Kubectl Cheat Sheet Kubernetes Io Pdf System Software

Kubectl Cheat Sheet Pdf Computer Engineering Software Engineering How can i config kubectl to use the cluster, user and authentication from this file as default in one command? i only see separate set cluster, set credentials, set context, use context etc. I have one pod running with name 'jenkins app 2843651954 4zqdp'. i want to install few softwares temporarily on this pod. how can i do this? i am trying this kubectl exec it jenkins app 2843651.

Kubectl Cheat Sheet Pdf I was running kubectl command to deploy my application in the gcloud. but suddenly the kubectl command stopped working. kubectl command is working fine but for everything else it say command not fo. Can i set the default namespace? that is: $ kubectl get pods n namespace it saves me having to type it in each time especially when i'm on the one namespace for most of the day. Kubectl needs a config file (commonly called as kubeconfig file) to work with cluster (here microk8s cluster) kubeconfig file consists of cluster server name, default context, user details, etc (means it may contain sensitive info). I have two pods running for a specific service. i want to get logs related to both the pods and check for specific text. for that i used ,as described here: kubectl logs l app=my app c my app con.

The Kubectl Cheat Sheet Kube Control Kubectl needs a config file (commonly called as kubeconfig file) to work with cluster (here microk8s cluster) kubeconfig file consists of cluster server name, default context, user details, etc (means it may contain sensitive info). I have two pods running for a specific service. i want to get logs related to both the pods and check for specific text. for that i used ,as described here: kubectl logs l app=my app c my app con. I've had a "stuck" namespace that i deleted showing in this eternal "terminating" status. 12 a solution to retrieve all containers running in a pod is to run kubectl get pods pod name here o jsonpath={.spec.containers[*].name}, however this command line does not provide the init containers. is there a way to cleanly retrieve all containers running in a pod, including init containers?. From the kubectl get secret documentation, it seems the standard way to get a secret returns the whole thing, in a specified format, with the values base64 encoded. Say, i have two namespaces k8s app1 and k8s app2 i can list all pods from specific namespace using the below command kubectl get pods n <namespace> we need to append namespace to all comma.
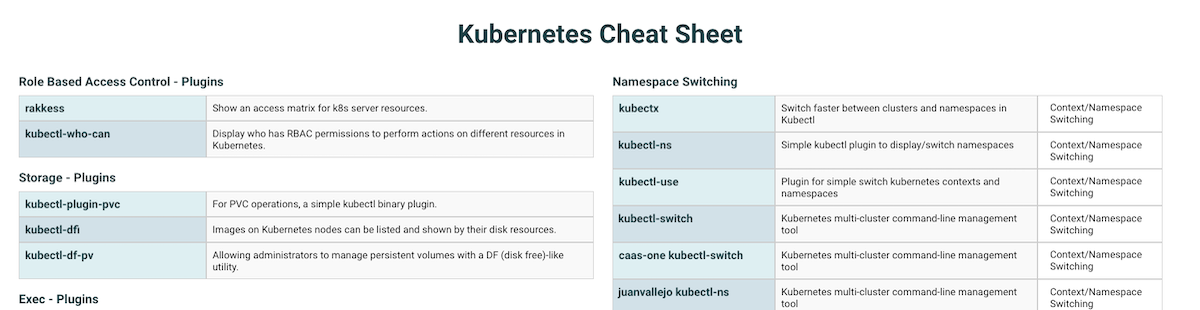
Kubectl Cheat Sheet Logit Io I've had a "stuck" namespace that i deleted showing in this eternal "terminating" status. 12 a solution to retrieve all containers running in a pod is to run kubectl get pods pod name here o jsonpath={.spec.containers[*].name}, however this command line does not provide the init containers. is there a way to cleanly retrieve all containers running in a pod, including init containers?. From the kubectl get secret documentation, it seems the standard way to get a secret returns the whole thing, in a specified format, with the values base64 encoded. Say, i have two namespaces k8s app1 and k8s app2 i can list all pods from specific namespace using the below command kubectl get pods n <namespace> we need to append namespace to all comma.

Download Kubectl Cheatsheet From the kubectl get secret documentation, it seems the standard way to get a secret returns the whole thing, in a specified format, with the values base64 encoded. Say, i have two namespaces k8s app1 and k8s app2 i can list all pods from specific namespace using the below command kubectl get pods n <namespace> we need to append namespace to all comma.
Comments are closed.