Raman Spectra Pdf Scattering Raman Spectroscopy

Raman Spectra Pdf Scattering Raman Spectroscopy The name "raman spectroscopy" typically refers to vibrational raman spectroscopy using laser wavelengths which are not absorbed by the sample. Raman spectroscopic analysis is based on the raman scattering effect discovered by indian scientist c.v. raman (raman) and analyzes the scattering spectrum with different frequencies from the incident light to obtain information on molecular vibration and rotation.

Raman Spectra Pdf Raman Spectroscopy Spectroscopy For raman spectroscopy, a compound's fundamental vibrational energy is active only if the corresponding stretch or bend results in a change in the polarizability of its electrons. What is raman spectroscopy? raman spectroscopy is a chemical analysis technique which involves illuminating a substance with a laser and analyzing the light that is scattered off the surface of the substance. Learn the fundamentals of raman spectroscopy and how you can apply this technology to your research, analytical and qa qc activities. find basic raman tutorials, advanced raman webinars on sample applications, and a helpful instrument guide to build your confidence in raman spectral analysis. Raman spectroscopy, a type of vibrational spectroscopy that provides a highly specific molecular fingerprint, is similar to ir. however, there are differences between raman and ir that influence where they are used in industrial applications.
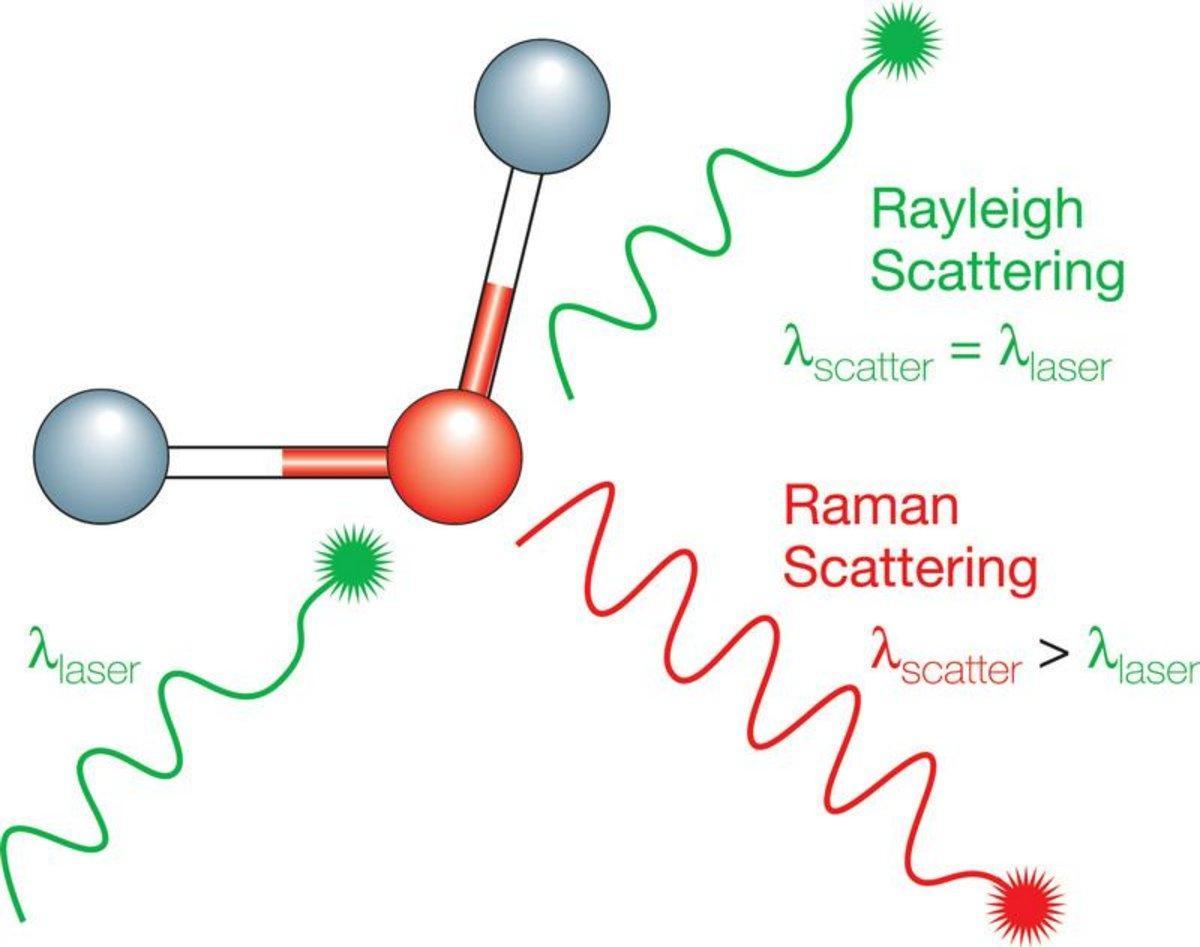
What Are The Raman Effect And Raman Scattering Learn the fundamentals of raman spectroscopy and how you can apply this technology to your research, analytical and qa qc activities. find basic raman tutorials, advanced raman webinars on sample applications, and a helpful instrument guide to build your confidence in raman spectral analysis. Raman spectroscopy, a type of vibrational spectroscopy that provides a highly specific molecular fingerprint, is similar to ir. however, there are differences between raman and ir that influence where they are used in industrial applications. Raman imaging is a powerful microscopy technique that creates detailed images based on a sample’s chemical makeup, revealing what it is made of at a microscopic level. Raman technology may not be the newest kid on the block anymore, but the technology still has an air of mystery around it. in this introduction to raman spectroscopy, we’ll clear up some of the questions surrounding the technology, starting with the basics. Raman is a light scattering technique, whereby a molecule scatters incident light from a high intensity laser light source. most of the scattered light is at the same wavelength (or color) as the laser source and does not provide useful information – this is called rayleigh scatter. Sir chandrasekhara venkata "c. v." raman ( ˈrɑːmən rah muhn; [2] tamil: சந்திரசேகர வெங்கட ராமன், romanised: cantiracēkara veṅkaṭa rāmaṉ; 7 november 1888 – 21 november 1970) was an indian physicist [3] known for his work in the field of light scattering. [4] using a spectrograph that he developed, he and his student k. s. krishnan.

Raman Spectroscopy Chempedia Raman imaging is a powerful microscopy technique that creates detailed images based on a sample’s chemical makeup, revealing what it is made of at a microscopic level. Raman technology may not be the newest kid on the block anymore, but the technology still has an air of mystery around it. in this introduction to raman spectroscopy, we’ll clear up some of the questions surrounding the technology, starting with the basics. Raman is a light scattering technique, whereby a molecule scatters incident light from a high intensity laser light source. most of the scattered light is at the same wavelength (or color) as the laser source and does not provide useful information – this is called rayleigh scatter. Sir chandrasekhara venkata "c. v." raman ( ˈrɑːmən rah muhn; [2] tamil: சந்திரசேகர வெங்கட ராமன், romanised: cantiracēkara veṅkaṭa rāmaṉ; 7 november 1888 – 21 november 1970) was an indian physicist [3] known for his work in the field of light scattering. [4] using a spectrograph that he developed, he and his student k. s. krishnan.
Comments are closed.