If A Vector Is A Constant Vector Show That A Vector Del Vector R

If A Vector Is A Constant Vector Show That A Vector Del Vector R If a vector is a constant vector show that a vector * (del vector *r vector) = del vector ( a vector . r vector) ( a vector . del vector) r vector. play quiz games with your school friends. click here. please log in or register to answer this question. Explanation: to solve the expression ∇×(a×r), where a is a constant vector and r is the position vector, we can use the vector identity for the curl of a cross product. the identity states that for any vector fields a and b, ∇× (a×b)=b(∇⋅a)−a(∇⋅b) (a⋅∇)b−(b⋅∇)a.

If A Vector Is A Constant Vector Show That A Vector Del Vector R Example: if ais a constant vector, and ris the position vector, show that r(ar) = (ar)r= a in lecture 13 we showed that r(ar) = afor constant a. hence, we need only evaluate (ar)r = ai @ @x. ∇f is the gradient of a function, i.e. the direction of the vector ∇f is the direction of the maximum rate of change of f, and the magnitude of ∇f tells you how big or small the rate of change is. If a is a constant vector . prove that del (a .r) =a . problem on divergence curl and gradients. Del operator the del operator is a mathematical operator used very often in different branches of science in cartesian coordinates.
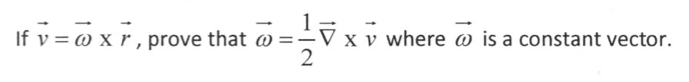
Solved If Vector V Vector W X Vector R Prove That Vector Chegg If a is a constant vector . prove that del (a .r) =a . problem on divergence curl and gradients. Del operator the del operator is a mathematical operator used very often in different branches of science in cartesian coordinates. The theorem says that if $\vec r \cdot \vec r$ is constant, then $\vec r \cdot \vec {r^\prime} = \vec 0$. as usual, all the interesting proofs are left "as an exercise to the reader". ∇ (r . a)=a. hence proved. find physics textbook solutions? still have questions? answer: r is a vector quantity and is given by [tex]r=xi yj zk [ tex]a is a constant vector and is given by [tex]a {x}i a {y}j a {z}k [ tex]explanation: to prove: …. The del operator is essential in vector calculus because it allows us to define three fundamental operations: gradient, divergence, and curl. these operations are crucial in describing various physical phenomena, such as electric and magnetic fields, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer. A constant l is called limit of vector function ⃗(t) by taken t approaches to a ( t a) . it is written as ⃗ = l [ it is studied as ⃗ as t ].
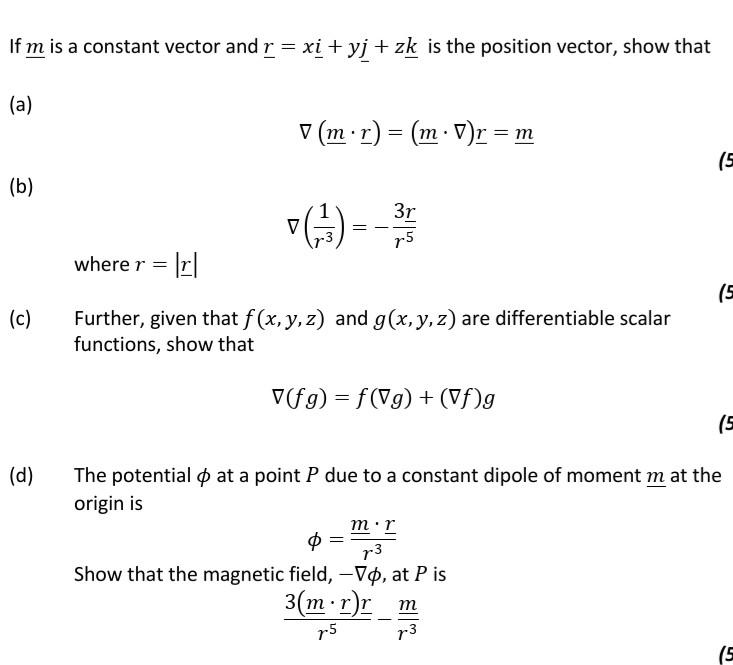
Solved If M Is A Constant Vector And R Xi Yj Zk Is The Chegg The theorem says that if $\vec r \cdot \vec r$ is constant, then $\vec r \cdot \vec {r^\prime} = \vec 0$. as usual, all the interesting proofs are left "as an exercise to the reader". ∇ (r . a)=a. hence proved. find physics textbook solutions? still have questions? answer: r is a vector quantity and is given by [tex]r=xi yj zk [ tex]a is a constant vector and is given by [tex]a {x}i a {y}j a {z}k [ tex]explanation: to prove: …. The del operator is essential in vector calculus because it allows us to define three fundamental operations: gradient, divergence, and curl. these operations are crucial in describing various physical phenomena, such as electric and magnetic fields, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer. A constant l is called limit of vector function ⃗(t) by taken t approaches to a ( t a) . it is written as ⃗ = l [ it is studied as ⃗ as t ].
Comments are closed.