Introduction To Hashmap Hashtable In Java

Java Hashmap Mytebass The hashmap is the second implementation, which was introduced in jdk 1.2. both classes provide similar functionality, but there are also small differences, which we’ll explore in this tutorial. Hashmap is not synchronized, so it's not safe for concurrent access by multiple threads unless you manually synchronize it (or use collections.synchronizedmap()). hashtable is synchronized, so.
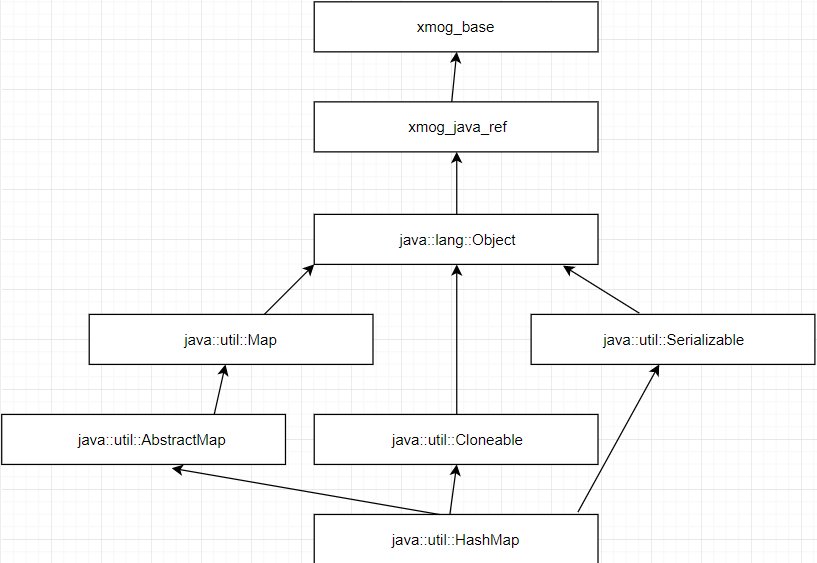
Java Hashmap Example Java Tutorial Network Explore the key differences between hashmap and hashtable in java, including performance, synchronization, and use cases. In java, both hashtable and hashmap are used to store key value pairs. they are part of the java collections framework and are quite similar in functionality at a glance. however, there are several key differences between them that developers need to be aware of when choosing the right data structure for their applications. How does hashtable work in java? hashtable is an abstract class and has two subclasses that extend this class — hashmap and linkedhashmap. the hashmap provides the set of elements stored in it, while the linkedhashmap allows insertion of new items at any position. Hashmap and hashtable are implementations of the map interface in java, with differences in synchronization and null handling. hashmap is unsynchronized and allows null keys and values; hashtable is synchronized and does not allow null keys or values.
Hashmap In Java First Code School How does hashtable work in java? hashtable is an abstract class and has two subclasses that extend this class — hashmap and linkedhashmap. the hashmap provides the set of elements stored in it, while the linkedhashmap allows insertion of new items at any position. Hashmap and hashtable are implementations of the map interface in java, with differences in synchronization and null handling. hashmap is unsynchronized and allows null keys and values; hashtable is synchronized and does not allow null keys or values. Explore the inner workings of hashmaps, learn techniques like chaining and open addressing, and delve into hashmap implementation in java. gain a thorough understanding of how hashmaps work, their underlying mechanisms, and practical applications. follow along with provided code examples and resources to enhance your learning experience. Hashmap in java provides a non synchronized, high performance key value store for quick data retrieval in single threaded contexts. hashtable in java offers synchronized access, making it suitable for multi threaded environments where thread safety is critical. Discover essential differences between java hashtable and hashmap for optimal performance and usage.
Comments are closed.