Projectile Motion Equations Physics Lecture Notes

Projectile Motion Short Notes Pdf Motion of a projectile (section 12.6) projectile motion can be treated as two rectilinear motions, one in the horizontal direction experiencing zero acceleration and the other in the vertical direction experiencing constant acceleration (i.e., gravity). To study projectile motion, we let θ be the angle at which the object is thrown relative to the horizontal; this is called the elevatio n angle. when a pro ojectile is launched d at an an ngle, the in nitial velo ocity has.

4 Projectile Motion Pdf Theory Module 1 Pdf Projectiles Section motion. which ball hit the floor first? remember the demonstration of free fall vs. projectile • projectile motion demonstration = yv = xv if an object is fired horizontally, what are its velocity components? why? projectiles launched horizontally. So, instead of pounding out some awful calculus to describe the motion of a projectile, we can see that the motion of a projectile is just the combination of constant speed along the horizontal axis and freefall along the vertical axis. Quantitative analysis of projectile motion: acceleration the equations of motion for velocity and constant acceleration are used to analyze projectile motion quantitatively. Explore projectile motion equations, range, max height, and their ratios. physics notes for high school early college. includes excel formula.
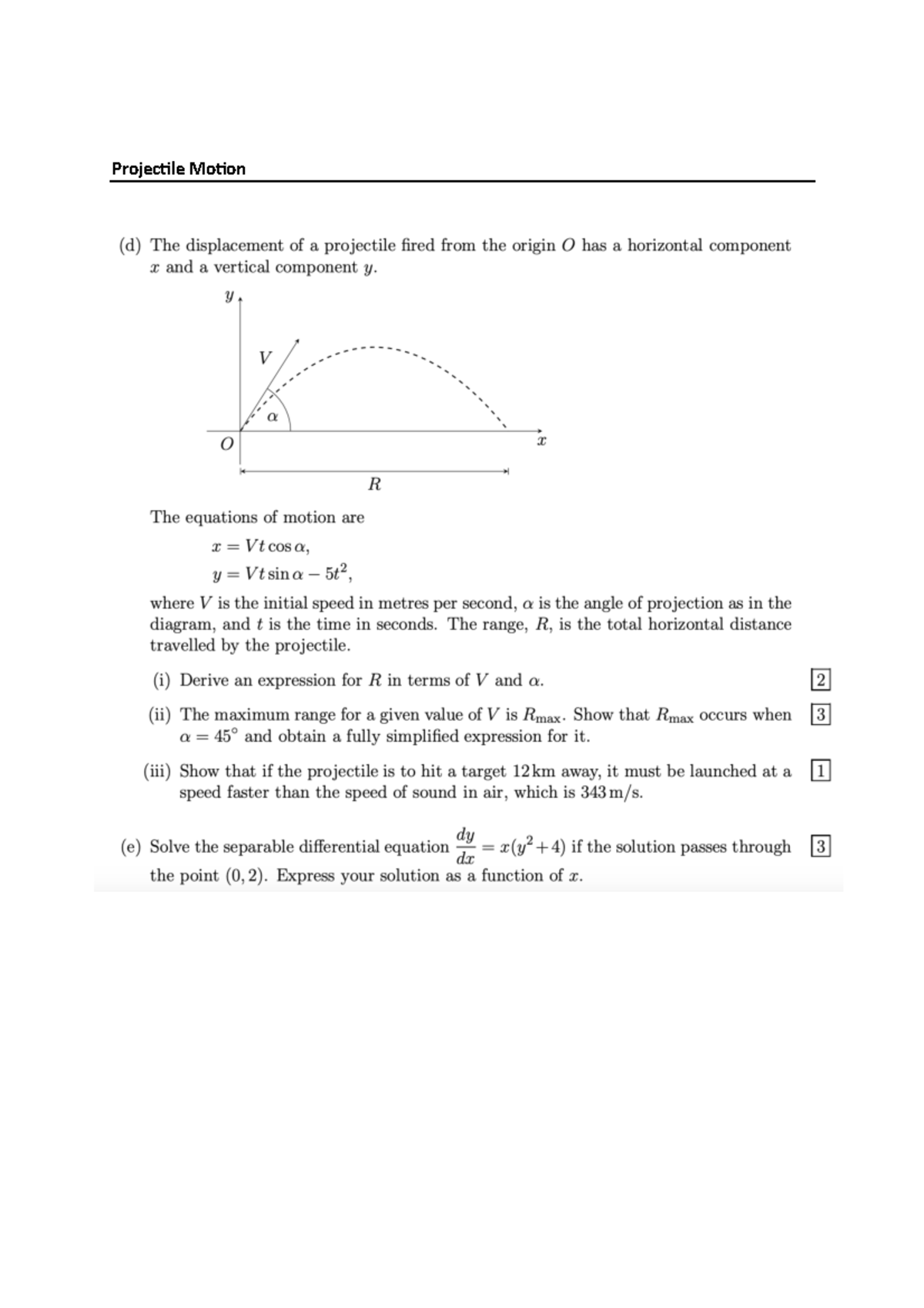
Projectile Motion Physics Notes Pm Studocu Quantitative analysis of projectile motion: acceleration the equations of motion for velocity and constant acceleration are used to analyze projectile motion quantitatively. Explore projectile motion equations, range, max height, and their ratios. physics notes for high school early college. includes excel formula. Lecture 3.2 projectile motion last time we were talking about two dimensional motion and introduced all important characteristics of this motion, such as position, displacement, velocity and acceleration. Projectile motion is no diferent. to further study objects and forces acting on them, we use so called free body diagrams that display all the forces acting on a body along with the direction of motion. Motion of a projectile (section 12.6) projectile motion can be treated as two rectilinear motions, one in the horizontal direction experiencing zero acceleration and the other in the vertical direction experiencing constant acceleration (i.e., gravity). This is how to derive the equations for projectile motion. the acceleration in the x direction is always zero and the acceleration in the y direction is always due to gravity.
Comments are closed.