Mac Layer Explained The Top Sublayer Of Data Link Layer
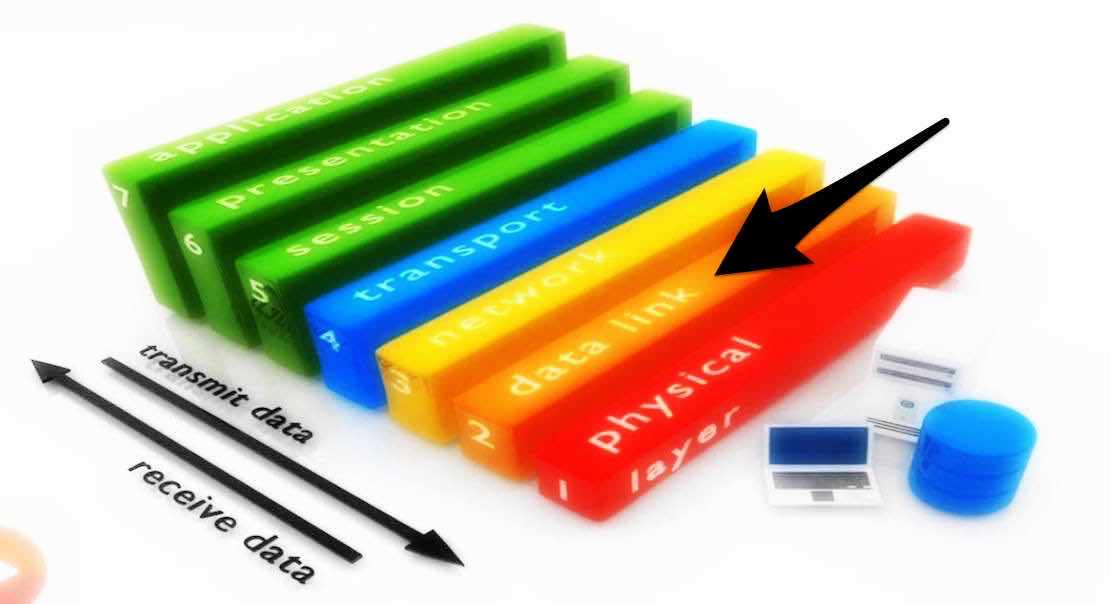

Mac Layer Explained The Top Sublayer Of Data Link Layer In ethernet networks, the mac sublayer is responsible for assigning unique mac addresses to devices and managing data transmission over the physical medium (e.g., cables). The medium access control (mac) is a sublayer of the data link layer of the open system interconnections (osi) reference model for data transmission. it is responsible for flow control and multiplexing for transmission medium.
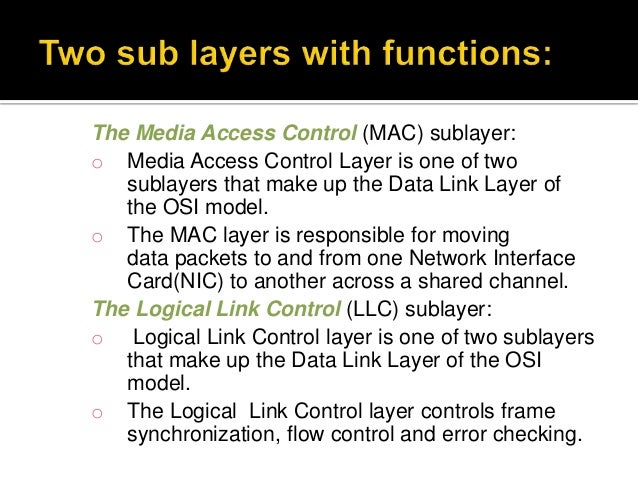
Ppt Data Link Layer Basic No Mac Sublayer Powerpoint Presentation This post gives a brief overview of the two sub layers of the data link layer, namely llc (logical link control) and mac (media access control). the post also briefly describes the different types of llc service modes. To communicate or transfer data from one computer to another, we need an address. in computer networks, various types of addresses are introduced; each works at a different layer. a mac address, which stands for media access control address, is a physical address that works at the data link layer. The data link layer is divided into logical channel management (llc) sublayer and media access control (mac) sublayer. llc provides network layer service, and the mac sublayer regulates access to a shared physical environment. The mac layer is the lower of the two sublayers. it acts as an interface between the llc sublayer and the physical layers. it does this by encapsulating data frames to make them suitable for transmission over the physical medium and by governing access to that medium so signals do not collide.

Ppt Layer 2 Data Link Layer Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The data link layer is divided into logical channel management (llc) sublayer and media access control (mac) sublayer. llc provides network layer service, and the mac sublayer regulates access to a shared physical environment. The mac layer is the lower of the two sublayers. it acts as an interface between the llc sublayer and the physical layers. it does this by encapsulating data frames to make them suitable for transmission over the physical medium and by governing access to that medium so signals do not collide. This blog post will delve into the two sub layers of the data link layer: the logical link control (llc) and the media access control (mac) sublayers. we will explore their responsibilities and how they contribute to effective data transmission. Layer 2 (data link layer) uses a mac (media access control) address. these are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications at the data link layer. Within the osi model, the mac layer plays a critical role in layer 2, the data link layer, working alongside the logical link control (llc) layer. it acts as a bridge to the physical layer, facilitating communication between the network’s hardware components and higher level functions. The medium access control (mac) layer is a sublayer of the data link layer (layer 2) in the osi model. it plays a crucial role in controlling how data packets are transmitted over a shared communication medium, whether it’s wired or wireless. the primary functions of the mac layer include:.

Solution Data Link Layer Mac Studypool This blog post will delve into the two sub layers of the data link layer: the logical link control (llc) and the media access control (mac) sublayers. we will explore their responsibilities and how they contribute to effective data transmission. Layer 2 (data link layer) uses a mac (media access control) address. these are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications at the data link layer. Within the osi model, the mac layer plays a critical role in layer 2, the data link layer, working alongside the logical link control (llc) layer. it acts as a bridge to the physical layer, facilitating communication between the network’s hardware components and higher level functions. The medium access control (mac) layer is a sublayer of the data link layer (layer 2) in the osi model. it plays a crucial role in controlling how data packets are transmitted over a shared communication medium, whether it’s wired or wireless. the primary functions of the mac layer include:.
Data Link Layer Within the osi model, the mac layer plays a critical role in layer 2, the data link layer, working alongside the logical link control (llc) layer. it acts as a bridge to the physical layer, facilitating communication between the network’s hardware components and higher level functions. The medium access control (mac) layer is a sublayer of the data link layer (layer 2) in the osi model. it plays a crucial role in controlling how data packets are transmitted over a shared communication medium, whether it’s wired or wireless. the primary functions of the mac layer include:.

Unit Iii Data Link Layer And Mac Sublayer Cse306 Computer Networks
Comments are closed.