Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large Vision Language
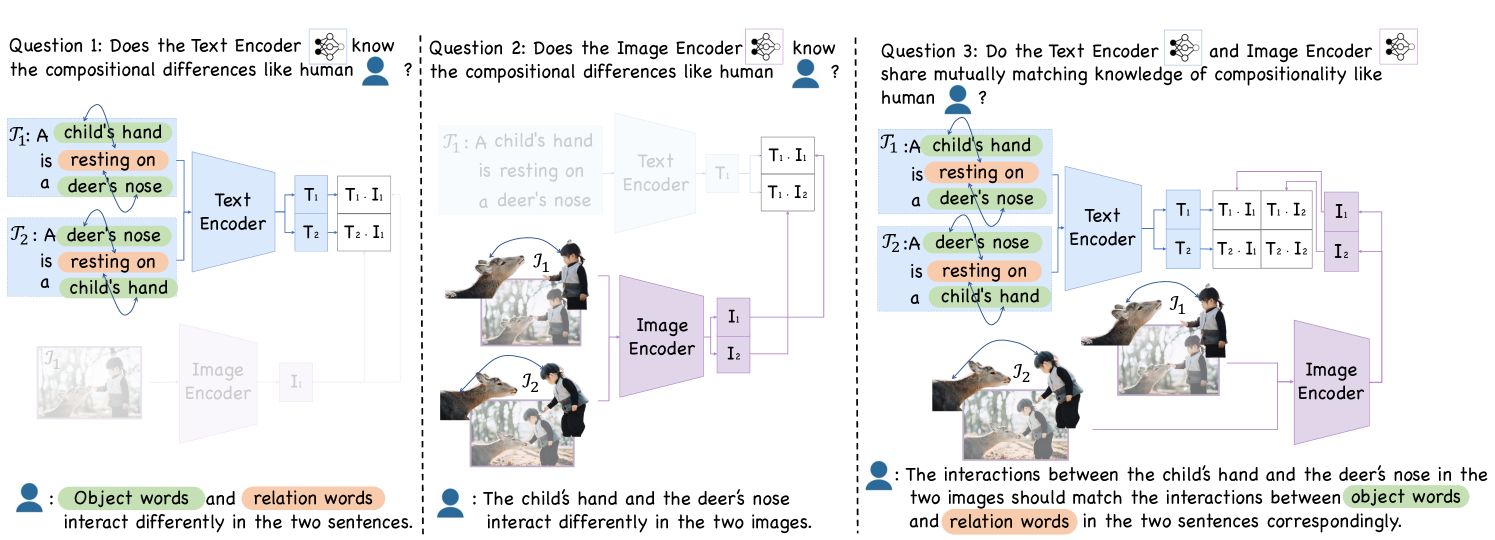
Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large Vision Language Moreover, prior work suggests that compositionality doesn't arise with scale: larger model sizes or training data don't help. this paper develops a new iterated training algorithm that incentivizes compositionality. In this paper, we design an iterated learning algorithm that improves the compositionality in large vision language models, inspired by cultural transmission theory in cognitive science.
