Lowess R Smoothing Function 2 Example Codes Normalization By Lowess Regression Smoother Span

Lowess R Smoothing Function 2 Example Codes For Lowess Regression How to use the lowess function to smoothen lines and scatter plots in the r programming language. more details: statisticsglobe lowess r smoothin. Whether you’re new to r or a seasoned pro, this step by step guide will walk you through the process of performing lowess smoothing, generating data, visualizing the model, and comparing different models with varying smoother spans.

Lowess R Smoothing Function 2 Example Codes For Lowess Regression Loess smoothing is a non parametric form of regression that uses a weighted, sliding window, average to calculate a line of best fit. within each "window", a weighted average is calculated, and the sliding window passes along the x axis. one can control the size of this window with the span argument. Loess regression, sometimes called local regression, is a method that uses local fitting to fit a regression model to a dataset. the following step by step example shows how to perform loess regression in r. The lowess function performs the computations for the lowess smoother (see the reference below). lowess returns a an object containing components x and y which give the coordinates of the smooth. Lowess smoothing in r, the term “locally weighted scatterplot smoothing” is used in statistics to describe the process of creating a smooth curve that matches the data points in a scatterplot.
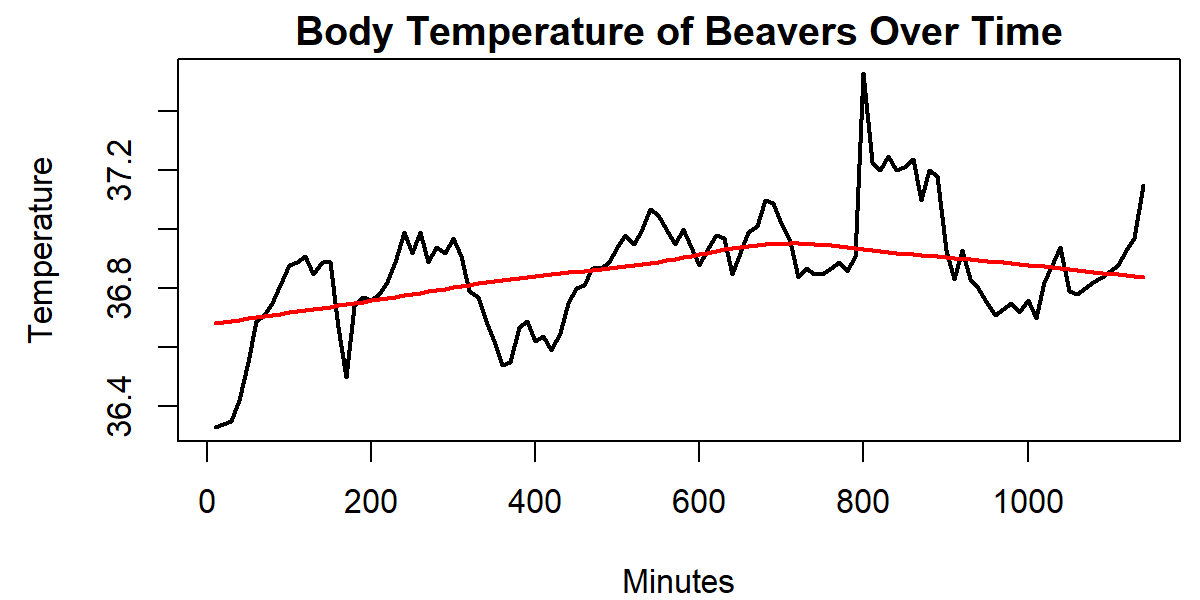
Lowess R Smoothing Function 2 Example Codes For Lowess Regression The lowess function performs the computations for the lowess smoother (see the reference below). lowess returns a an object containing components x and y which give the coordinates of the smooth. Lowess smoothing in r, the term “locally weighted scatterplot smoothing” is used in statistics to describe the process of creating a smooth curve that matches the data points in a scatterplot. We look for the n window closest points to the point x=10 and then run through the distance, scaled distance, tricube weights and then use the wls regression to find the lowess value of x=10. here's an example of a comparison of the lowess with the density parameter turned on (the red line) and off. Lowess is defined by a complex algorithm, the ratfor original of which (by w. s. cleveland) can be found in the r sources as file ‘ src library stats src lowess.doc ’. normally a local linear polynomial fit is used, but under some circumstances (see the file) a local constant fit can be used. Lowess returns a list containing components x and y which give the coordinates of the smooth. the smooth can be added to a plot of the original points with the function lines: see the examples.

Lowess R Smoothing Function 2 Example Codes For Lowess Regression We look for the n window closest points to the point x=10 and then run through the distance, scaled distance, tricube weights and then use the wls regression to find the lowess value of x=10. here's an example of a comparison of the lowess with the density parameter turned on (the red line) and off. Lowess is defined by a complex algorithm, the ratfor original of which (by w. s. cleveland) can be found in the r sources as file ‘ src library stats src lowess.doc ’. normally a local linear polynomial fit is used, but under some circumstances (see the file) a local constant fit can be used. Lowess returns a list containing components x and y which give the coordinates of the smooth. the smooth can be added to a plot of the original points with the function lines: see the examples.
Comments are closed.