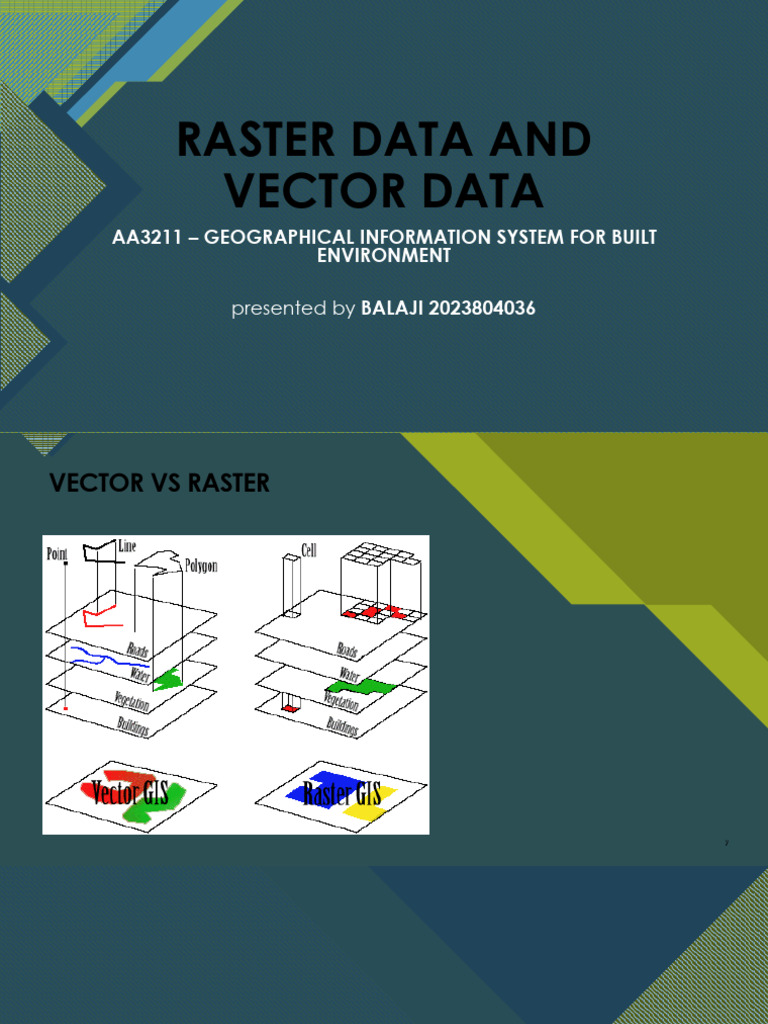
Vertex Graph Theory Types Of Vertices See Also References External Vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to represent features more accurately through their precise coordinates. while raster data has simpler analysis and storage, vector data provides much higher spatial resolution and accuracy. The vector data model is more suited to the question of “what do i know about this geographic feature? the raster data model answers the question, “what geographic phenomenon occurs at this location.”.

Graph Theory Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Graph Theory In this case spatial data are stored as part of the gis data structure, and attribute data are stored in a relational dbms. this approach allows integration of existing databases with graphics by the allocation of a unique identifier to each feature in the gis. Based on the georelational data model, an arcinfo coverage has two components: graphic files for spatial data and info files for attribute data. the label connects the two components. 40. In this unit, we will discuss the basic concepts of raster and vector data models in gis along with their advantages and disadvantages. you will get an idea of spatial data structures. Benefits of vector data structures relate to the ‘naturalness’ of the irregular features that may represented and the efficiency of not storing redundant data.

Graph Theory Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Mathematical Concepts In this unit, we will discuss the basic concepts of raster and vector data models in gis along with their advantages and disadvantages. you will get an idea of spatial data structures. Benefits of vector data structures relate to the ‘naturalness’ of the irregular features that may represented and the efficiency of not storing redundant data. Raster data is a fundamentally different way of encoding spatial information. a specific geographic location. points have no area or length. lines have length. lines may encode direction information. Discipline that deals all aspect of spatial data handling is called geoinformatics. spatial data is also called geographic data that identified by geometry, geographic location and att. Raster data excels at representing continuous phenomena, such as vegetation, temperature, or elevation changes, while vector data is best for accurately mapping discrete features like geological boundaries or road networks. Define, recognize, and explain the difference between shapefiles and feature classes. define raster data and describe raster data structure. define and clearly explain file explorer and it's purpose within gis, knowing when to and when not to use it with spatial data.

Graph Theory Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Mathematics Raster data is a fundamentally different way of encoding spatial information. a specific geographic location. points have no area or length. lines have length. lines may encode direction information. Discipline that deals all aspect of spatial data handling is called geoinformatics. spatial data is also called geographic data that identified by geometry, geographic location and att. Raster data excels at representing continuous phenomena, such as vegetation, temperature, or elevation changes, while vector data is best for accurately mapping discrete features like geological boundaries or road networks. Define, recognize, and explain the difference between shapefiles and feature classes. define raster data and describe raster data structure. define and clearly explain file explorer and it's purpose within gis, knowing when to and when not to use it with spatial data.

Graph Data Structure Pdf Vertex Graph Theory Graph Theory Raster data excels at representing continuous phenomena, such as vegetation, temperature, or elevation changes, while vector data is best for accurately mapping discrete features like geological boundaries or road networks. Define, recognize, and explain the difference between shapefiles and feature classes. define raster data and describe raster data structure. define and clearly explain file explorer and it's purpose within gis, knowing when to and when not to use it with spatial data.
Raster Vector Data Pdf Geographic Information System
Comments are closed.