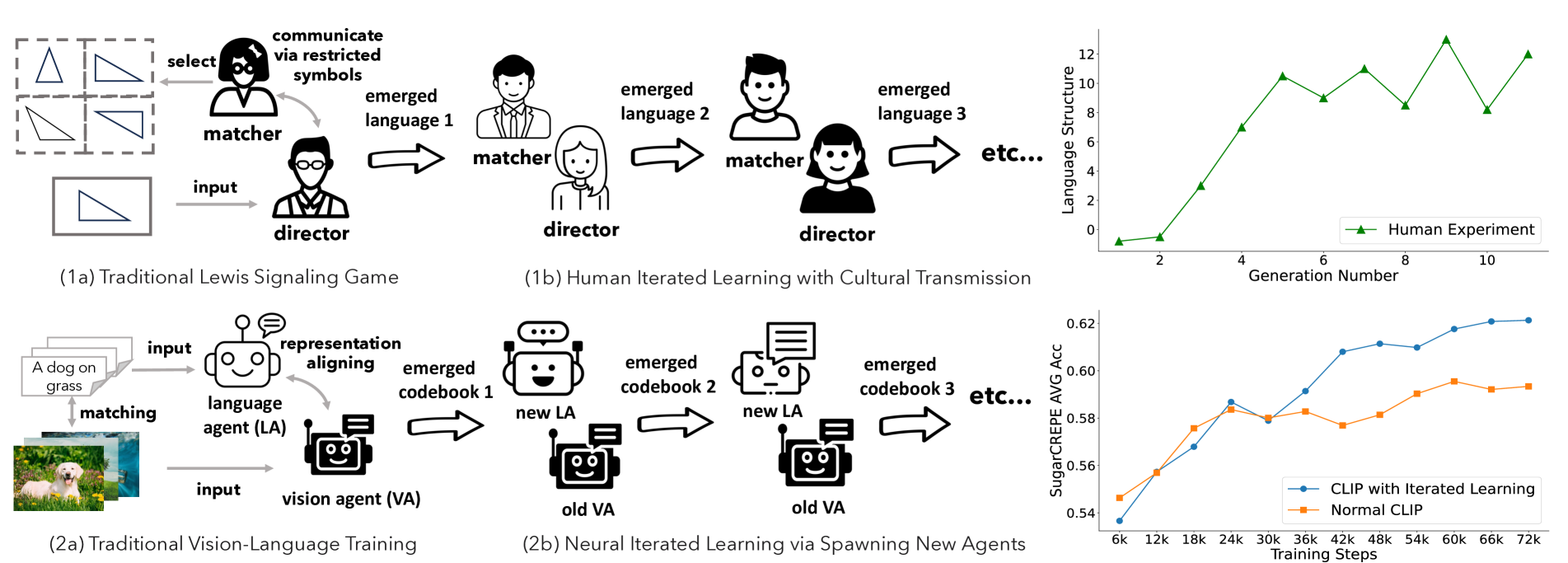
Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large Vision Language We design an iterated learning algorithm that improves the compositionality in large vision language models, inspired by cultural transmission theory in cognitive science. We develop immersive vr experiences aimed at encouraging exercise. urban rush lets the player to have fun in a narrative based exploration while completing activities in a unique, procedurally generated city environment. this project was done with rahmy salmon and kalpit haresh sutariya. Title: iterated learning improves compositionality in large vision language models abstract: a fundamental characteristic common to both human vision and natural language is their compositional nature. yet, despite the performance gains contributed by large vision and language pretraining, recent investigations find that most if not all our state of the art vision language models struggle at. This work proposes an effective neural iterated learning algorithm that, when applied to interacting neural agents, facilitates the emergence of a more structured type of language.

Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large Vision Language Title: iterated learning improves compositionality in large vision language models abstract: a fundamental characteristic common to both human vision and natural language is their compositional nature. yet, despite the performance gains contributed by large vision and language pretraining, recent investigations find that most if not all our state of the art vision language models struggle at. This work proposes an effective neural iterated learning algorithm that, when applied to interacting neural agents, facilitates the emergence of a more structured type of language. More over, prior work suggests that compositionality doesn't arise with scale: larger model sizes or training data don't help. this paper develops a new iterated training algorithm that incentivizes compositionality. Here we test whether the contextual information encoded in large language models (llms) is beneficial for modelling the complex visual information extracted by the brain from natural scenes. Moreover, il clip (zheng et al. 2024) introduces an iterated learning algorithm based on the unified vd, which improves compositionality in large vision language models. In response to these issues, we present caption expansion with contradictions and entailments (cece), a principled approach that leverages natural language inference (nli) to generate entailments and contradictions from a given premise.
