Ipv4 Ipv6 Dual Stack What It Is And How It Works
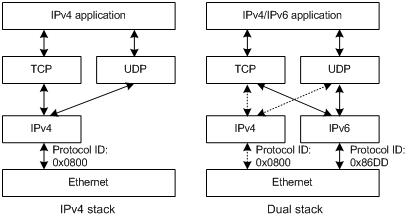
Ipv4 Ipv6 Dual Stack What It Is And How It Works This simple ip address transition solution involves both protocols in parallel in a dual stack configuration. in a dual stack network, each device is configured with ipv4 and ipv6 connectivity. dual stack makes both network families active. devices can communicate over ipv4 or ipv6 as needed. A dual stack network is a network setup that supports both ipv4 and ipv6 at the same time. instead of forcing users to pick one or the other, dual stack allows devices to communicate over both protocols, choosing the best option automatically.

Ipv4 Ipv6 Dual Stack What It Is And How It Works On the dual stack network, ipv6 and ipv4 service data is forwarded on different forwarding planes. logically, two forwarding planes are considered as two networks to facilitate network deployment. the dual stack technology supports smooth transition to the ipv6 network. Doing an ipv6 implementation project does not involve tearing down an aging ipv4 network and replacing it with a new ipv6 enabled network. instead, the ipv4 and ipv6 networks will run in parallel in what the industry calls a "dual stack" network. In a dual stack environment, both ipv4 and ipv6 protocols coexist, allowing devices, networks, and applications to support both addressing schemes. this approach ensures seamless communication and compatibility while facilitating a gradual transition to the enhanced capabilities of ipv6. Learn about the dual stack and mpls tunnel techniques for coexistence of ipv4 and ipv6 networks, and make an informed decision about your network infrastructure.

Dual Stack Infrastructure Download Scientific Diagram In a dual stack environment, both ipv4 and ipv6 protocols coexist, allowing devices, networks, and applications to support both addressing schemes. this approach ensures seamless communication and compatibility while facilitating a gradual transition to the enhanced capabilities of ipv6. Learn about the dual stack and mpls tunnel techniques for coexistence of ipv4 and ipv6 networks, and make an informed decision about your network infrastructure. Other strategies, such as manually or dynamically configured tunnels and translation devices exist, but dual stacking is often the preferable solution in many scenarios. the dual stacked device can interoperate equally with ipv4 devices, ipv6 devices, and other dual stacked devices. Ipv4 and ipv6 are versions of the internet protocol (ip), which is the set of rules that dictate how data is sent and received over the internet. a dual stack network supports both ipv4 and ipv6 addresses, allowing devices to operate on either protocol. Devices equipped with dual stack functionality can communicate over both ipv4 and ipv6 networks. each device is assigned an ipv4 address and an ipv6 address, enabling them to interact with other devices across varying network configurations. Understand the concept of dual stack networking and its importance in the transition from ipv4 to ipv6. explain how applications can be designed to seamlessly communicate over both ipv4 and ipv6. utilize the getaddrinfo() function for protocol agnostic hostname resolution in esp idf.

Ken Felix Security Blog Dual Stack Ipv4 Ipv6 Other strategies, such as manually or dynamically configured tunnels and translation devices exist, but dual stacking is often the preferable solution in many scenarios. the dual stacked device can interoperate equally with ipv4 devices, ipv6 devices, and other dual stacked devices. Ipv4 and ipv6 are versions of the internet protocol (ip), which is the set of rules that dictate how data is sent and received over the internet. a dual stack network supports both ipv4 and ipv6 addresses, allowing devices to operate on either protocol. Devices equipped with dual stack functionality can communicate over both ipv4 and ipv6 networks. each device is assigned an ipv4 address and an ipv6 address, enabling them to interact with other devices across varying network configurations. Understand the concept of dual stack networking and its importance in the transition from ipv4 to ipv6. explain how applications can be designed to seamlessly communicate over both ipv4 and ipv6. utilize the getaddrinfo() function for protocol agnostic hostname resolution in esp idf.
Comments are closed.