Pathogenesis Of Multiple Sclerosis Ms Biorender Science Templates

Pathogenesis Of Multiple Sclerosis Ms Biorender Science Templates In pathology, pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. it can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. [1]. Pathogenesis is the biological process describing how a disease originates and develops within a host organism. it encompasses the entire journey of a disease, from its initial triggers to its observable manifestations and progression.
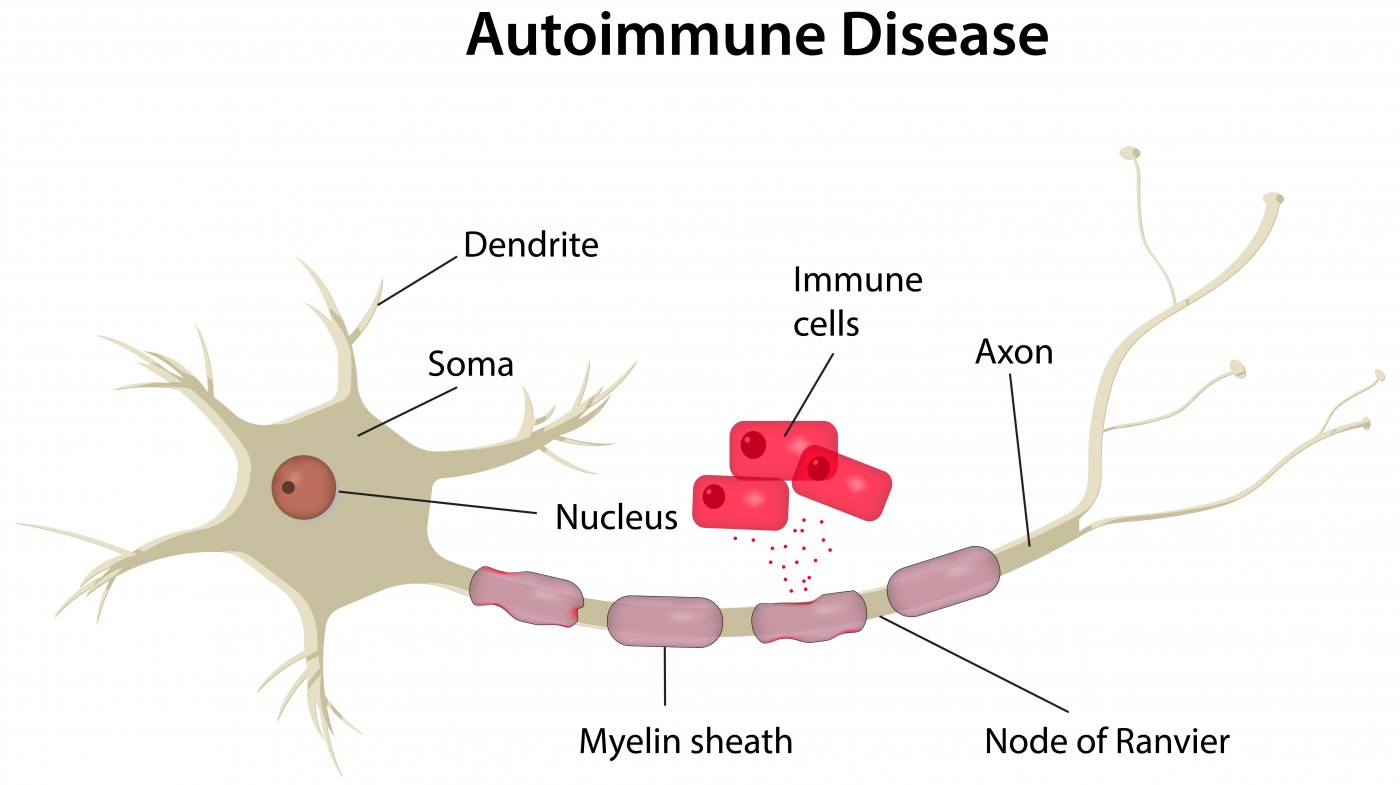
Potential Mechanism In Ms Pathogenesis Seen In Study Multiple To cause disease, a pathogen must successfully achieve four steps or stages of pathogenesis: exposure (contact), adhesion (colonization), invasion, and infection. Pathogenesis, the intricate process by which diseases develop within living organisms, is a fundamental concept in the field of medicine. this article explores the multifaceted nature of pathogenesis, highlighting the key factors and mechanisms that contribute to disease onset and progression. Pathogenesis is the process by which an infection leads to disease. pathogenic mechanisms of viral disease include (1) implantation of virus at the portal of entry, (2) local replication, (3) spread to target organs (disease sites), and (4) spread to sites of shedding of virus into the environment. The meaning of pathogenesis is the origination and development of a disease.

Role Of Cytokines In Pathogenesis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Ra And Pathogenesis is the process by which an infection leads to disease. pathogenic mechanisms of viral disease include (1) implantation of virus at the portal of entry, (2) local replication, (3) spread to target organs (disease sites), and (4) spread to sites of shedding of virus into the environment. The meaning of pathogenesis is the origination and development of a disease. Pathogenesis involves complex interactions between a pathogen or injurious factor and host tissues. for infectious diseases, the process generally begins with entry and colonization, followed by replication and spread. microbes employ virulence factors such as adhesins, toxins, invasion proteins and immune modulators to establish infection. The development of morbid conditions or of disease; more specifically the cellular events and reactions and other pathologic mechanisms occurring in the development of disease. adj., adj pathogenet´ic. miller keane encyclopedia and dictionary of medicine, nursing, and allied health, seventh edition. © 2003 by saunders, an imprint of elsevier, inc. Pathogenesis is a central concept in understanding the development and progression of infectious diseases caused by unicellular eukaryotic parasites, parasitic helminths, and other eukaryotic pathogens. Pathogenesis is defined as the process by which disease develops, involving mechanisms such as the imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors, activation of myofibroblasts, and abnormal cytokine signaling.
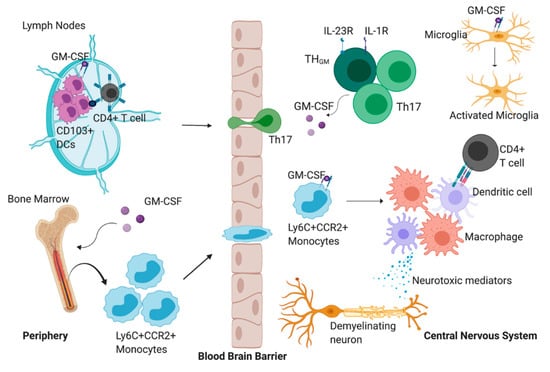
Cells Special Issue Cellular And Molecular Mechanisms In Pathogenesis involves complex interactions between a pathogen or injurious factor and host tissues. for infectious diseases, the process generally begins with entry and colonization, followed by replication and spread. microbes employ virulence factors such as adhesins, toxins, invasion proteins and immune modulators to establish infection. The development of morbid conditions or of disease; more specifically the cellular events and reactions and other pathologic mechanisms occurring in the development of disease. adj., adj pathogenet´ic. miller keane encyclopedia and dictionary of medicine, nursing, and allied health, seventh edition. © 2003 by saunders, an imprint of elsevier, inc. Pathogenesis is a central concept in understanding the development and progression of infectious diseases caused by unicellular eukaryotic parasites, parasitic helminths, and other eukaryotic pathogens. Pathogenesis is defined as the process by which disease develops, involving mechanisms such as the imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors, activation of myofibroblasts, and abnormal cytokine signaling.
Comments are closed.