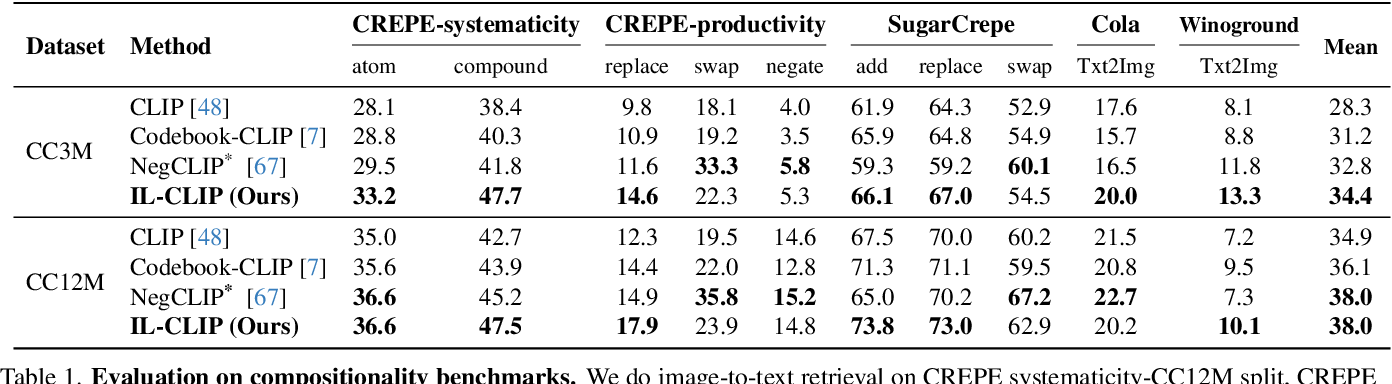
Table 1 From Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large More over, prior work suggests that compositionality doesn't arise with scale: larger model sizes or training data don't help. this paper develops a new iterated training algorithm that incentivizes compositionality. Here we test whether the contextual information encoded in large language models (llms) is beneficial for modelling the complex visual information extracted by the brain from natural scenes. Moreover, il clip (zheng et al. 2024) introduces an iterated learning algorithm based on the unified vd, which improves compositionality in large vision language models. In response to these issues, we present caption expansion with contradictions and entailments (cece), a principled approach that leverages natural language inference (nli) to generate entailments and contradictions from a given premise.
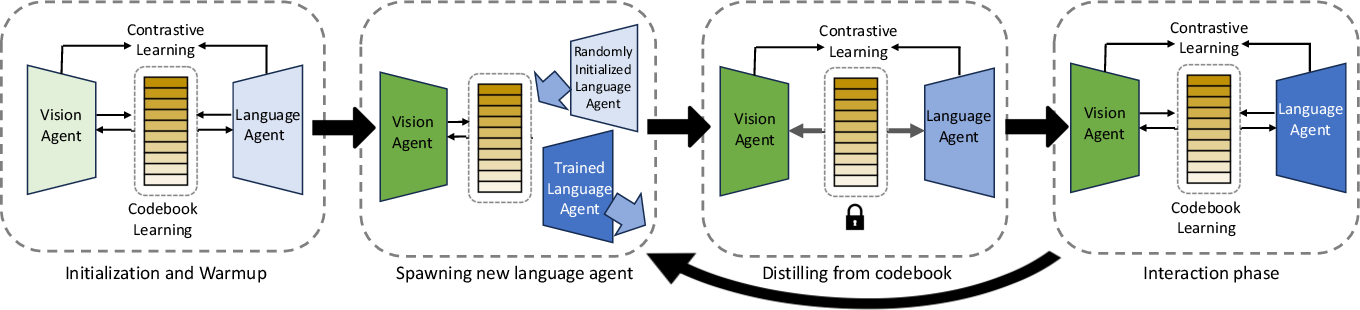
Figure 2 From Iterated Learning Improves Compositionality In Large Moreover, il clip (zheng et al. 2024) introduces an iterated learning algorithm based on the unified vd, which improves compositionality in large vision language models. In response to these issues, we present caption expansion with contradictions and entailments (cece), a principled approach that leverages natural language inference (nli) to generate entailments and contradictions from a given premise.
Comments are closed.